Design Principles
Intro
SAP Fiori for Wear OS provides a consistent and holistic user experience for SAP software on wearables. Wearables are computer technologies that users wear on their bodies, creating a more personalized experience. Common types of wearable devices are smartwatches.
The purpose of wearables is to support an activity in the real world by providing additional information, for example, evaluations based on sensors tracking the body’s vitals, or glanceable instructions without touching the device.
Differences Between Mobile and Wearable Devices
Designing for smartwatch apps presents a fundamentally different approach from designing for mobile apps. Not only is the screen that users interact with much smaller, but also the way and duration users interact with the smartwatch app is different compared to mobile apps. Therefore, the most important aspect of creating a smartwatch app is to define focused wearable requirements instead of trying to mirror the scope of the mobile app. In addition, the user experience on a smartwatch cannot be compared to the experience of a mobile device and therefore follows different design principles.
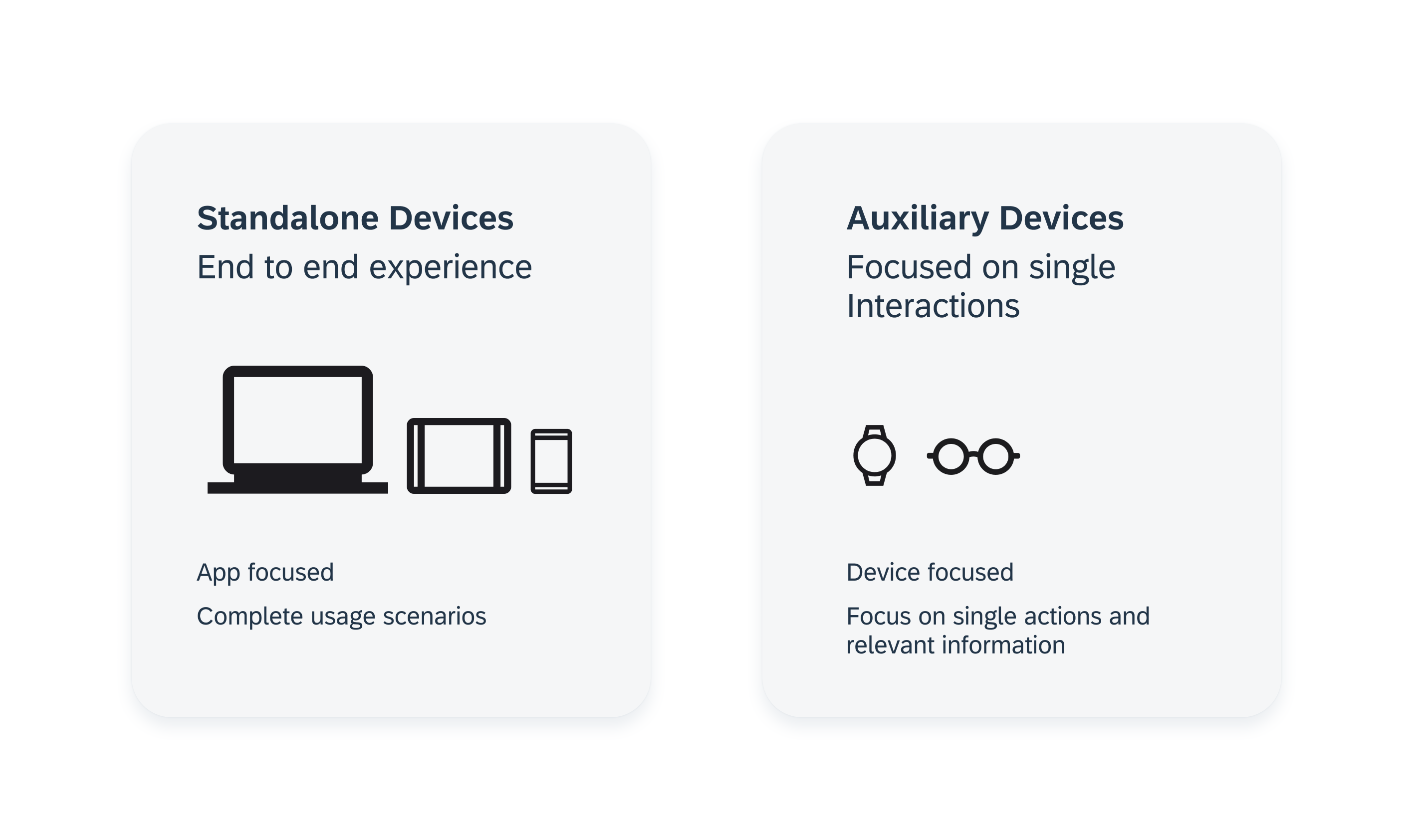
Mobile devices as standalone devices with app focus and wearables as optional devices with device focus
In contrast to a smartwatch app, apps on a mobile device represent an end-to-end experience. That means, while the mobile device contains the complete app, the smartwatch version focuses more on informing the user selectively, with, for example, relevant notifications or complications, and a maximum of one or two functions that can be performed quickly.
