- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Handling Busy States
Intro
This article describes how to handle the busy state in SAP Fiori apps in general. You can set a busy indicator locally at control level (for example, on a page or for a button) using a busy state, or set it globally using the busy dialog. In SAP Fiori, the aim is to keep the blocking of UIs to a minimum, and to unblock areas where user interaction is possible. Because response time depends on available bandwidth and server performance, unblocking can take a second or more. In this case, we need to inform the user that the process is ongoing.
Usage
Busy indicators are used in the following areas:
- Initial page loading
- Dynamic fields and forms (asynchronous loading of fields based on user preselection)
- Lazy loading of content, for example, in lists and tables
- Searching and filtering, for example, lists, tables, and global searches
- Primary actions such as Save, Update, and Delete
- Deleting and updating lists or modifying tables
- Partial loading of content
Setting the Busy State
The challenge here is to decide at what level and when the busy state needs to be set. The options are as follows:
- Show the entire UI as busy (including SAP Fiori launchpad shell bar) using a busy dialog
- Set a busy state at control level (for example, on a page or for a button)
To make the right decision, we first need to understand how a page or app is loaded.
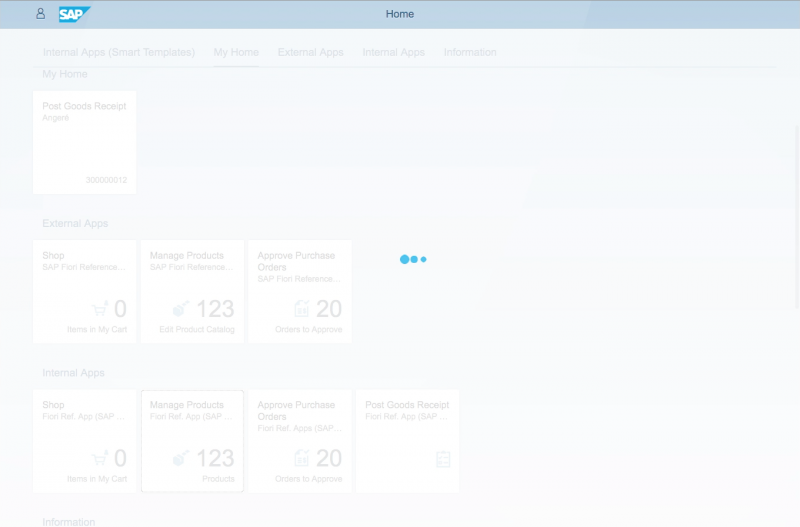
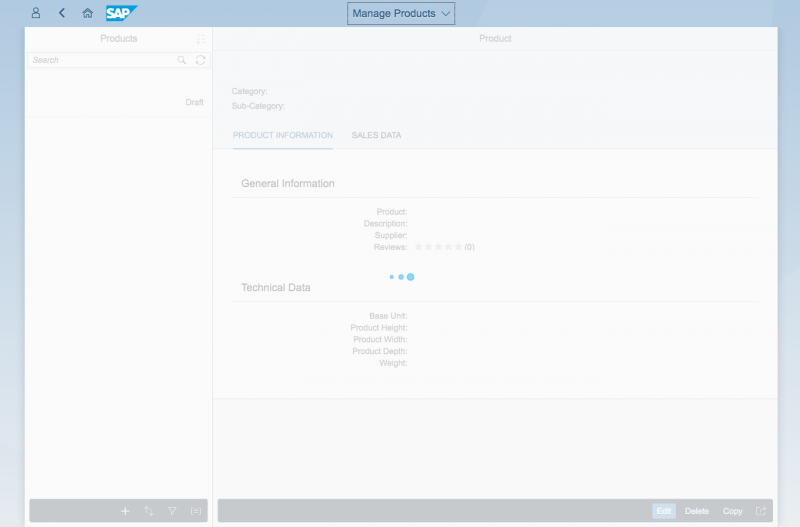
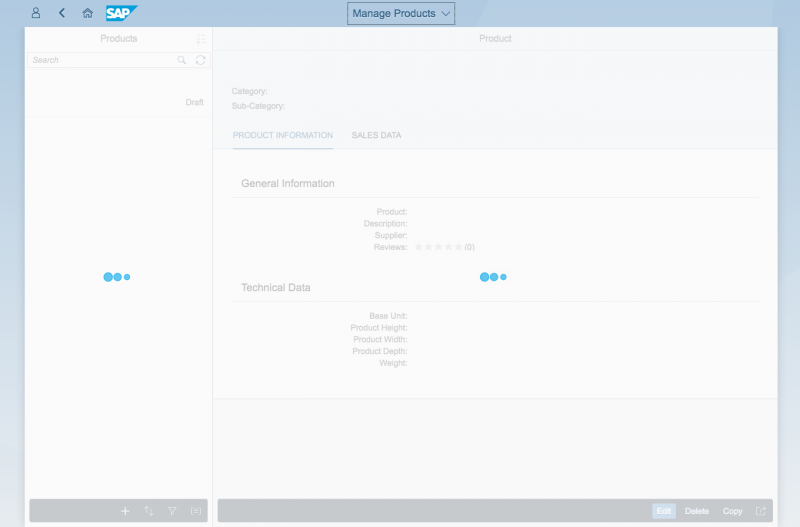
