- Latest SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
- Latest SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Object Page (Floorplan + SAP Fiori Element)
Intro
The object page floorplan allows the user to display, create, or edit an object. This is now the recommended floorplan for representing both simple and complex objects in SAP Fiori, and is set to replace the flat object view floorplan and object view floorplan. The object page floorplan comes with a flexible header, a choice of anchor or tab navigation, and a flexible, responsive layout. These features make it adaptable for a wide range of use cases.
You can implement the object page floorplan in two ways:
- Use the pre-built SAP Fiori element (formerly known as a smart template). This implementation uses OData annotations, and allows you to speed up development if the supported feature set matches your requirements.
- Implement the floorplan yourself using the respective SAPUI5 controls.
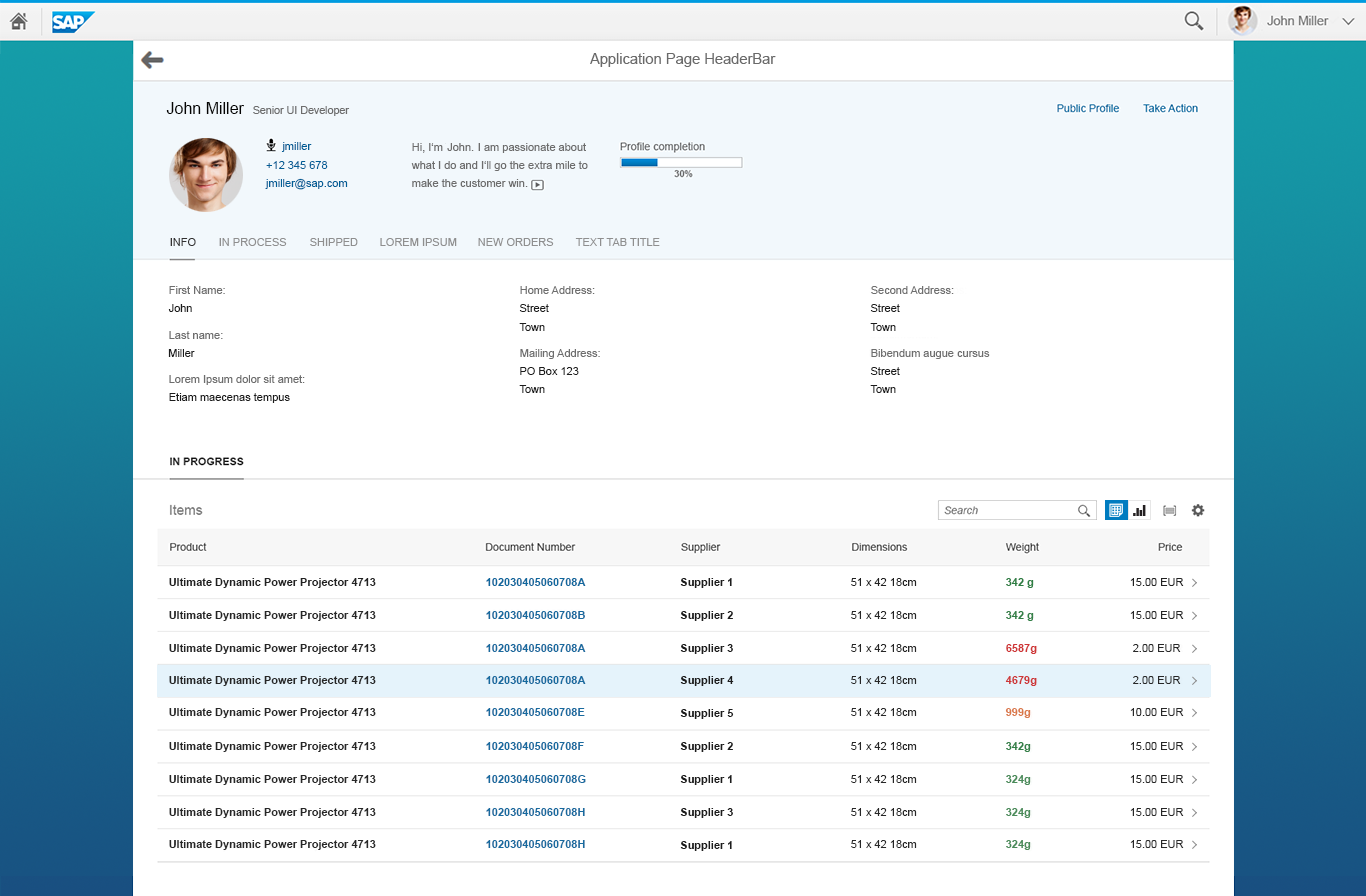
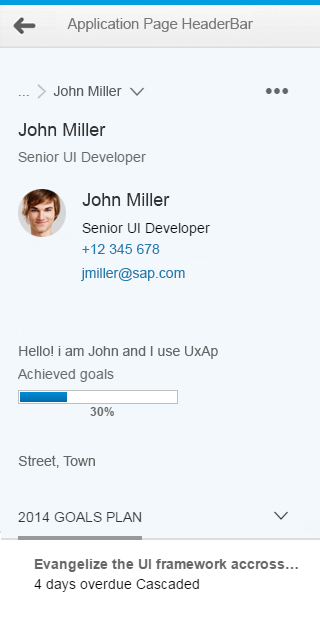
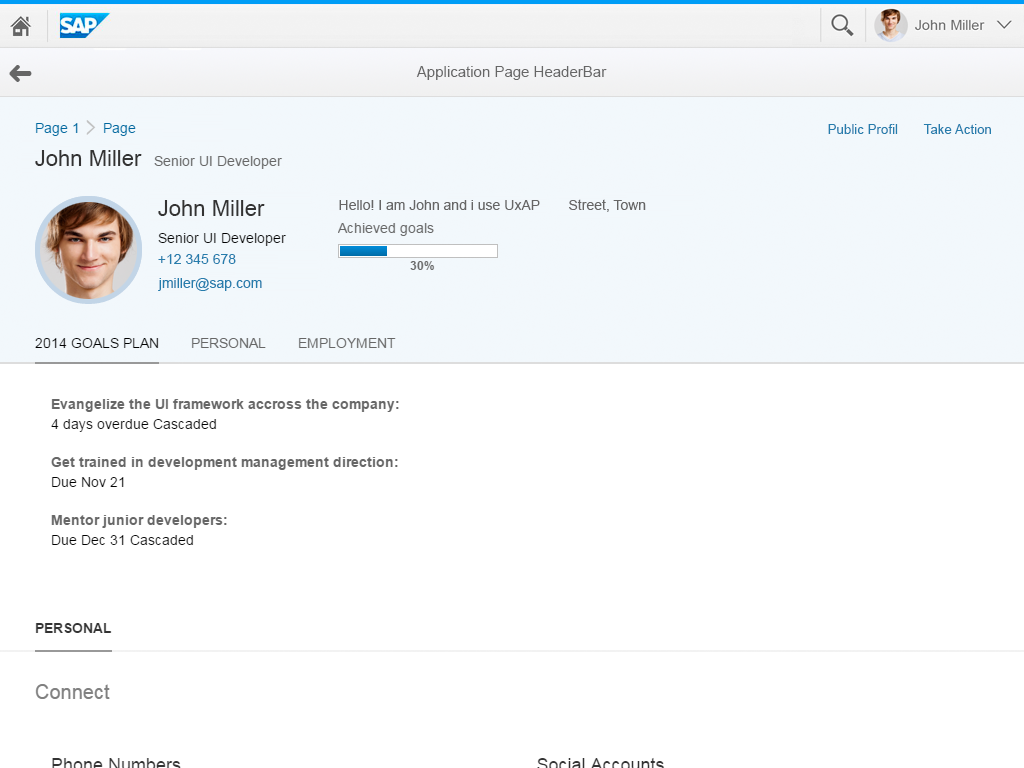
Object page floorplan
Usage
Use the object page floorplan if:
- You need to let users display, create, or edit an object.
