- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Chart – Color Palettes
Intro
This article explains what the three chart visualization color palettes are designed to do and how you can leverage their unique properties.
Palette Overview
For color names and HEX values, see palette colors – values and names.
Semantic Color Palette
Designed to communicate good, bad, critical and neutral values.

Sequential Color Palette
Designed to visualize high to low values using six shades for different measures.
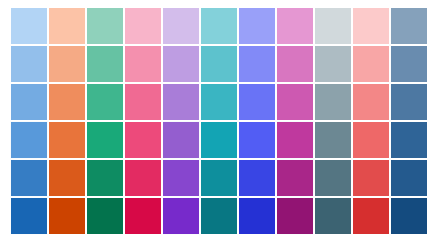
Qualitative Color Palette
Designed to provide visual differentiation between data points using a specific sequence of colors.

Rules
- Only use colors contained in the SAP Fiori chart palettes
You should only use colors from the SAP Fiori color palettes to ensure that we maintain visual design consistency across all charts used in all SAP Fiori applications. - Only use one palette per chart
Do not combine colors from different palettes in the same chart. Each palette has been carefully designed to serve a distinct purpose. - Ensure color names are referenced in the code – not HEX values!
Colors are defined by names in order to support our theming capabilities. This means that the HEX values of the colors may not be exactly the same in past, present and future SAP Fiori visual design themes. This flexibility is made possible by the fact that the color names will stay the same across all past, present and future SAP Fiori visual design themes. You can get the color names and corresponding HEX values from the article on color palettes – values and names. - Do not use color to distinguish between forecast, actual and target values
Use sematic patterns instead.
Default Colors
By default, every chart type comes with built-in colors that are applied automatically, based on your dataset. Here are three examples:
1. When only one series is displayed, the first color from the qualitative palette is automatically applied to each item.
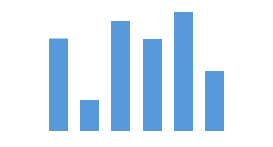
Column chart: One series
2. When multiple series are displayed, more colors from the qualitative palette are automatically applied to each item in the predetermined sequence.
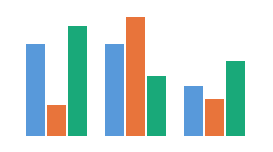
Column chart: Three series
3. Colors from the sequential palette are automatically applied to the heatmap.
Changing the Colors
There are three ways to change the colors in charts:
By Category Item
In the example below, one category has been highlighted using the second color from the qualitative palette.
Column chart with a highlighted category
By Series
In the example below, the series use different shade of the same color because one series must be more visible than the other.
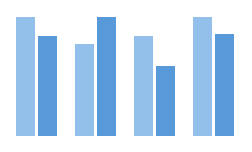
Two series column chart
Based on Value
In the example below, the data points are red if their value is below a certain threshold, green if their value is above another threshold, and orange if their value is between the two.
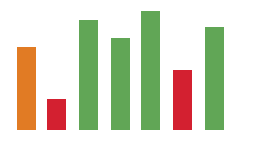
Column chart with encoded values
Qualitative Palette
The colors in the qualitative palette do not carry semantic meaning. The palette has been designed to provide visual differentiation between data points by virtue of the fact that each color is visually distinct.
Therefore, we recommend using the colors in the sequence illustrated above as opposed to using any colors simply because you prefer them.
For edge cases where you have more than 11 categories, an additional 11 colors were added. These are darker versions of the same colors.
For color names and HEX values, see palette colors – values and names.
Highlight Category Items
By default all the categories will use the first color from the qualitative palette. However, you can use other colors from the qualitative palette if you want to highlight category items.
Using the qualitative palette to focus on a category item
Group Items by Color
You can use the qualitative palette to group items into categories. In this example, we use green for Europe, blue for America, and orange for Asia.
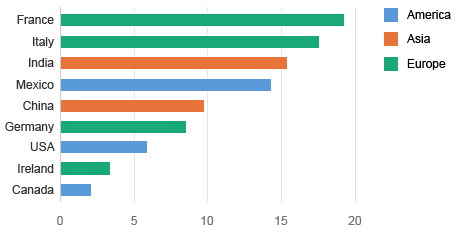
Using the qualitative palette to show a hierarchy
Semantic Palette
The semantic palette is designed to communicate good, bad, critical and neutral values using three universally recognized colors in six shades. This allows you to visualize each semantic level.
For color names and HEX values, see palette colors – values and names.
Here are some ways you can use the palette:
Illustrate the Top Three Values
This column chart uses the semantic palette to display sales revenue per month. The color green is used to highlight the top three months with the highest revenue.
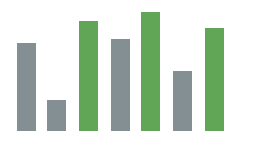
Column chart: Top three values
Show Positive and Negative Series
These stacked bars represent the availability of materials. The available series is green, the inspection series is orange, and the blocked series is red.
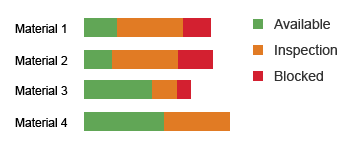
Stacked bars: Good and bad values
Denote Good or Bad Values
Each data point has a color based on its value. Data points are now red if their value is below a certain threshold, green if their value is above another threshold, and orange if their value is between the two.

