- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Chart – Embedding
Intro
This article explains how to embed an SAP Fiori chart in an app in such a way that it has the correct size and scrolling behavior.
Vertically-Scrolled Page vs. Frame
The optimal way to embed a chart component in an app depends on the layout pattern of the app. Embedding a chart component in a split-screen layout is different from embedding one in a full screen layout.
Two main layout patterns must be considered:
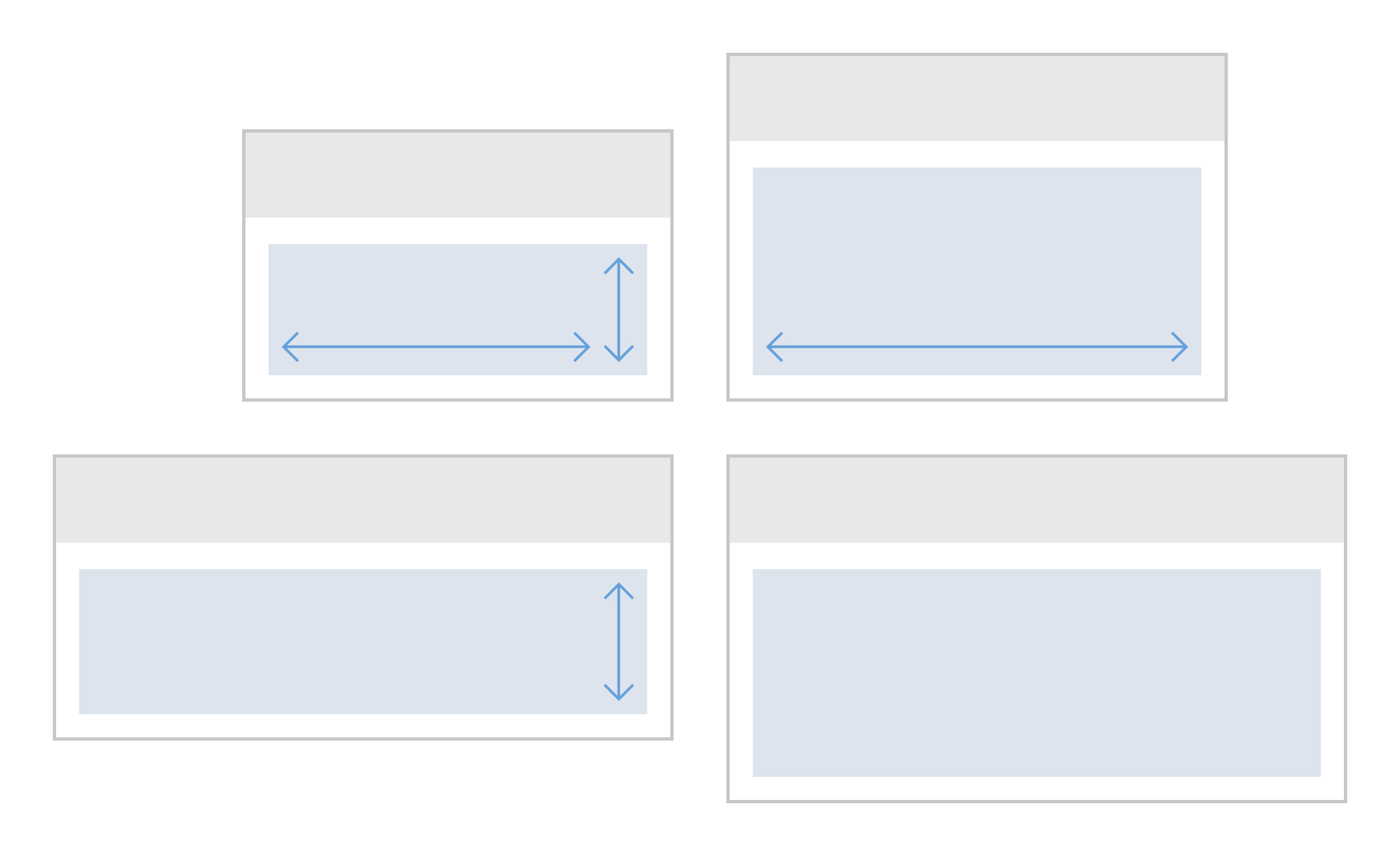
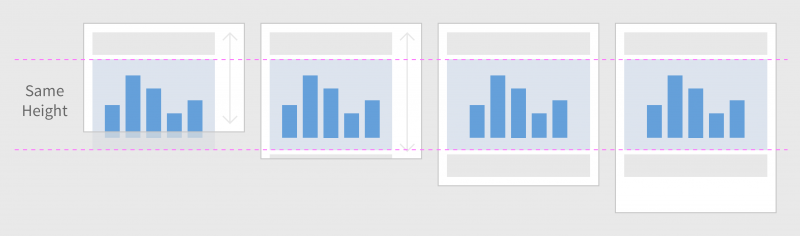
Vertically-Scrolled Page
In this layout pattern, the page scrolls vertically. If the page content cannot be seen in full, a vertical scroll bar appears.
