- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Form
sap.ui.layout.form.Form | sap.ui.layout.form.SimpleForm | sap.ui.comp.smartform.SmartForm (smart form since version 1.36)
Intro
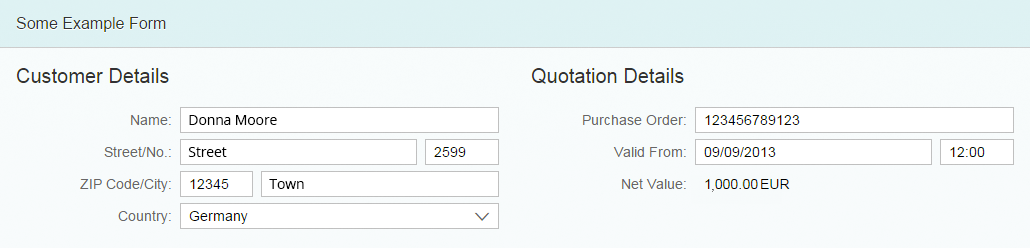
A form is used to present data to the user and to allow users to enter data in a structured way.
The form acts as a container for other UI elements (such as labels, input fields, checkboxes, and sliders), while structuring these into a specific layout.
In SAPUI5, forms can be built using two different controls:
- Form – sap.ui.layout.form.Form (API)
- Simple form – sap.ui.layout.form.SimpleForm (API)
The simple form control gives you the same result as the form control, but in a much easier way:
The layout and structure are defined by the content that is entered.
- Form containers and form elements are created automatically according to the content type.
- A title (sap.ui.core.Title (API)) automatically starts a new form group (form container), and a label (sap.m.Label (API)) automatically starts a new row (form element).
Types
There are three types of forms:
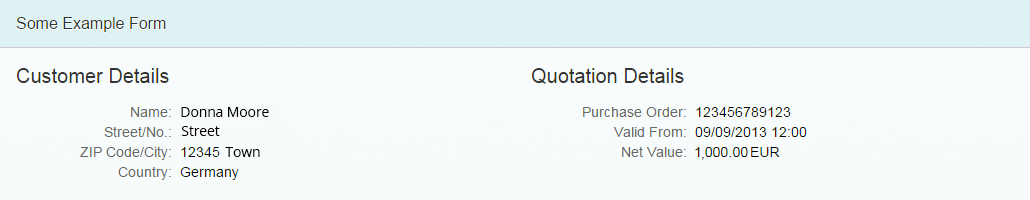
- Read-only: the data is presented only as label-value pairs.
- Editable: users can enter data.
- Mixed: some fields are editable and some are not.
The form/simple form property “editable” only changes the height of labels for vertical alignment to a field (editable = true) or text (editable = false). It does not switch the entire form from editable to read-only mode, or vice versa.
Responsiveness
There is a specific set of form layout controls for forms and simple forms. You must assign one of these form layout controls to each form and simple form by using the property “layout”.
The form layout control defines how labels and fields are arranged on the screen. Always use the responsive grid layout (sap.ui.layout.form.ResponsiveGridLayout). Please do not use any other form layout control, as these are only available to enable downward compatibility.
By using the responsive grid layout, the form offers a responsive layout based on a 12-column grid. There are two breakpoints, which result in three supported sizes: L, M, and S. These breakpoints are not the L, M, and S breakpoints of the page. In contrast to the page’s breakpoints, which react to the screen width, the breakpoints of the responsive grid layout react to the width of the form.
Note: For downward compatibility reasons, the default form layout control for the form and simple form is not the responsive grid layout. Therefore, you need to assign the responsive grid layout manually to each form or simple form by using the layout property.
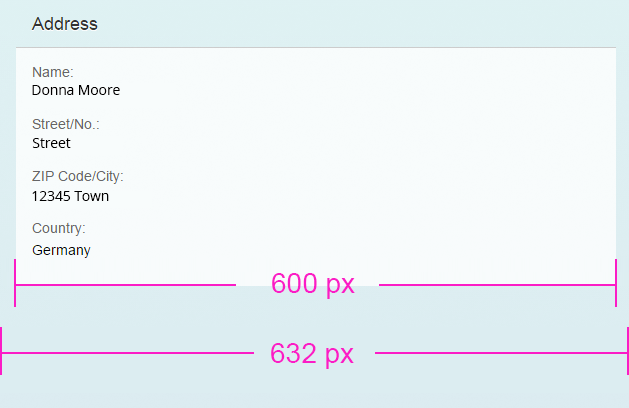
If the value of breakpointM is 600, size S is shown when reaching a width of 600 px .