- You want to offer a flat page with no navigation for a simple object.
- You want to use tabs or anchor navigation for a more complex object.
Do not use the object page floorplan if:
- You need to guide the user through a series of steps when a new object is created.
- You need a progressive disclosure approach for the creation process.
- The creation process is not linear, but can have different paths, depending on the information selected.
- The user is not familiar with the creation task.
In all these cases, consider using the wizard floorplan instead.
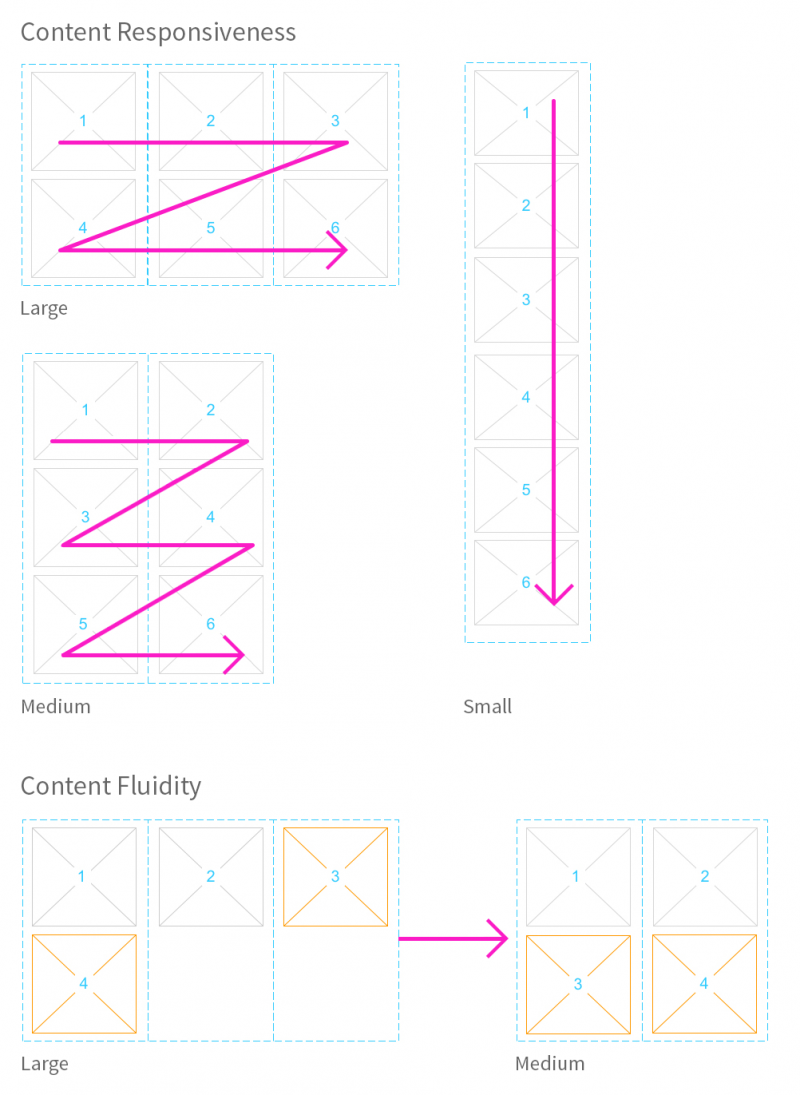
The layout for size XL (large display) contains four columns.
The default layout for size L (desktop) contains three columns. You can also use an optional two-column layout.
Structure
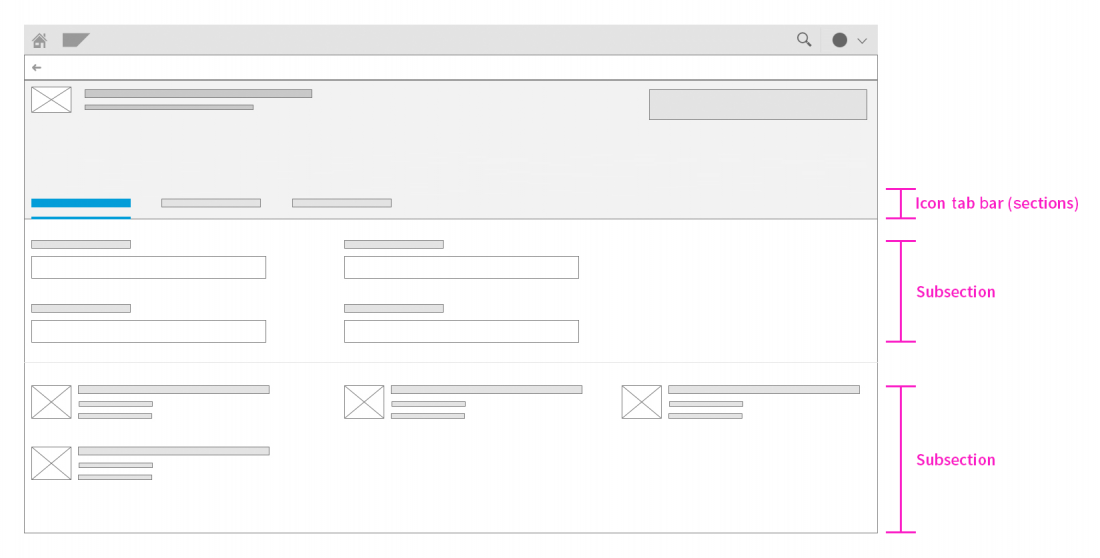
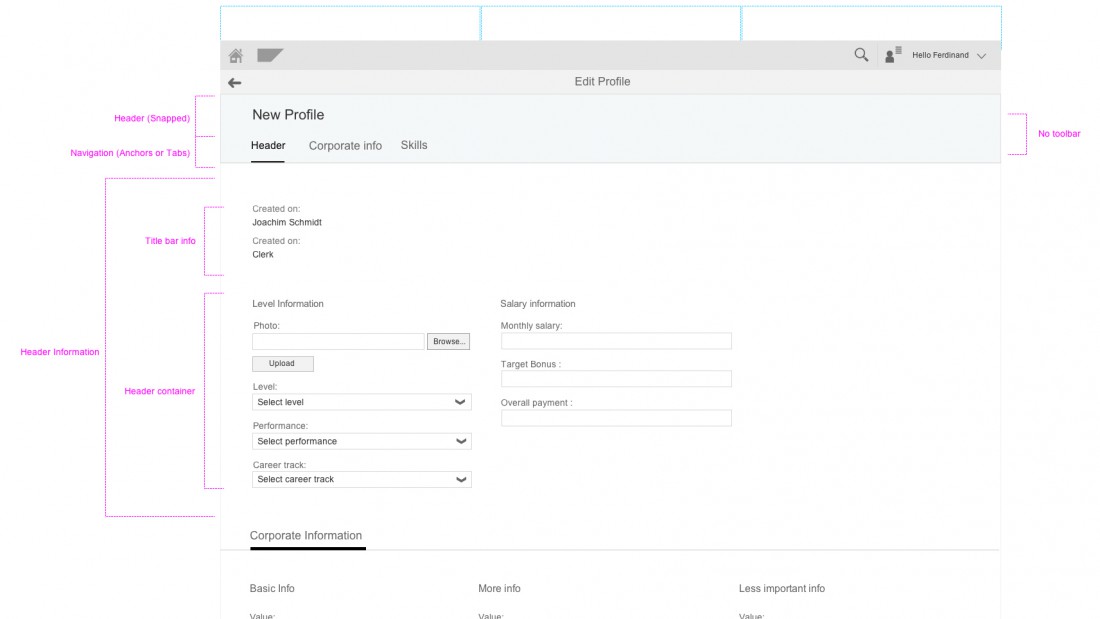
The object page is a full screen floorplan with a display mode, a create mode, and an edit mode.