Layout examples:
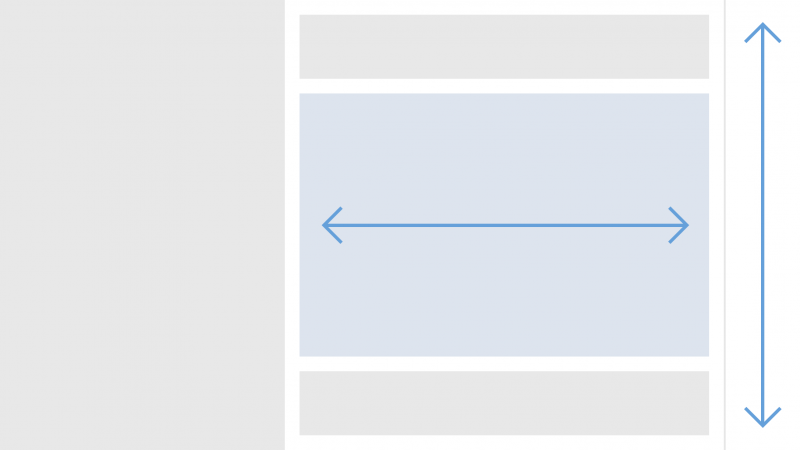
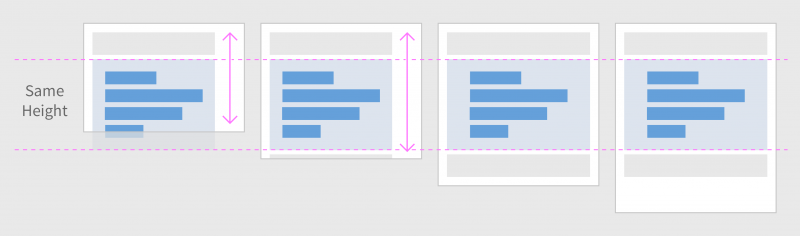
Frame
In this layout pattern, the page contains multiple frames and does not scroll horizontally or vertically. If the page content cannot be seen in full, the frames are resized so that they remain visible. Some frames may remain with a fixed size, while other frames are resized. When a chart is embedded in a frame, the frame is generally resized.
Layout examples:
Scrolling Direction of the Chart
How you embed a chart component in an app also depends on its scrolling direction. Embedding a chart that scrolls horizontally is different from embedding one that scrolls vertically.
For more information, see the article on the scrolling direction of charts.
As a design principle, you should avoid having two vertical scroll bars on the same page. The chart component should be large enough to avoid a vertical scroll bar appearing inside the component. The height of the chart component must equal the height of its content.
When the content of the chart changes, make sure that the height of the chart adapts to its content. That will happen each time the data set changes.
When the scroll bar of the page appears, the chart toolbar could disappear when scrolling. This is why this layout should be applied only for a small amount of data.
For a large amount of data, it is better to embed the chart in a frame.
Estimating the Height of a Vertically-Scrolled Chart
You can estimate the height by using the following formula:
bar heights = Nb of bars * (24 px or 48 px)
+ gaps betweens bars = (Nb of bars – 1) * bar.width * 0.125
+ gap between categories (if categories exist) = bar.width * (Nb of categories-1)
+ margin before first bar and after last bar = 2 * bar.width * 0.4375
+ height of axis = 27
+ title + gap below the title (if title exist) = 41
Note: This is only an estimation. Add some pixels to make sure the vertical scroll bar will not appear.
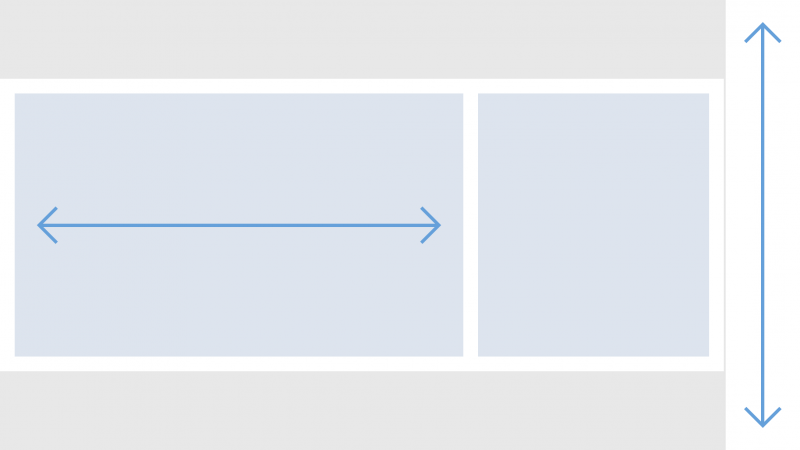
Embedding in Frames
In this layout pattern, the screen contains multiple frames and does not scroll horizontally or vertically. The scrolling is instead managed by each of the frames. When the chart component is embedded in a frame, it is resized to occupy the full height and width of the frame.
The chart component manages the scroll bars as necessary and displays the appropriate data point correctly.
Charts embedded in a frame
Bidirectional Scrolled Chart
Charts that have no main scrolling direction should be managed on a case-by-case basis.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.
Implementation
- Chart Container (SAPUI5 samples)
- FixFlex (SAPUI5 samples)
- Size of the Chart Container (How to use the property: autoAdjustHeight of the ChartContainer)




 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.