Due to padding of the container in which the form is placed, this width is usually reached before the page width reaches its breakpoint from M to S. This means that the form changes from M to S before the page does. To set the form’s breakpoint individually and synchronize it with the page, you can use the property breakpointM.
The property breakpointL between sizes L and M works in the same way. The default value of breakpointL is 1024.
For each size, you can define how many grid columns are used for labels, fields (implicitly), and empty grid columns (emptySpanL, emptySpanM, emptySpanS). The optional empty grid columns are placed after the input elements. They avoid excessive stretching of the entry fields where necessary. This ratio is displayed in this document as x:y:z, where x is the number of grids used by the labels, y stands for the fields, and z for empty columns.
To define grid columns for labels, use the layoutData property for the label.
Exception for labelSpan:
- labelSpanL is used for labels in forms with several form groups arranged in more than one column. It applies for both M and L screen sizes.
- labelSpanM is used for labels in forms arranged in one column. It applies for both M and L screen sizes.
- labelSpanS is used only for screen size S, as expected.
Input controls such as input fields can be displayed in both cozy and compact mode. To horizontally align a label next to a field, the form has different CSS in cozy mode and compact mode.
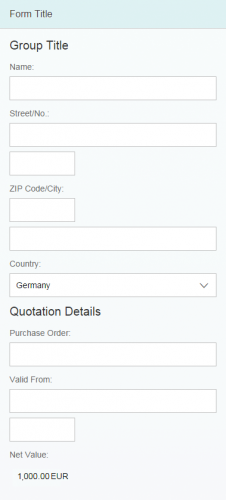
Size S (Smartphones and Dialogs)
The form uses a single-column layout in size S by default (not to be confused with the underlying grid columns). The form groups are positioned below each other in a single column. The labels are positioned above the input field or value to avoid truncation.
The label-field ratio is 12:12:0 (12 grid columns used by the labels, 12 grid columns used by the fields, and 0 grid columns used by empty columns).
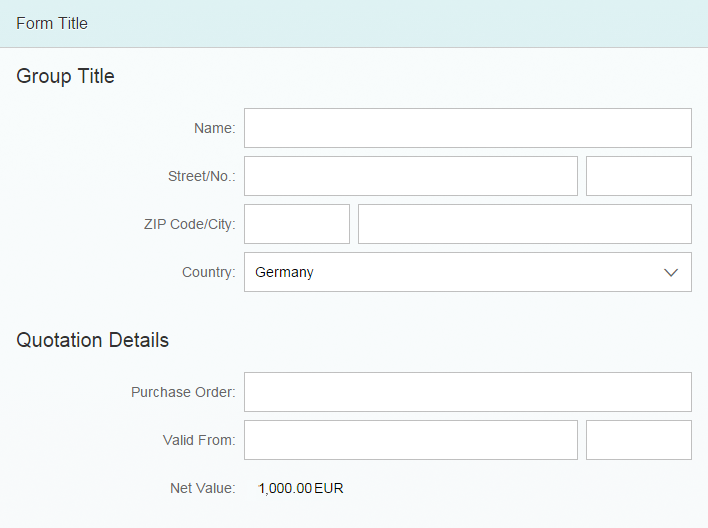
Size M
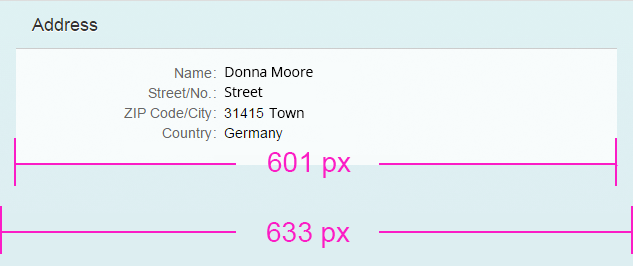
The breakpoints for size M are set by default to 600 px (breakpointM = 600) and 1024 px (breakpointL = 1024). This means that if the form has more than 600 px, but no more than 1024 px available, it renders the M layout. The M layout ranges from 601 px to 1024 px. It can be changed with the properties breakpointM and breakpointL, which are properties of the responsive grid layout. If you are using a simple form, set these properties directly in the simple form control.