In all modes, the object page contains:
- A snapping header
- A navigation bar
- A content area
The edit and create modes differ from the display mode in two respects:
- The header does not contain a toolbar.
- Instead, a footer toolbar is used for actions and messaging.
The following sections explain these components in more detail.
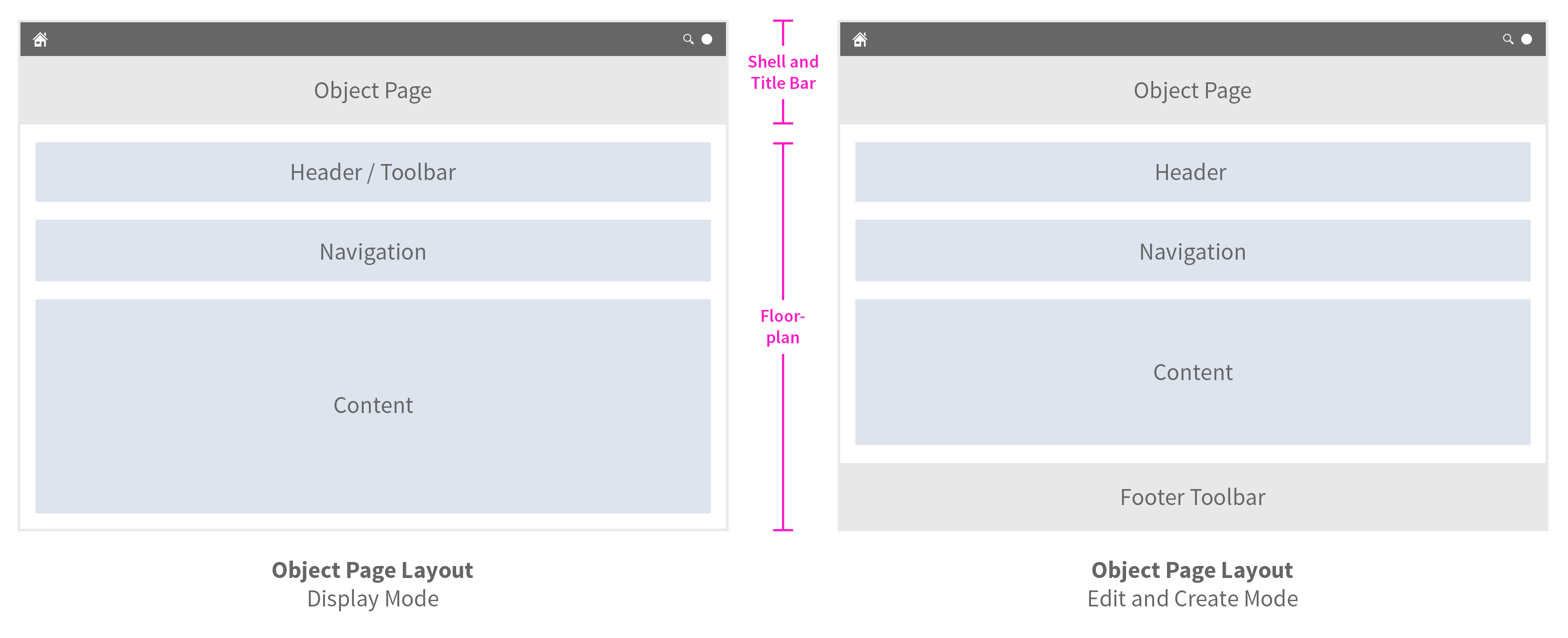
Schematic visualization of object page
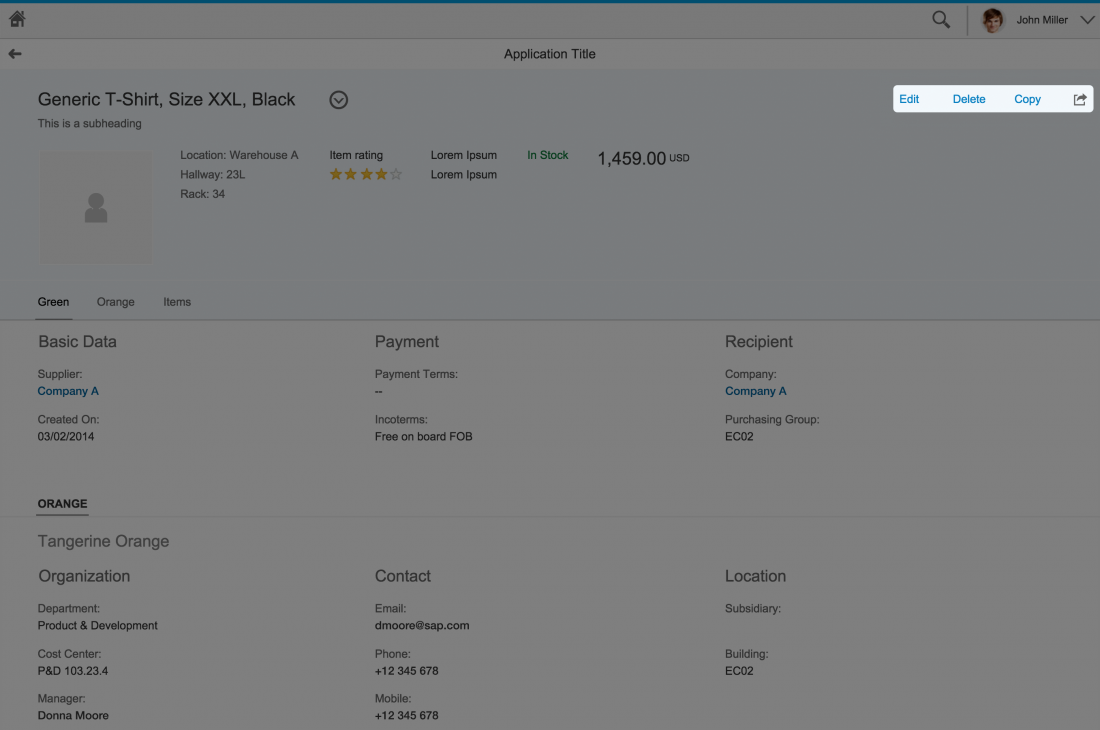
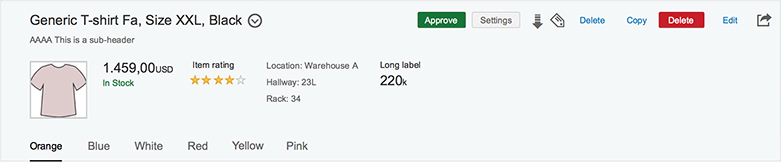
Snapping Header
The snapping header is the uppermost element of the object page floorplan. It contains key information about the business object and provides the user with the necessary context. In display mode, the header also contains global actions for the object.