Passive use and brief glance interactions with the end device predominate on the smartwatch:
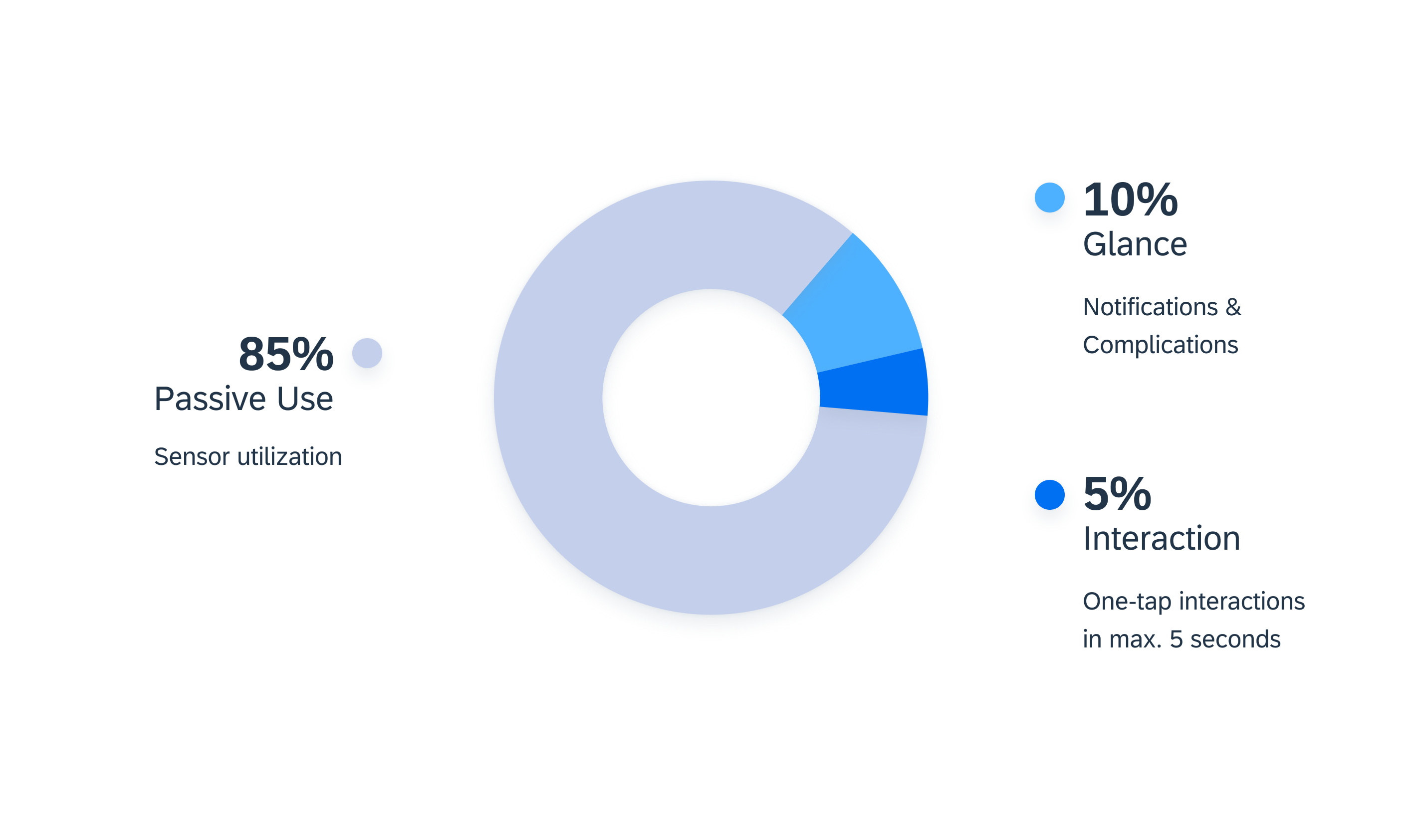
Smartwatch usage categories
In general, the usage of smartwatches is divided into the following categories:
- 85 % passive use, such as usage of the sensor
- 10 % looking at the smartwatch, such as notifications, complications
- 5 % performing actions, such as setting timers
The image above shows that the way users interact with smartwatch apps differs greatly from mobile apps – especially in terms of passive usage. As a result, the design process for watch apps must start with specifying the requirements. If guidelines for wearables are not considered, not only will the added value of a smartwatch app quickly decrease, but also the general user experience of the app will be negatively affected. This may cause users to discontinue using the smartwatch app because they do not depend on it.
- Focus on single actions and relevant information.
- Try to use one-tap interactions.
- Minimize hierarchies within the app.
- Leverage a “favourites” or “recents” feature as well as usage patterns to infer user-based relevance of content.
- Don’t translate mobile app capabilities to the smartwatch.
- Don’t apply mobile app information architecture to the smartwatch.
- Don’t assume that the mental model for the mobile app is the same as for the smartwatch app.
Differences Between watchOS and Wear OS
Keep in mind that there are also platform-specific differences when it comes to smartwatch apps. The following table shows a rough overview of the most important differences of the operating systems Wear OS from Google and watchOS from Apple that influence the design of a smartwatch app.
| Feature | Wear OS (Google) |
watchOS (Apple) |
|---|---|---|
| Tiles Component | Tiles offer users glanceable actions and information. Users can configure which tiles they want to be displayed so that they can access them by swiping from the watch face. | Instead of tiles, watchOS supports dock cards that have similar properties as tiles. |
| Back Navigation/Cancel | Swipe right or hardware button. | Back button in title area or hardware button. |
| Text Layout | Mostly centered. | Mostly left-aligned. |
| Icon Buttons | Very common. | Rather uncommon. |
| Text Resizing | Can be deactivated. | Cannot be deactivated. Components need to be optimized for that feature. |
| Display Form Factors | Round, square and rectangular displays. | Square display only. |
| Handover Feature | Default feature. | Not supported by default. |