The M size form has a single-column layout by default in which the labels are positioned in the same row as the corresponding input field or value. The form groups are positioned below each other.
The label-field ratio is 2:10:0 (2 grid columns used by the labels, 10 grid columns used by the fields, and 0 grid columns used by empty columns).
We highly recommend changing this default layout according to your app’s needs. For more information, see the recommended layouts in the Layout section.
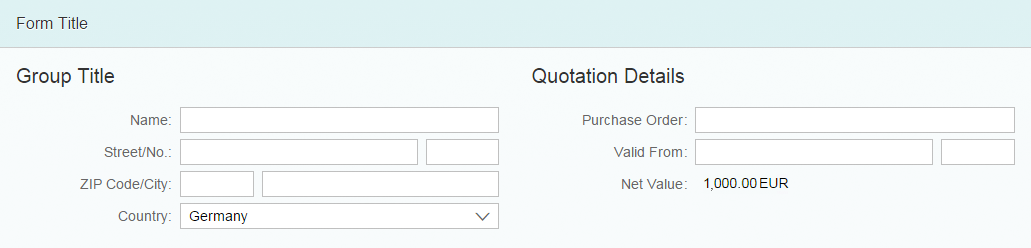
Size L
The breakpoint for size L is set by default to 1024 px. This means that if more than 1024 px are available, the form is rendered in L layout. It can be changed with the property breakpointL, which is a property of the responsive grid layout. If you are using a simple form, set these properties directly in the simple form control.