Toolbar
The object page follows a “one toolbar” approach:
- In display mode, place all actions in the header toolbar. Do not use the footer toolbar.
- In create or edit mode, place all actions in the footer toolbar.
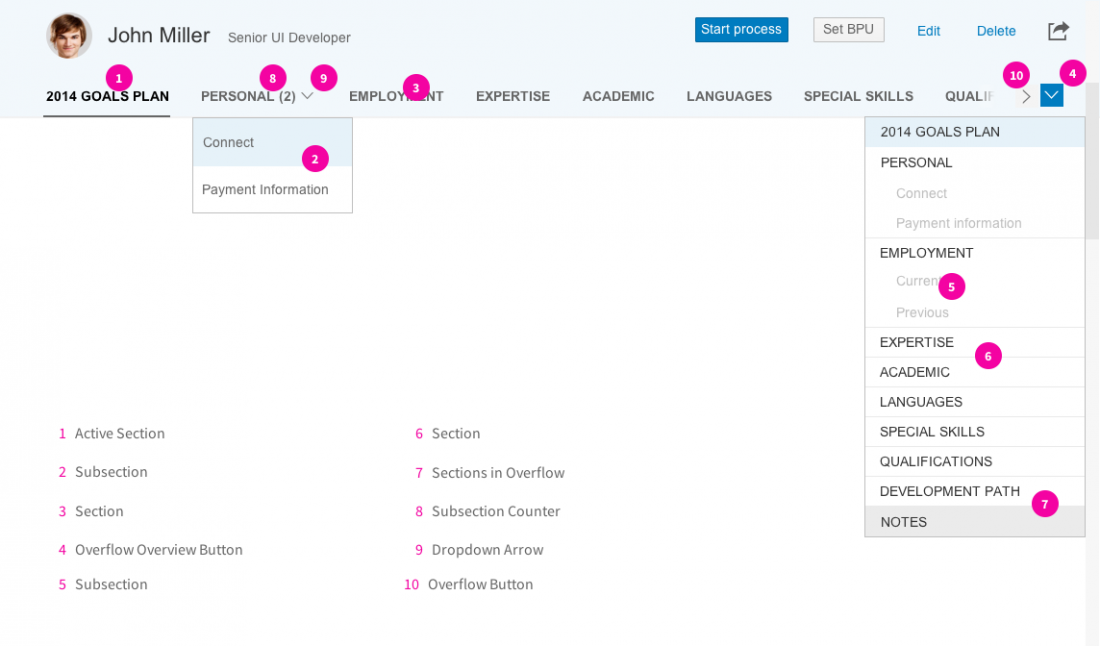
Anchor Bar and Overflow
The anchor bar is the default navigation control for the object page. It consists of a series of anchor links, which are arranged horizontally at the top of the page. The anchors represent sections or subsections of the page. Clicking on these links directs the user to specific sections of the page. The anchor links remain visible when the user scrolls down the page.
If there are more anchors than the screen can accommodate, the remaining anchors move into an overflow menu. The overflow button on the right of the navigation bar (down arrow) opens a hierarchical dropdown list of all sections and subsections.
You might also see a small right arrow on the anchor bar. This arrow allows you to scroll horizontally to reveal the any hidden content, and only appears when you hover over the overflow menu. In the meantime, this arrow has been replaced by the overflow arrow button, but is still supported technically for legacy reasons.
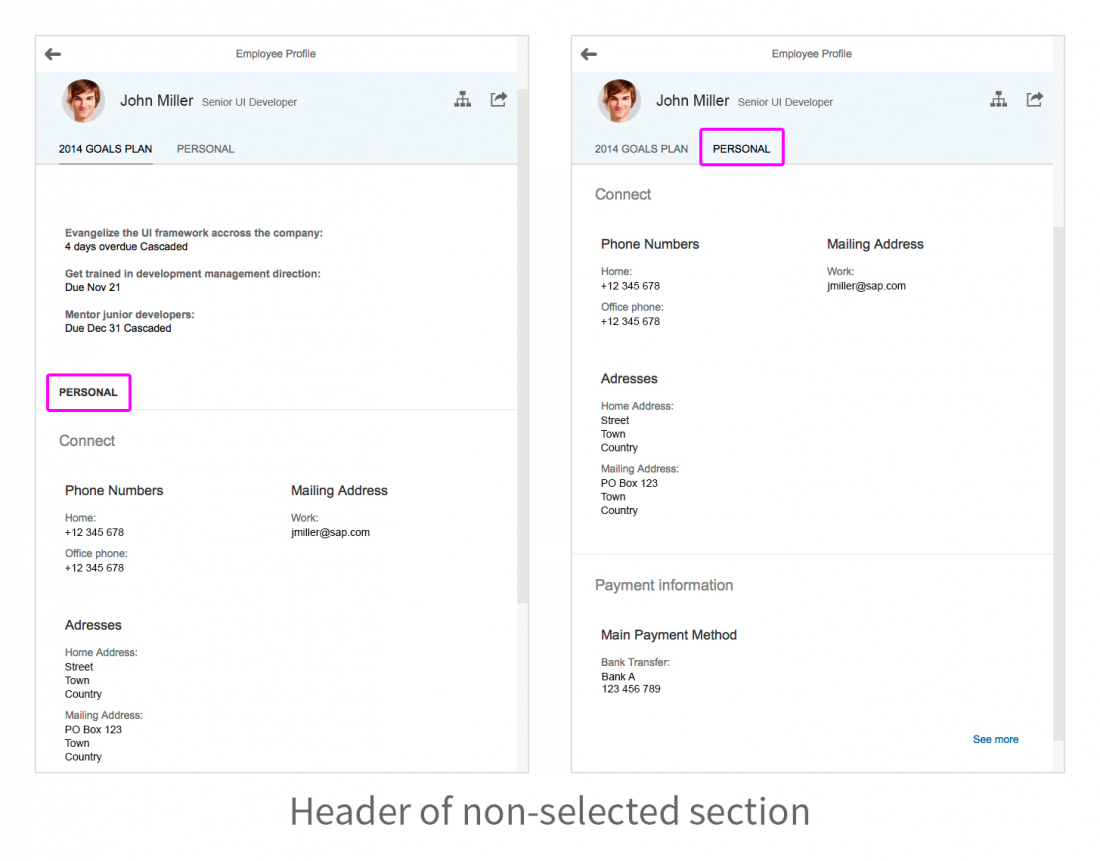
When the header content is folded, the navigation bar becomes part of the header. To avoid duplicating the title, the object page hides the title of the uppermost section (active or selected). Instead, the selected anchor link in the anchor bar acts as the title. If a section contains only one subsection, the title of the subsection becomes the name of the section. In this case, there is no subsection submenu.
