- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Animation
Intro
In SAP Fiori, animations are used to emphasize actions, provide orientation, and help users to perform actions by providing transitions and additional multiple actions. The aim is to improve the overall user experience.
Responsiveness
The same transitions (swipes, drop effects, and dissolve effects) are used for all devices and screen sizes.
Types
Curves
Timing : To focus the user’s attention on certain objects, changes in acceleration or deceleration should be smooth during an animation. The variation in speed gives motion a personality and an aesthetic look, thus avoiding monotonous linear movement.
This reference can be applied to all kinds of translations (transitions), rotation, and scaling done to any object in SAP Fiori.
Normally we use: EaseIn-Out and to add more detail it is possible to implement the following functions:
easeInExpo, easeOutExpo, easeInOutExpo, easeInSine, easeOutSine, easeInOutSine, easeInQuead, easeOutQuead, easeInOutQuead, easInCubic, easOutCubic, easInOutCubic, easInQuart, easeOutQuart, easeInOutQuart, easeInQuint, easeOutQuint, easeInOutQuint.
In SAP Fiori, we differentiate between three animation types: transitions, interactive motions, and functional animations.
Transitions
These help the user to remain oriented while navigating through the user interface. The user gets a sense of moving along a path. To keep this metaphor alive, a new screen always needs to appear from the right, while backwards navigation brings in the old screen from the left.
Interactive Motions
These are driven by the user and enhance the user experience by giving responsive feedback through motion. They are objects that move or change shape on the screen, such as to indicate a loading process. Interactive motions tell the user that something is happening. For example, a change in the state of a button helps the user understand that the system is reacting to the user’s input.
Behavior and Interaction
There are different animations in SAP Fiori. Starting an app from the launchpad requires a different transition than navigating within an app. An overview of all animations in SAP Fiori is shown below.
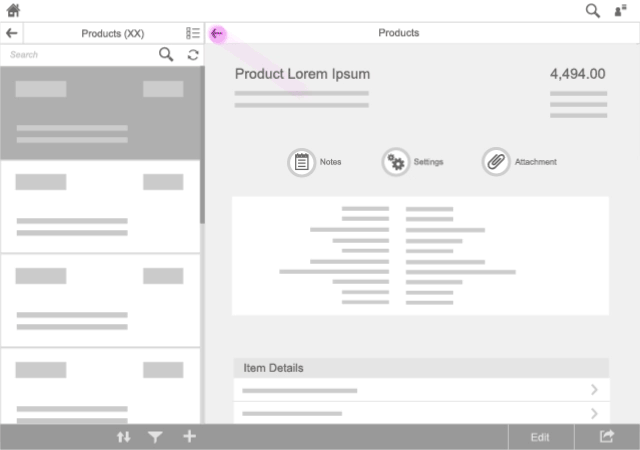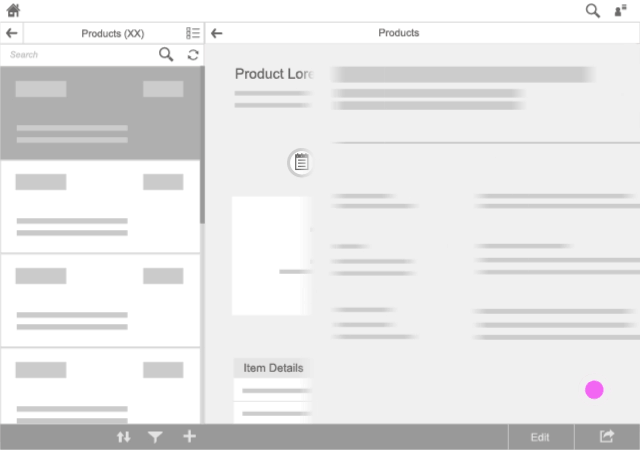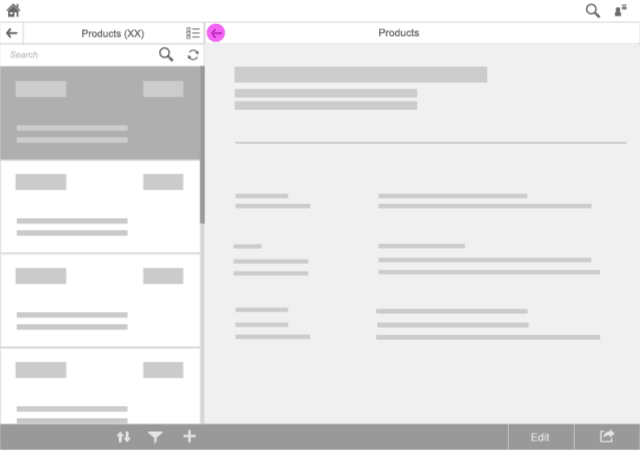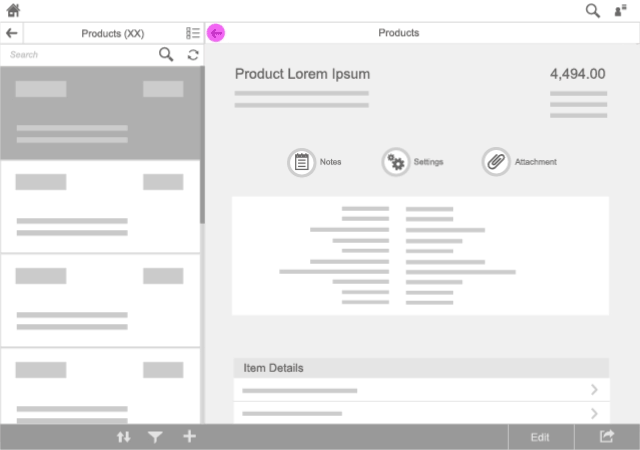
Launch App
When an app is launched, maintain the following choreography:
- Launchpad: The user clicks or taps a tile on the home page.