Column chart: Good and bad values
Visualize Different Levels
In this geomap, green is used to indicate states with good performance, and red is used to indicate states with bad performance. In this example the different shades express different levels of good and bad performance.
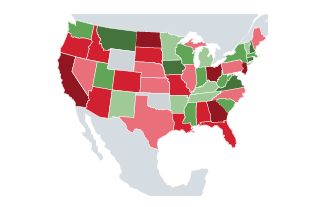
Geomap: Levels of performance
Default Color Shade Names
The default color shade names are:
- sapUiChartPaletteSemanticNeutral
- sapUiChartPaletteSemanticGood
- sapUiChartPaletteSemanticBad
- sapUiChartPaletteSemanticCritical

Column chart: Level 1 of the semantic palette
Selecting the Correct Combination of Shades (Semantic Palette)
The semantic palette contains six shades of each color so you can express up to six levels of each semantic. Therefore, it’s important to select the correct combination of shades according to the number of levels you want to express. The table below shows you how to do this for bad – the same principle can be applied to good and critical.
Number of Levels
Shades to Use
Color Names
Sequential Palette
The sequential color palette is designed to visualize high to low values for different measures.
Generally speaking, the lighter the shade, the lower the value. The darker the shade, the higher the value.
For color names and HEX values, see palette colors – values and names.
Here are some ways you can use the palette:
Distinguish between Past and Present
These two series use different shades of the same color to distinguish between last year and the current year.

Column chart: Two series
Show Time Gradation
These stacked bars represent payable aging by country. The different gradations of brightness are used to represent different time periods.
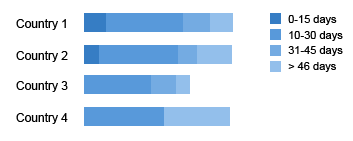
Stacked bars: Time gradation
Visualize Different Levels
This bullet chart shows direct costs in a dark shade and indirect costs in a light shade.
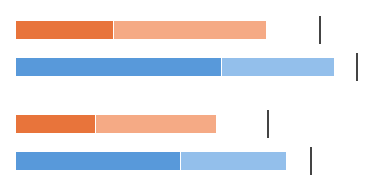
Bullet chart: Different levels
This geomap contains two measures. Shades of blue are used to visualize high and low values for one measure while shades of orange are used to visualize high and low values for the other measure.
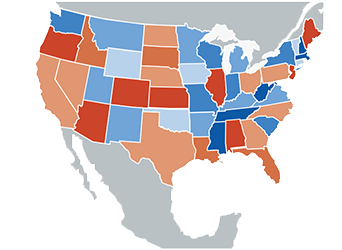
Geomap: Multiple levels in two groups
Ranked Values
In this bubble chart, the size of the bubbles represents future sales deals. The probability of converting these deals is expressed using different shades of blue.

Bubble chart: Ranked values
Selecting the Correct Combination of Shades (Sequential Palette)
The sequential palette contains six shades of each color so you can express up to six different values per measure. Therefore, it’s important to select the correct combination of shades according to the number of values you need to express. The table below shows how to do this for the blue category item color – the same principle can be applied to the other colors in the palette.
Number of Values
Shades to Use
Color Names
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.















 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.