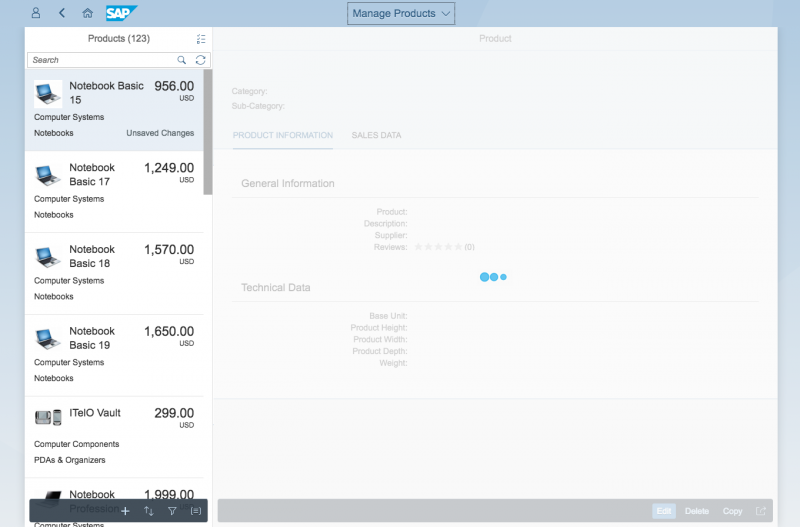
In this example, we will use the reference app “Manage Products”, based on the split-screen layout. We will also assume that the necessary data for labels, tables, and so on is loaded asynchronously, and that the mapping is done via binding.
The app is launched from a tile on the home page. The busy indicator is shown until the initial application data is available.
First, the UI description and metadata are loaded. This is the minimum for a basic functional UI. Until this data is available, the app UI needs to be blocked. In this case, we set the busy state from the split-screen layout control (sap.m.SplitApp).
Do not use the busy dialog to block the entire UI. Otherwise, this would also affect the shell bar, and the user would not be able to access shell features such as Sign Out or Search.
Guidelines
- Only use the busy dialog if you do not want to allow the user to use the shell, for example, to navigate to the home page. In some cases, long-running processes require the user to be informed about the result in order to continue, for example, to a second step.
-
If multiple busy indicators overlap, the SAPUI5 framework ensures that only the one at the uppermost level is shown.
- Do not use the busy dialog for app or page loading. Set the busy state at app level.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.
Implementation
- Busy Indicator (SAPUI5 samples)
- Busy State (SAPUI5 samples)
- Busy Dialog (SAPUI5 samples)

 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.