Layout and Responsiveness
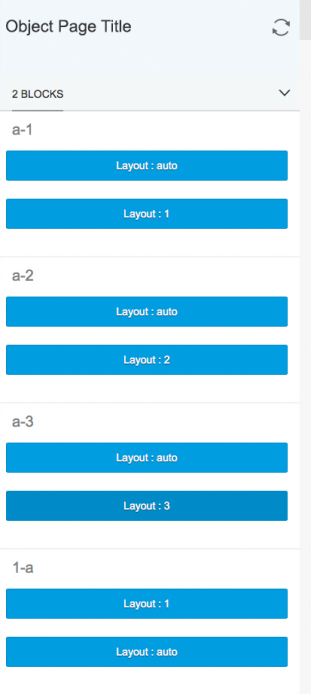
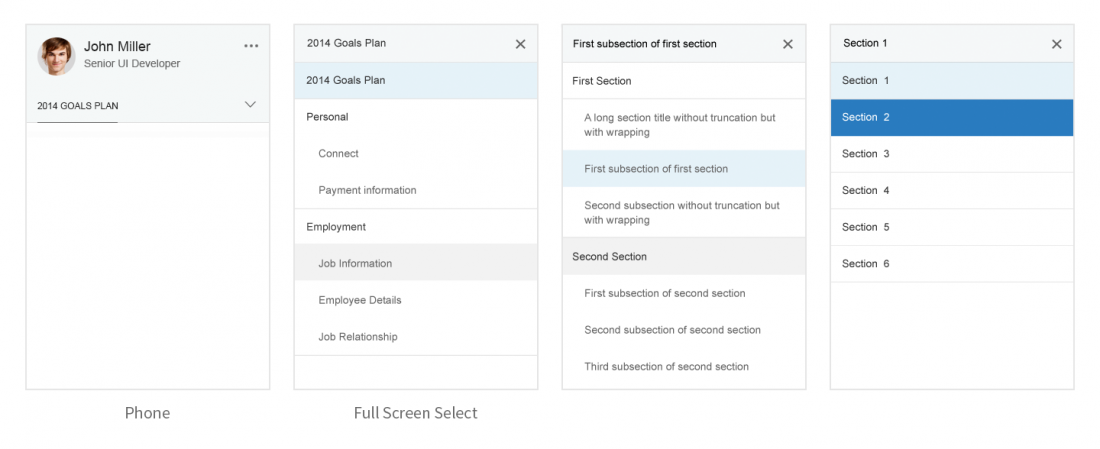
On small screens, the anchor bar becomes a dropdown list. The text field of the dropdown list shows the section currently selected. Clicking the dropdown menu opens a hierarchical list with all the sections and subsections of the document.
Behavior and Interaction
- Clicking an anchor link scrolls the page to the selected section.
- Clicking a section anchor that contains more than one subsection opens a subsection menu.
- Clicking a subsection scrolls the page to the selected subsection.
- The keyboard left and right arrows allow the user to move between the anchor links.
- Hovering over the fade area to the left or right of the anchor bar causes an overflow arrow button to appear (compact mode only). The overflow arrow button is always visible in cozy mode.
- Clicking the overflow scroll button (right arrow) scrolls the anchors horizontally to bring anchors that are hidden in the overflow into view.
- Clicking the overflow menu button (down arrow) displays a hierarchical dropdown list with all the sections and subsections of the document. Clicking an item in the overflow list scrolls to the respective section or subsection.
Important: Use title case for the anchor bar texts. To do this, you need to change the default capitalization (block caps) by changing the the property upperCaseAnchorBar to “false”.
Hiding the Navigation
You can also hide the navigation bar, leaving a flat, scrollable object. We recommend using this flat view for simple content that doesn’t require anchor navigation.
Tab Navigation
As an alternative to anchor navigation, you can also opt for tab navigation. The tab bar works in a similar way to the icon tab bar, but is not the same control. Tab navigation for the object page is a variant of the anchor bar, and is handled by the object page layout control.
If you set the tab bar property (useIconTabBar = “true”), the navigation bar displays tabs instead of anchors. The object page only supports text-only tabs; icon tabs and icon/text tabs are not available. The object page sections and subsections are reflected in the tab navigation: sections of the object page become the tabs, and subsections become the internal content of the tab. The tabs can have an item counter, which is displayed in parentheses next to the title of the tab.
On small screens, the tab bar uses the same horizontal carousel overflow pattern as the icon tab bar. This differs from the dropdown approach used for the anchor bar.
Tab Bar Subnavigation
To make it easier to reach specific content on a long tab page, tabs can have subnavigation. Subnavigation is optional and the default state is “false”. If the state is set to “true”, a dropdown arrow is shown next to the tab. Clicking on the tab displays a dropdown menu with the subsection anchors for that tab.
Breadcrumbs
If the object page uses a hierarchical parent-child drilldown, you can offer a breadcrumb for navigation. The breadcrumb is part of the snapping header.
Content Area
The object page content consists of sections and subsections arranged in a column layout. For large documents, you can enable a lazy loading mechanism (property: enableLazyLoading) to mitigate the loading time.
Sections
Sections are containers for subsections. They provide the basic structure for navigation, and are directly reflected in the navigation bar. Sections can have a title, subsections, and actions. However, they cannot contain controls.
Use title case for the section title (property titleUppercase = “false”). The title can have an item counter, which is displayed in parentheses. If a section contains only one subsection, the title of the subsection is used as the name of the section. In this case, there is no subsection submenu in the anchor bar.
Global actions are always placed at subsection level. Sections can only contain subsections, not content. Because of this, the object page only provides toolbars for global actions at the subsection level.
Subsections
Subsections are the containers for actual content. Always place individual controls inside the subsections. Subsection content is arranged according to the column layout approach for the respective screen size. A subsection can include containers for different controls (mixed content).
Subsections have a progressive disclosure mechanism to show and hide content. App developers can specify which content is shown initially, but the user can also display everything by selecting the Show All button at the bottom right of the subsection.
Each subsection can have a toolbar, which is placed at subsection header level on the right. The toolbar contains actions that affect the content of the subsection.
Subsections within the same section are separated by a gray horizontal line. Subsections can have an item counter, which is displayed in parentheses next to the subsection header.
You can include various types of related content in one subsection. The layout blocks for the object page give you the flexibility to combine different content types.
Forms
Forms follow the standard layout of the object page:
- Large: 3 columns
- Medium: 2 columns
- Small: 1 column
Forms are located within subsections. They follow the column design of the object page, whereby each form group is arranged into a column. The title of the form is given by the subsection header. Only use the form title if you are using several forms within the same subsection.
To best fit the column layout, we recommend using top-aligned labels for form fields. Top-aligned labels are known to reduce completion times, and are the best approach for forms requiring localization or long labels. Using top-aligned labels also avoids issues with the spacing between the label and form field, which can occur with left- and right-aligned labels.