To have all the information on one screen and avoid scrolling, the form groups are placed next to each other in two columns by default. In these columns, the labels are positioned in the same row as the corresponding input field or value. The form groups adopt the Z layout.
Layout
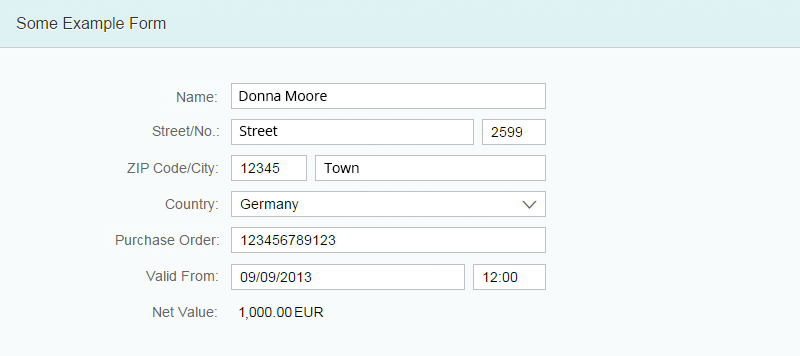
One Page, One Form
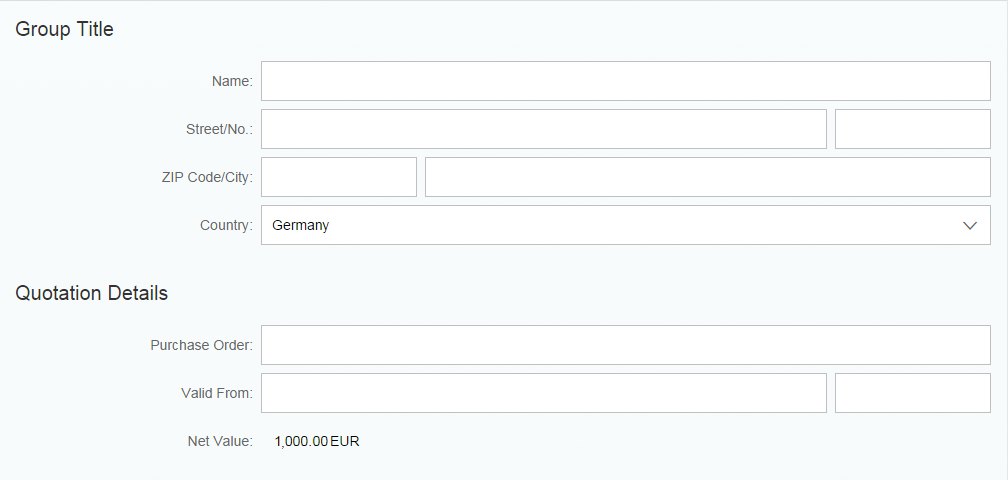
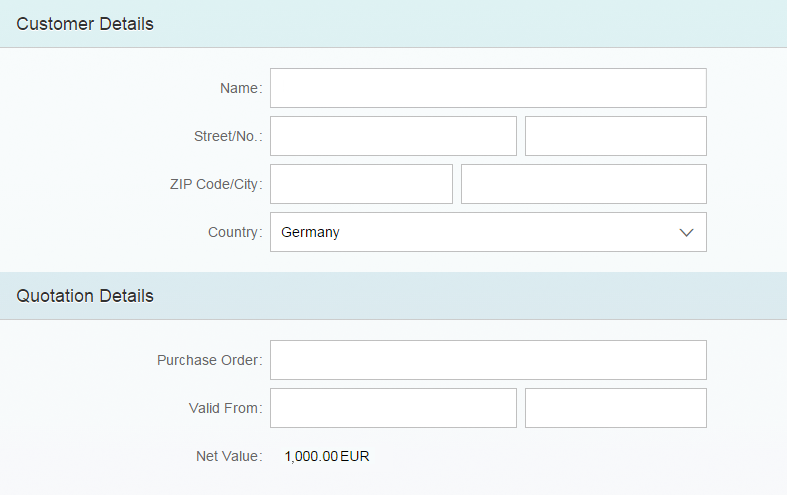
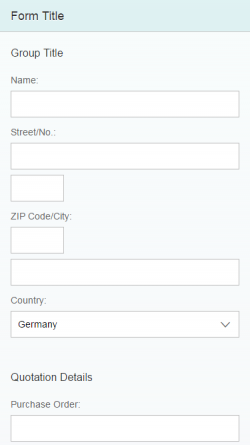
One form with one or more groups will usually meet your needs. In this case, use group titles, not the form title. If a form contains only one group, do not use a group title.
If the form is one of several elements on the page, such as tables and lists, you may also set a form title.
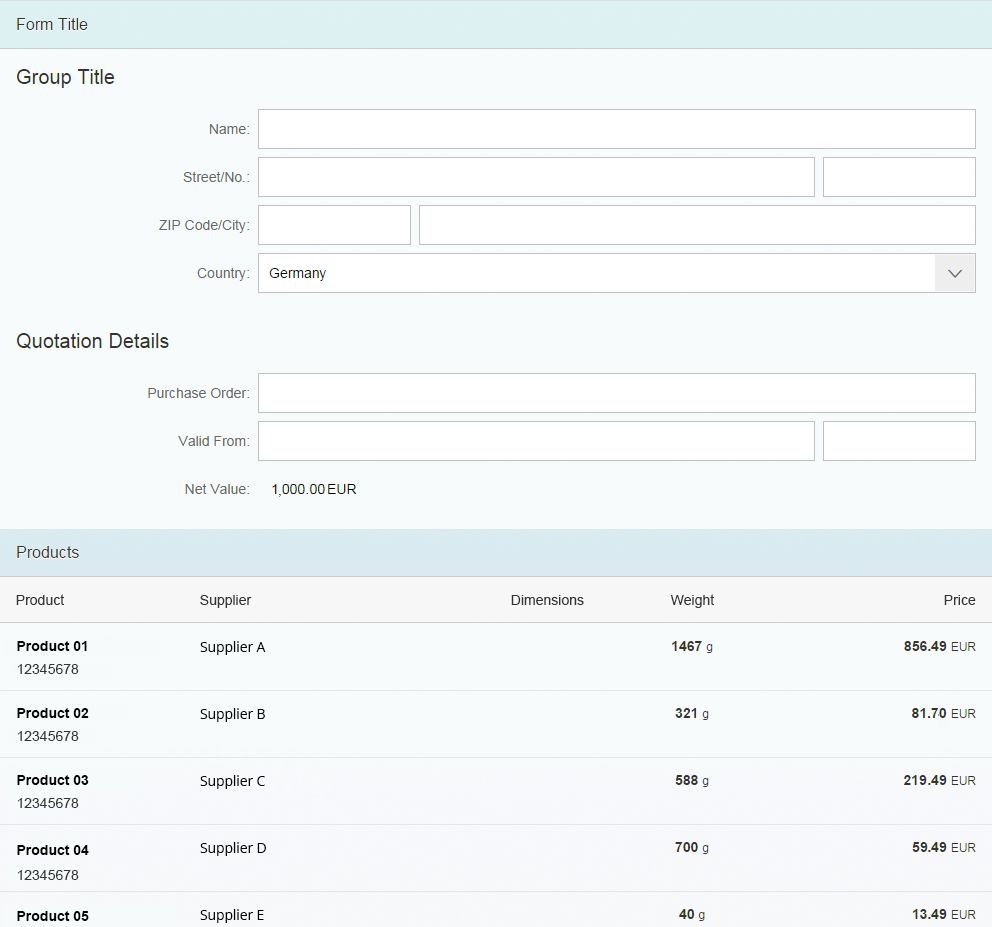
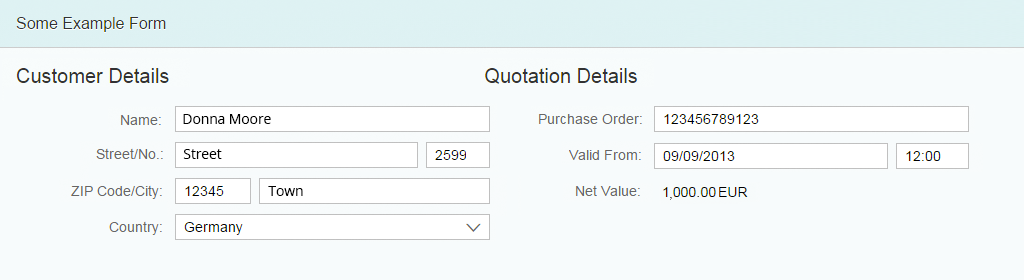
One Page, Many Forms
