- Latest SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
- Latest SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Formatting Numbers
sap.ui.core.format.NumberFormat
Intro
This article describes the international rules for number formats. The SAPUI5 number formatters will help you to comply with these rules.
Usage
Use number formatting if:
- You need to display numbers based on the user’s locale settings.
Do not use number formatting if:
- You need to display IDs.
- You need to display telephone numbers.
Types
You can use three different datatypes for numbers: integer, float, and currency. Each datatype can be formatted using a short, standard, or long format.
Integer
Use integer if no decimal places are required.
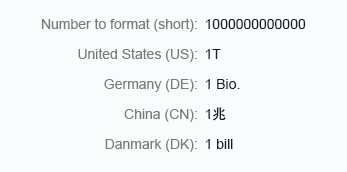
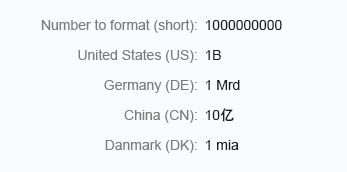
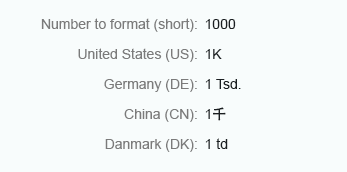
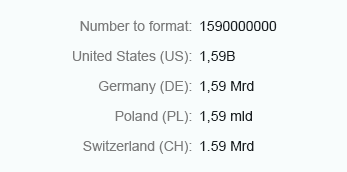
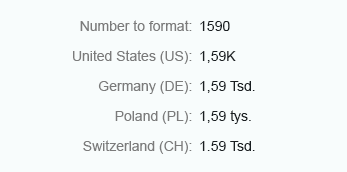
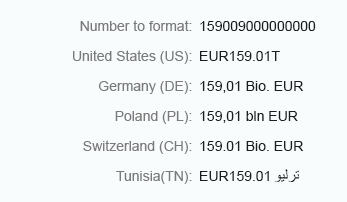
Short
Integer numbers formatted using the short form are truncated after three digits. When you use the short form, the units are shown as an abbreviation, such as K (thousand), M (million), B (billion), and T (trillion).
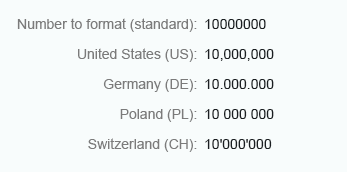
Standard
In general, use standard format. When you use standard format, integer numbers are displayed in full.
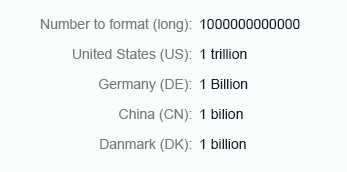
Long
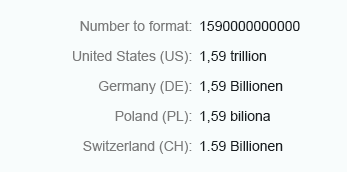
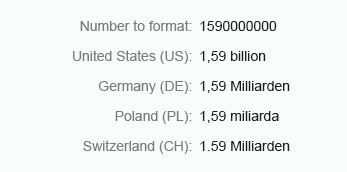
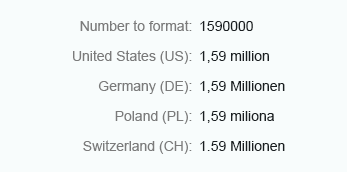
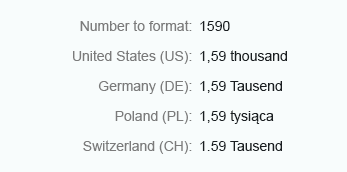
Integer numbers formatted using the long form are truncated after three digits. The units are shown as full text, such as thousand, million, and so on.
Integer (long)
Float
If you want to show decimal places, use float. The decimal places beyond the defined number of digits are truncated. If the minimum number of decimal digits is not restricted, only the trailing zeros are truncated, which could lead to very large numbers.
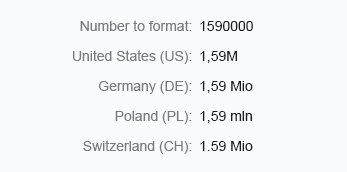
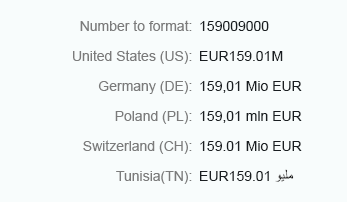
Short
Float numbers using the short form are displayed entirely without truncation of the trailing zeros. The units are displayed as an abbreviation, such as K (thousands), M (million), and so on.