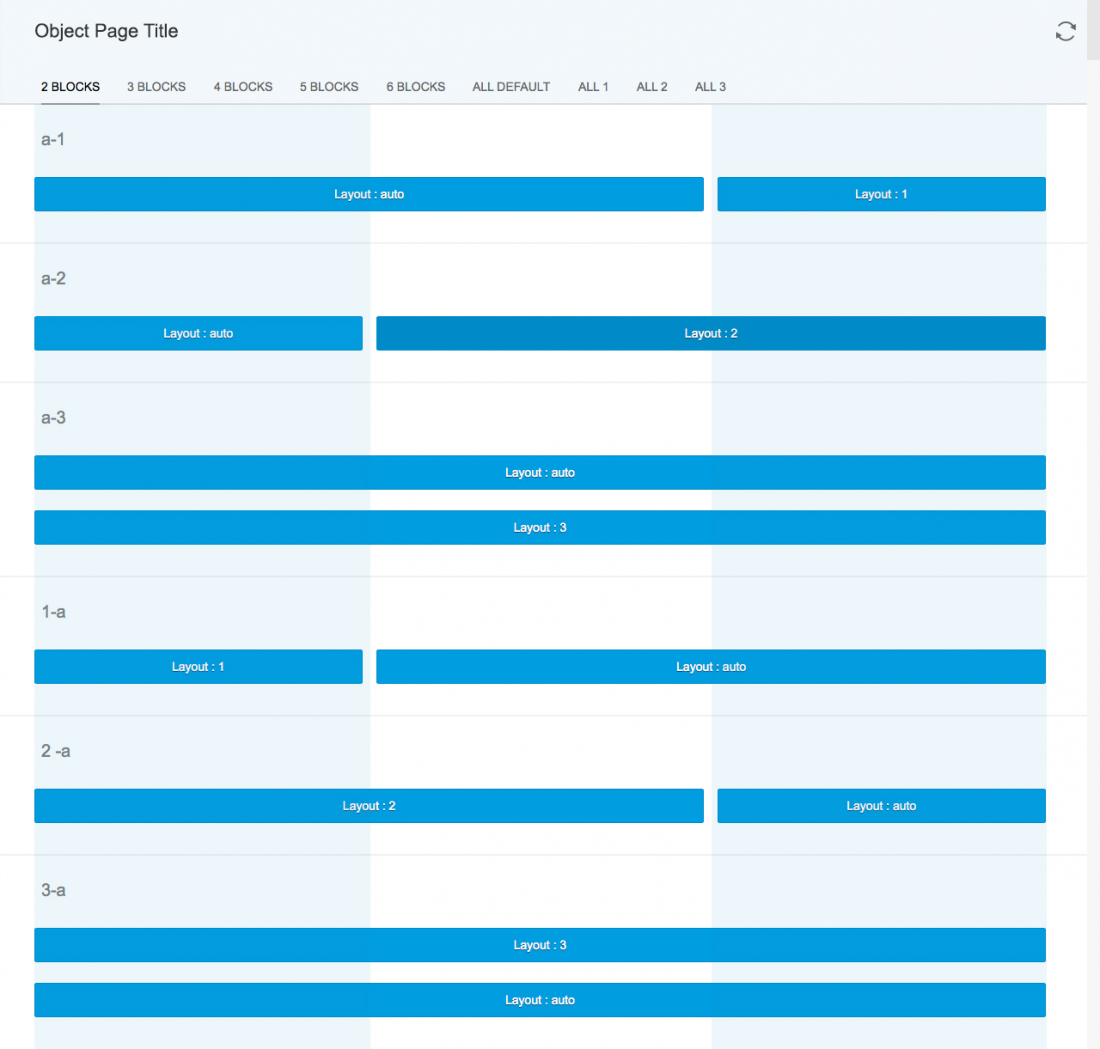
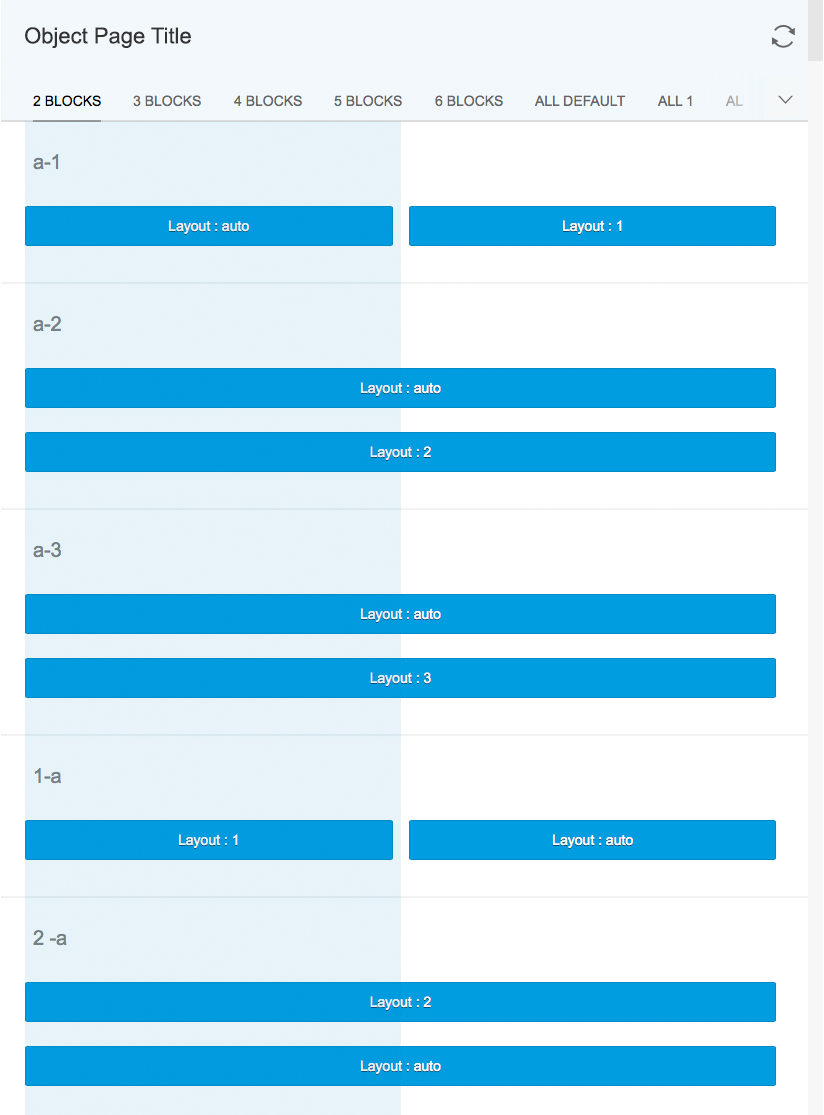
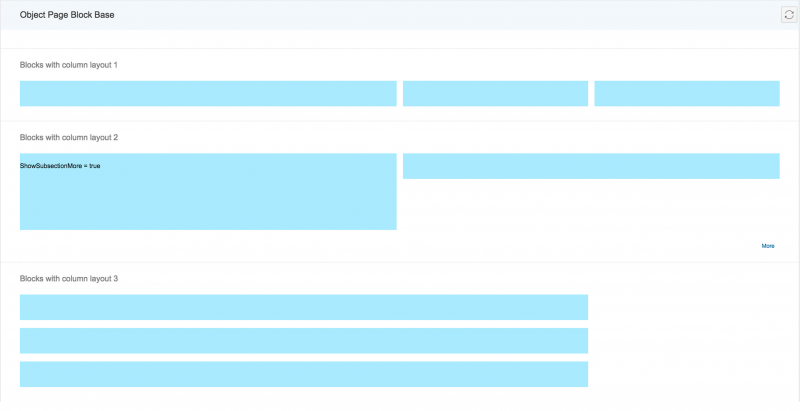
Blocks
Layout blocks allow content to be aligned within the columns as follows:
- Layout 1: Occupies the maximum available horizontal space of one column.