If you want to emphasize that some groups are very distinct, use several forms on a page instead of one form with several groups. Visually this looks more separated than using a single form with several groups. Give each form a meaningful title. If necessary, you can structure each form with groups as well. In this case, also give the groups a title.
Various Layouts
The following sections give guidance on how to configure the form so that it meets the needs of different sizes. Depending on where you place the form, we highly recommend changing the default and using one of the following layouts according to your app’s needs.
Size S (Smartphones and Dialogs)
Size M (Tablet) – Full Screen
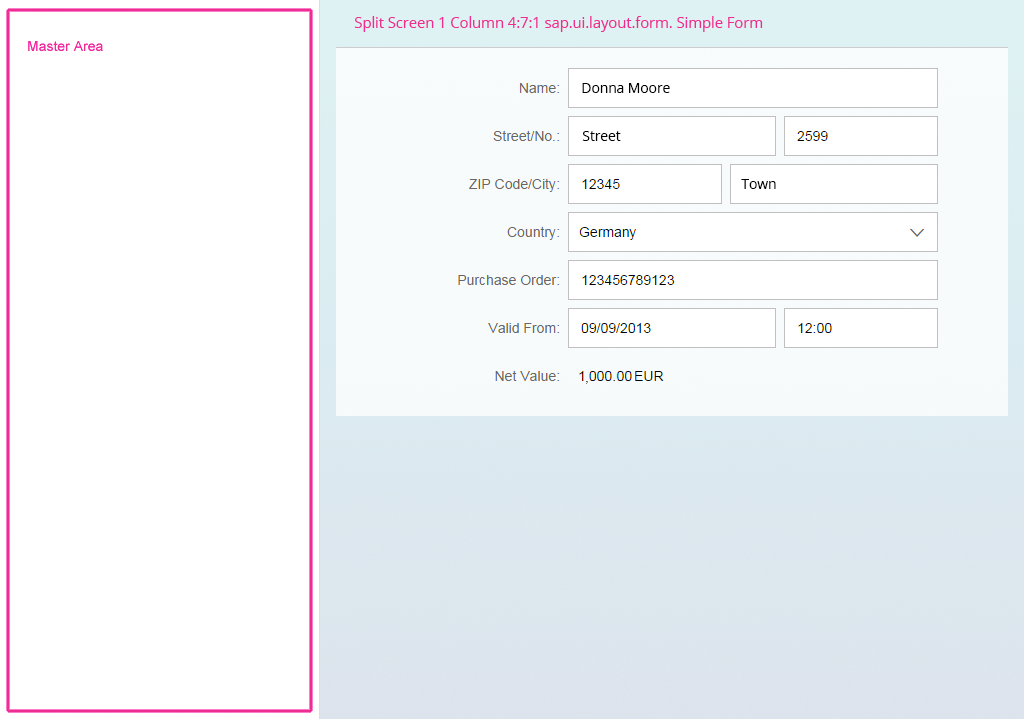
If you place the form in the details part of a split screen, use a single-column layout with the label-field ratio 4:7:1 (4 grid columns used by the labels, 7 grid columns used by the fields, and 1 grid column used by empty columns).