Float number - Short
Standard
In general, use the standard format. Numbers using the standard format are displayed in full.
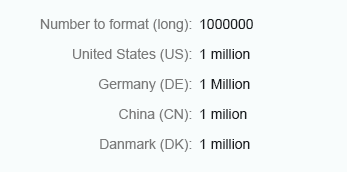
Long
Use the long format to show units as full text, such as thousand, million, and so on.
Float number - Long
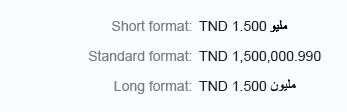
Currency
If you want to show currencies, use the currency formatter. Most currencies have two decimal places, although some need three digits after the decimal point, such as the Tunisian dinar. The currency formatter takes this into account. Currency amounts are rounded down automatically.
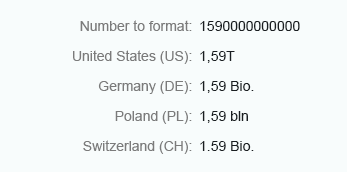
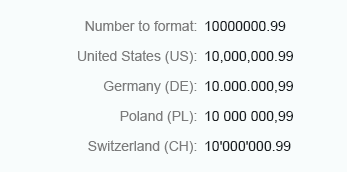
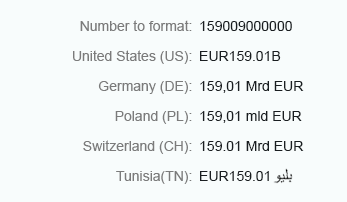
Short
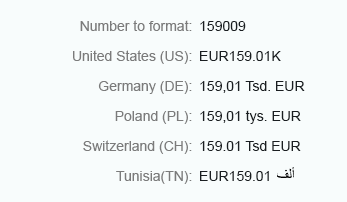
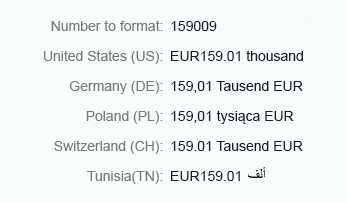
Currency amounts that are greater than 1,000 and use the short format are abbreviated.
Currency - Short
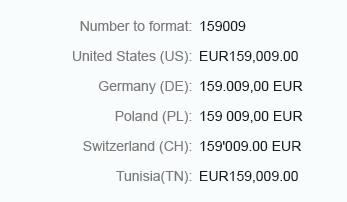
Standard
In general, use the standard format. Numbers using the standard format are displayed in full, including the decimal places.
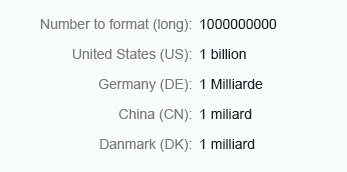
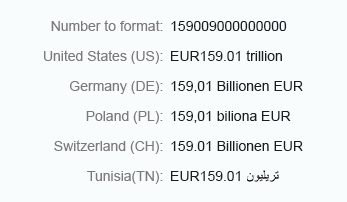
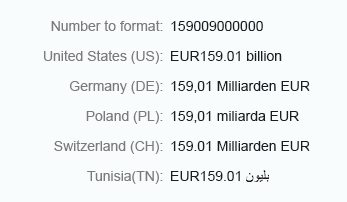
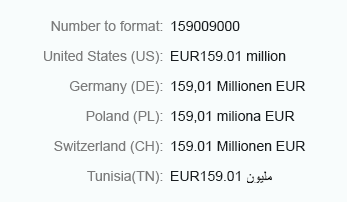
Long
Use the long format to show units as full text, such as thousand, million, and so on.
Currency (long)
Guidelines
- In general, use the standard format.
- Follow the rules of the corresponding control to format the data appropriately. (For example, show 1.7M instead of 1,700,000 in the object list item.)
- Use float numbers to prevent truncation of decimal places.
- If you need to display amount fields without a value, leave them blank. Do not display a text as N/A.
- Always use the correct format according to your language or locale setting to prevent confusion caused by incorrect formatting. (For example, “200,000” is interpreted as “two hundred thousand” in the United States, but “two hundred point zero” in Germany.)
- If you need to display decimal numbers, use float and keep the number of digits after the decimal point to a minimum.
- Use object numbers where possible, for example, to display amounts in forms and responsive tables.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.



 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.