- Layout 2: Occupies the horizontal space of only two columns. If there is only one column available, it occupies one column.
- Layout 3: Occupies the horizontal space of three columns. If there is only one column available, it occupies one column. If there are only two columns available, it occupies two columns.
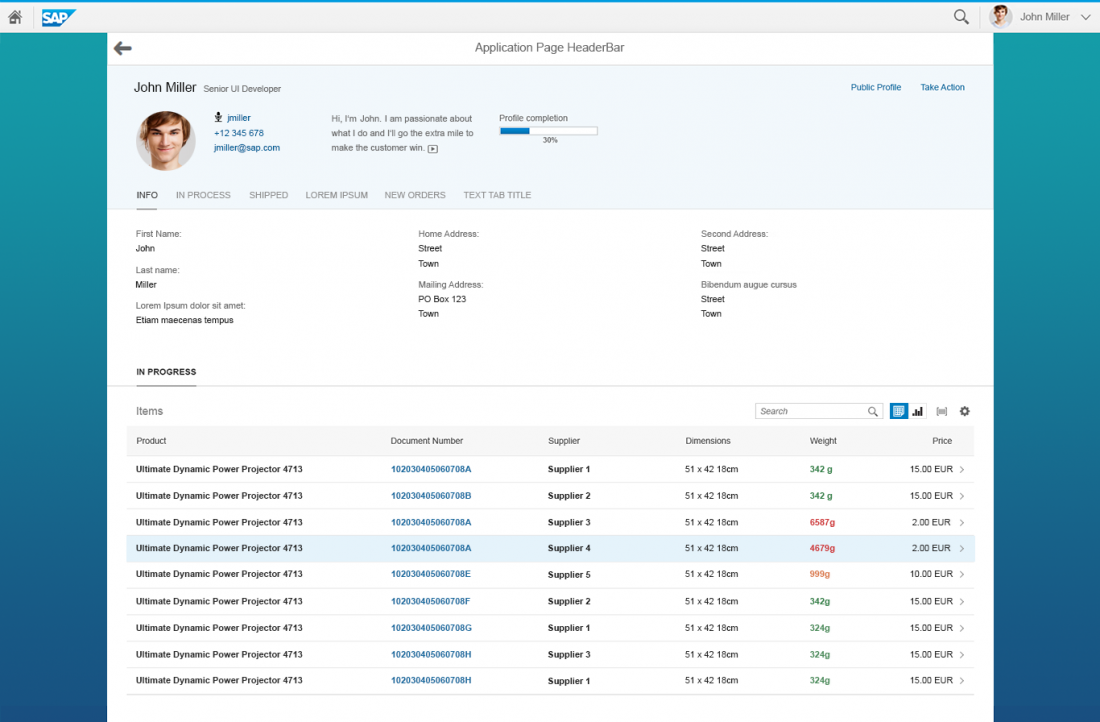
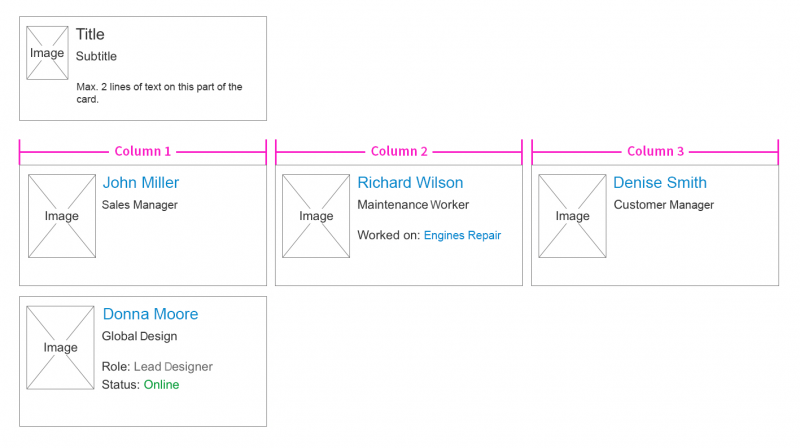
Contacts
The contacts on the object page are technically a list, but they can be represented visually as a card.
The cards can contain:
- An image (optional)
- A title (mandatory)
- A subtitle (optional)
- A text snippet consisting of two lines maximum (optional)
A single card covers the column’s entire horizontal space. To avoid alignment problems, all cards are the same height. The card with the most content defines the overall height for all cards. The image can be rectangular or round. It shows in the top left corner of the card. The content of the card never truncates. If there is not enough space to display the information, it wraps onto the next line.
Tables
If you need to include a long table in an object page, consider placing it at the end of the document. Do not use vertical scrollbars within tables, since this can hinder scrolling through the page itself. Similarly, do not use pagination in tables.
Child Page Representation
In object pages with drilldown navigation, child pages are represented in three ways:
- Visual representation in the header: A narrow blue band is displayed in the left margin of the snapping header.
- Breadcrumbs: A breadcrumb is displayed above the object title. Limit the breadcrumb to the drilldown levels within the object page.
- Item navigation arrows: Up and down arrows in the application toolbar allow the user to navigate between subitems without going back to the original list.
Behavior and Interaction
Edit
The basic layout of the object page in terms of header, navigation, and content remains the same in all modes (display, edit, create). However, in the edit and create modes, there is no header toolbar. Actions show in the footer toolbar instead. In edit mode, the object page can contain a mixture of editable and read-only content.
If the user needs to edit elements in the header, a header section is added in the content area for edit mode to enable editing.
Use the same content layout for both display and edit mode. Content should not change location when the user switches between display and edit modes.
For global and local editing guidelines, see Manage Objects – Create, Edit, Delete.