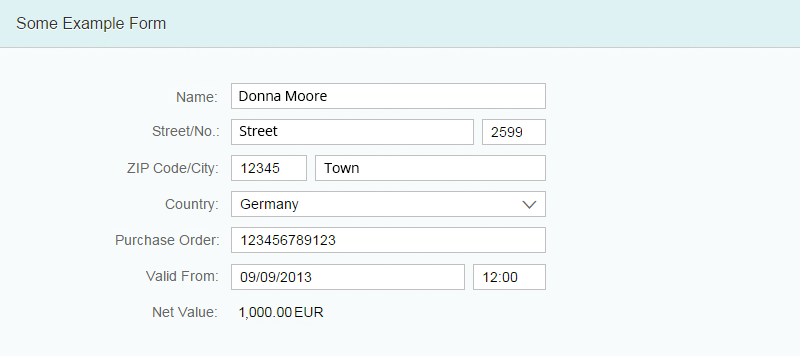
If you place the form in a full-screen app, use a single-column layout with the label-field ratio 3:5:4 (3 grid columns used by the labels, 5 grid columns used by the fields, and 4 grid columns used by empty columns).
Size M goes down to 601 px. In this size, the 3:5:4 approach may not be wide enough for longer labels and fields. So if you expect long labels or input values, use the label-field ratio 4:8:0 (4 grid columns used by the labels, 8 grid columns used by the fields, and 0 grid columns used by empty columns).
If you place the form in a full-screen app and it contains several form groups, use a two-column layout with the label-field ratio 12:12:0 (12 grid columns used by the labels, 12 grid columns used by the fields, and 0 grid columns used by empty columns).
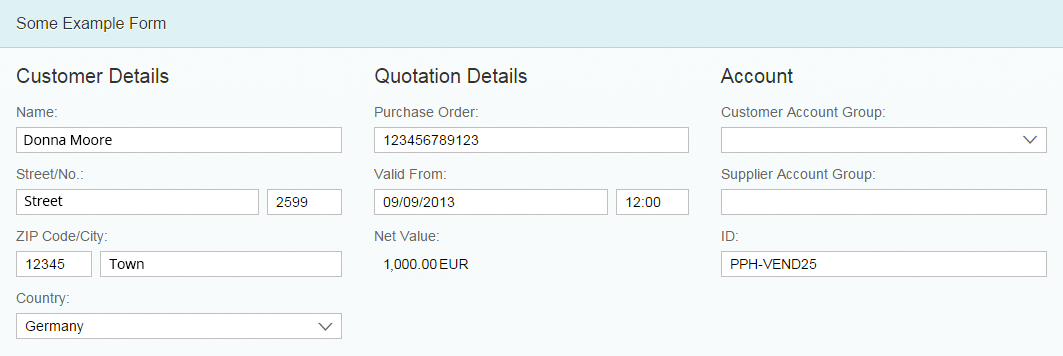
Size L (Wide Screens) – Full Screen
If the form contains a single form group, use a single-column layout with a label-field ratio of 3:5:4 (3 grid columns used by the labels, 5 grid columns used by the fields, and 4 grid columns used by empty columns).
If the form contains multiple form groups, use a two-column layout with a label-field ratio of 4:8:0 (4 grid columns used by the labels, 8 grid columns used by the fields, and 0 grid columns used by empty columns).
If the form is put into a full-screen app and it contains multiple form groups, you can also use a three-column layout with a label-field ratio of 12:12:0 (12 grid columns used by the labels, 12 grid columns used by the fields, and 0 grid columns used by empty columns).
Due to the early breakpoint from M to L (1024 px) and no breakpoint to XL for bigger sizes, L-sized screens must fit large screens as well as screens that are slightly bigger than 1024 px. So if you use a three-column layout for extra wide screens, all labels and fields must also fit on a screen that is slightly bigger than 1024 px. Truncating labels in particular may cause problems here, so they are placed above the fields.
If you use a three-column layout for size L screens, do not use a two-column layout for size M screens as it could create a lot of white space. In this case, use a single-column layout instead.