- Launchpad loading: The launchpad gets a white, semitransparent overlay and a flower-like “waiting” indicator.
- App: When the app has been loaded, the overlay is removed.
When the app screen becomes visible, there should be no animations or transitions after the SAP Fiori flower.
Load your app until the app structure is complete and you have reached a point where users understand what they are seeing.
It is permissible for a section of your app, like a graph, to be loading while the rest is complete.
Navigate (In-App)
Use the following transitions for in-app navigation:
- Forward navigation: Use a right-to-left slide transition.
- Backward navigation: Use a left-to-right slide transition.
These transitions appear in the screen area where the navigation takes place.
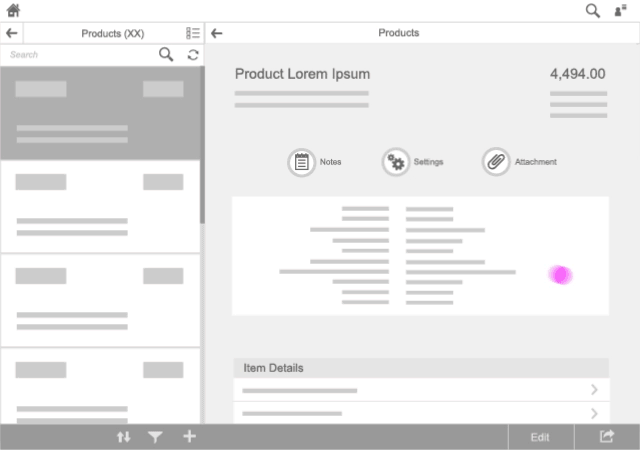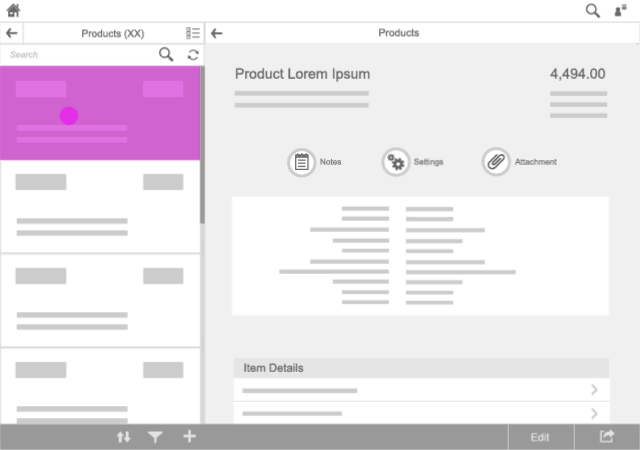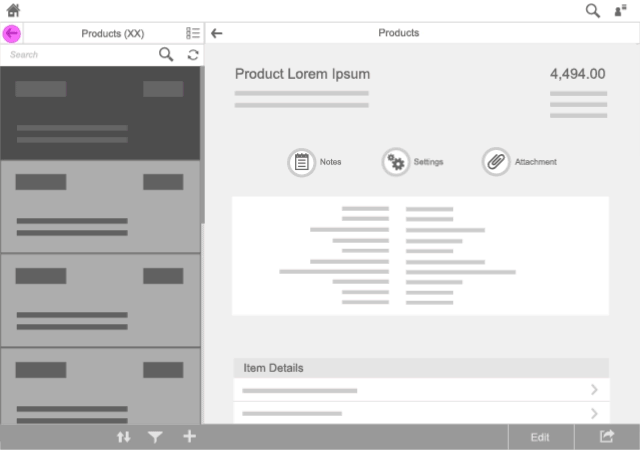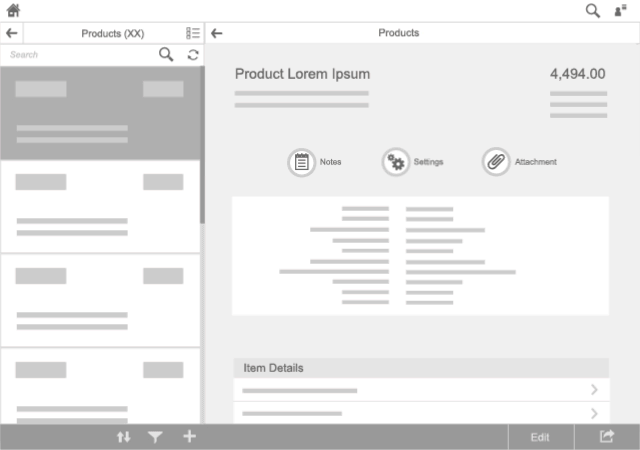
Master List
For navigation inside a (hierarchical) master list, use transitions only within the master list.
Details Area
For navigation inside a details area, use transitions only within this area. Side-swipe transition is used to go to lower-level pages and inverse swipe to return to higher levels inside this area.
Full Screen
Navigation on a full-screen app uses the whole page for transitional animations as this maintains a high level of detail. The same timing principle is adopted as for non-full-screen navigation. The same animation rules apply here as for loading an application; in other words, use the SAP Fiori flower animation.
Navigate (App to App)
Whether the user is navigating forward or backward, use the the SAP Fiori flower animation (as described above for starting an app from the launchpad).
An exception to this is when the user navigates back to the launchpad; in this case, use the backward transition (slide left to right).





 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.