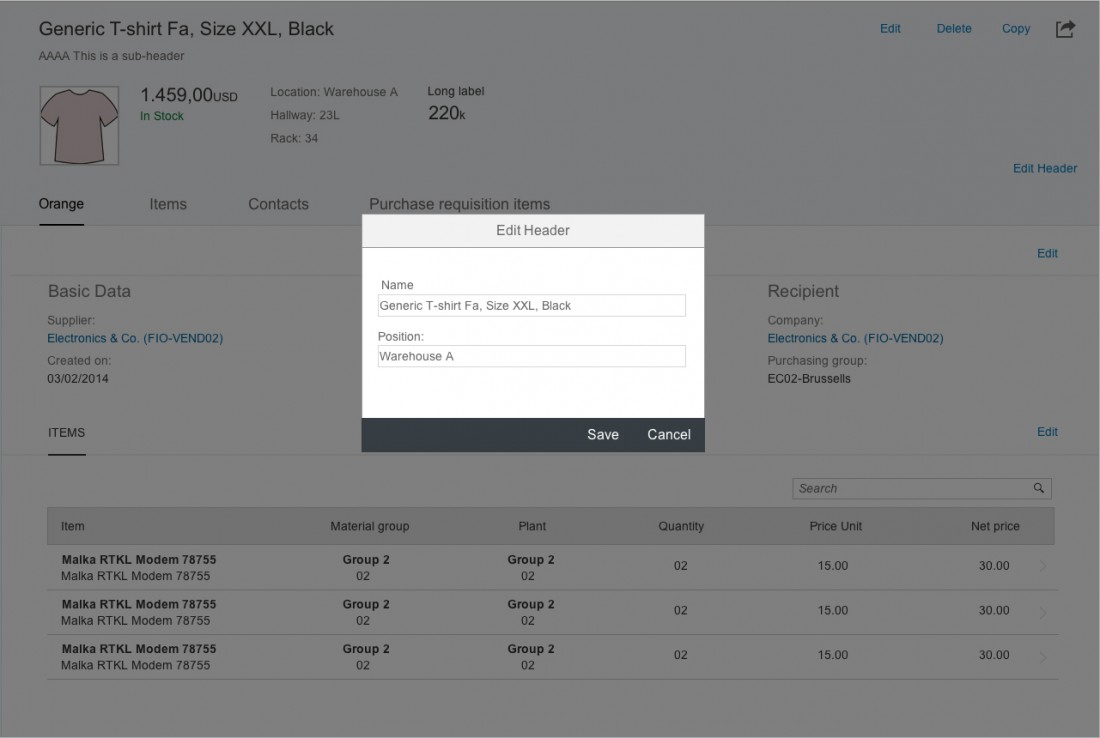
Editing the Header
The object page header can be edited in two ways:
- Global edit
- Partial edit
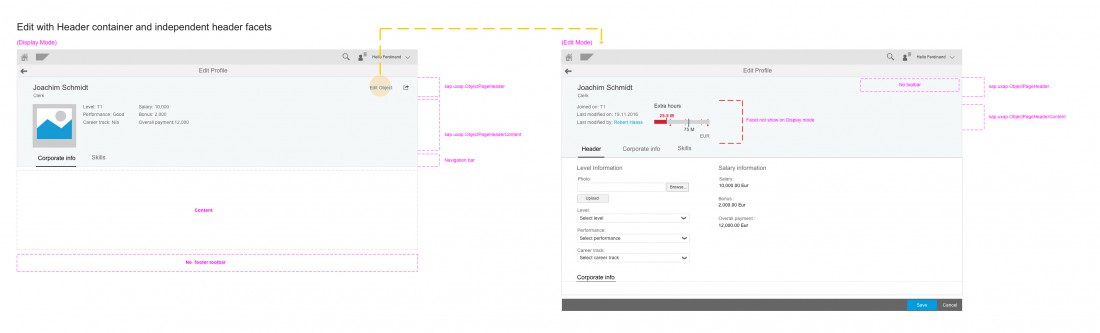
Global Edit
The header becomes editable when the entire object page is in edit mode. Because the header snaps on scroll, there are no editable forms in the header itself. Instead, a temporary header section is added before the other sections of the page. The title bar information and all editable fields from the header container move from the header to the new editable header section. Any non-editable content displays as read-only. You can leave out header content that doesn’t make sense in edit mode (for example, aggregated values that are calculated from several sources, KPIs, or micro charts).
If only a few fields in the header are editable, and they match an existing section, they are moved to that section. In this case, no editable header section appears.
The header container in edit mode may contain independent facets that are not included in the header content in display mode. These provide information to assist editing.
If the entire object page is in edit mode, but there is no editable information in the header, no editable header section is added.
Any changes made to the header are not reflected until the user saves them.
Partial Edit
The user can edit the header content separately from the other content on the page by pressing the Edit Header button.
If only a few elements are editable, the partial edit triggers a dialog. If there are too many elements to fit on a dialog, the partial edit triggers a subpage.
The subpage contains all editable information from the header. However, it differs from the “Header” section in global edit mode in that it has no action buttons in the toolbar, no navigation, and no breadcrumbs.
Unsaved Changes
If draft handling has been implemented, documents are automatically saved as draft versions in the background. An editing icon to the right of the object title indicates that a draft version exists. In other words, either the current user or another user has made changes, but not yet actively saved the document (“unsaved changes”). Do not show the editing icon for unsaved changes if draft handling is not supported.
Selecting the editing icon invokes a popover with more information about the unsaved changes. This normally states:
- Who made the changes
- When the last changes were made
The popover closes when the user clicks or taps the Close icon or anywhere outside the popover.

Unsaved changes popover (Mobile)
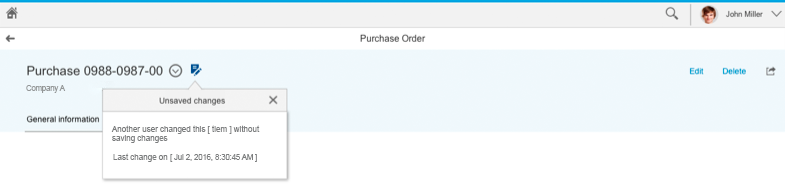
Unsaved changes popover (Desktop snapped)
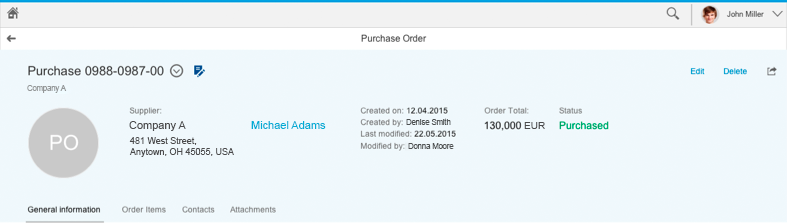
Unsaved changes popover (Desktop expanded)
Create
Create mode is similar to edit mode, except that the user creates a new object and defines a title for it. Until the new object title is known, use the placeholder text “New <Object>” (for example, “New Purchase Order”). Replace the placeholder text with the actual name or ID of the new object as soon as this has been entered or generated.
Consider using the wizard floorplan instead of the object page floorpan if:
- You need to guide the user through a series of steps when a new object is created.
- You need a progressive disclosure approach for the creation process.
- The creation process is not linear, but can have different paths, depending on the information selected.
- The user is not familiar with the creation task.
Guidelines
Header
Use the header to set the context. Ensure that it is clearly structured and contains only essential information. Too much information impedes the main purpose of providing a clear context.
Actions
Arrange the actions in the header toolbar with care, and consider what matters most to the user:
- Highlight actions that are common or most important.
- Differentiate between secondary and generic actions.
- Use either a text button or an icon for an action, but not both.
- Place the most important actions on the left (actions go into the overflow from right to left).
- Establish a coherent visual approach.
Tab Navigation
Use tab navigation if you need a facet approach to your content. This could be due to performance issues in a flat view, or in response to a specific user preference. If you need to use icons, tabs as process steps, or tabs as filters, use the object view floorplan.
Not a Content Dump
Avoid using the object page as a universal container for masses of information. You should use the object page in accordance with the SAP Fiori principles: role-based, coherent, simple, and adaptive.
Simplify Content for Your Users
Give your users quick and easy access to the information they need to complete their task(s). Use a progressive disclosure strategy to keep your interface clean. You can always provide additional information on request. Furthermore, only present your users with information that makes sense for their industry, role, activity, and task.
Dynamic Side Content
You can offer dynamic side content alongside the object page under the following conditions:
- Use the side panel only for contextual content. Do not place finalizing or global actions in the side panel. This is because opening the side panel occupies the whole right side of the screen. There is no way to show it only below the header and anchor bar.
- Do not place object information in the side panel. This information should always be in the content area of the object page.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.
Elements and Controls
- Snapping Header (guidelines)
- Object View Floorplan (guidelines)
- Flat Object View Floorplan (guidelines)
- Wizard Floorplan (guidelines)
- Smart Templates (SAP Help documentation)
- Object Page Smart Template (SAP Help Portal)
Implementation
- No Links.


 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.