- Recommended: L2-M2-S1, L2-M1-S1, L3,M1,S1
- Also possible: L1, M1, S1
- Not recommended: L3-M2-S1
Components
These are some examples of the types of UI elements that can be placed in the form container:
- Label and text elements, including dedicated text display containers such as object number, object status, sap.ui.unified.Currency, and so on
- Text input controls like input field and text area
- Selection controls such as select, combo box, date picker, radio button, and checkbox
- Icon
- Rating indicator
- Progress indicator
- Switch
- Slider
- Link
Guidelines
- Try to arrange form groups in size L in a way that the form:
- Is easy to read and understand.
- Does not contain too much white space (split groups if necessary).
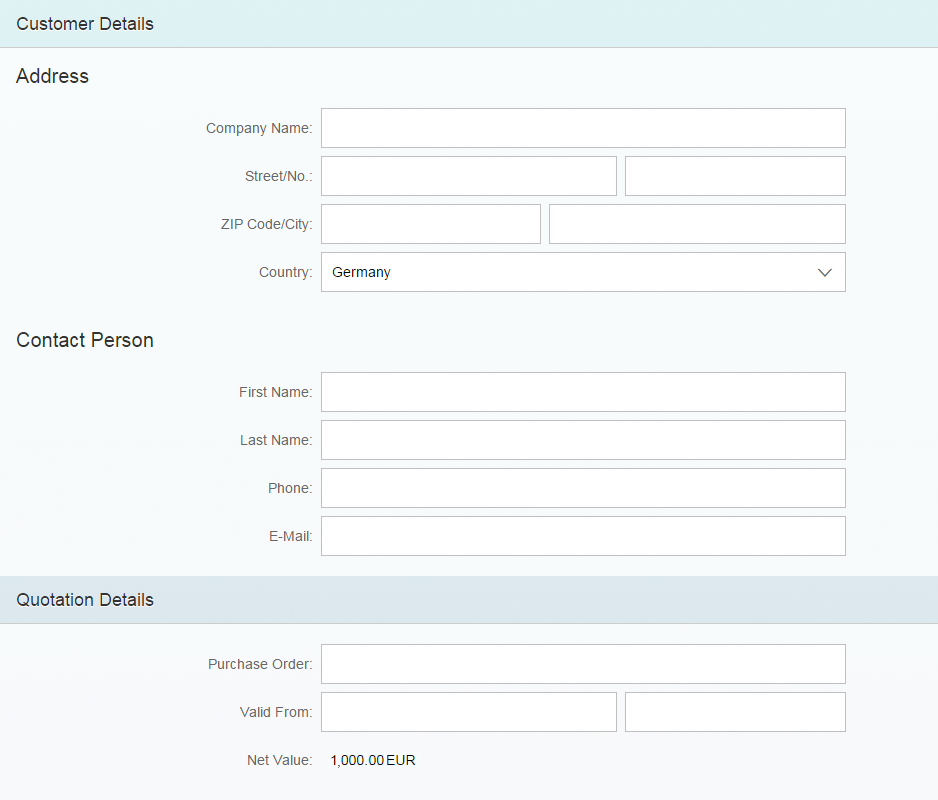
- Give each field a meaningful label. If you have combined fields that contain, for example, a postal code and the name of a city, you can provide one combined label (postal code and city) for this group.
- The label of a required field is marked with an asterisk (*). There is a corresponding property for this in the API. Do not write the asterisk manually in the label text.
- At the end of the label, the form container automatically inserts a colon “:”, which is triggered by the stylesheet. Do not write the colon manually in the label text.
- Use default settings for labels. (For example, note that labels are not supported for manual bold formatting.)
- If an input element is in an error or warning state, provide a meaningful message for the user. There is a corresponding property valueStateText in the sap.m.Input API.
Data Loss Message
Provide a data loss message if the user accidentally navigates away from the page, such as when selecting an item in the master list and then using the Back or Home button. For details about how the message is delivered and what text you can use, see message handling.
Placeholder
Provide a placeholder (or input prompt) as a short hint (a word or short phrase) to help the user with data entry. A hint can be a sample value or a brief description of the expected format.
Avoid using the placeholder attribute as an alternative to a label. This is important because the placeholder text is overwritten as soon as the form is filled out. Labels are necessary to indicate the meaning of the form fields when the placeholders are no longer visible.
Also do not use the placeholder as a repetition of the label.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.
Elements and Controls
- Manage Objects (guidelines)
- Label (guidelines)
- Text (guidelines)
- Link (guidelines)
- Input Field (guidelines)
- Text Area (guidelines)
- Select (guidelines)
- Combo Box (guidelines)
- Radio Button (guidelines)
- Checkbox (guidelines)


 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.