- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
- Latest Version 1.128
- Version 1.126
- SAPUI Version 1.124
- SAPUI5 Version 1.122
- SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- SAPUI5 Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Overview Page (Smart Templates/SAP Fiori Elements)
Intro
The overview page (OVP) is a new data-driven SAP Fiori app that provides all the information a user needs in a single page, based on the user’s specific domain or role. It allows the user to focus on the most important tasks, enabling faster decision-making as well as immediate action.
The overview page employs cards (containers of content), which are based on smart template technology, and which act as a UI framework for organizing large amounts of information on an equal plane within the page. The overview page is created by a developer based on annotated views of app data (meaning that app content can be tailored to the domain or role). Information can be visualized in an attractive and efficient way using different types of cards.
In short, the overview page is a simple, one-stop, data-driven SAP Fiori app that gives a role all essential information. It allows the user to view, filter, and react to information quickly.
Usage
Use the overview page if:
- The user has a specific role and needs to filter and react to information stemming from a range of applications.
- The user needs to gather information from different sources that support a specific task focus or information need.
- You want to offer different information formats (such as charts, lists, and tables) on a single page for a specific domain or role.
- You want to organize and display a set of (filterable) data to provide an entry-level view of content related to a specific domain or role.
Do not use the overview page if:
- A high-level or birds-eye view of application content is sufficient.
- You want give access to all available SAP Fiori apps for all groups or domains.
- You want to add or delete applications. Instead, consider using the SAP Fiori launchpad home page.
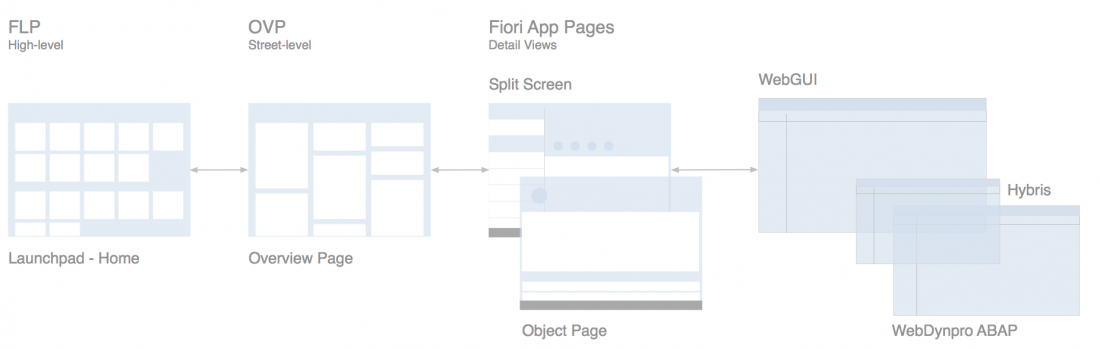
The Difference Between the SAP Fiori Launchpad Home Page, Overview Page and the Object Page
The launchpad home page contains all of a user’s favorite apps and offers access to them via tiles. This covers all the roles that a user would have, such as employee, manager, production worker, or quality manager.
An overview page, on the other hand, focuses on the tasks of a specific role. The user may therefore use multiple overview pages. For example, one overview page could be used to reflect the user’s role as manager, and allow him or her to manage the performance reviews of the team. Another overview page could be used to track quality issues and other relevant information pertaining to the machines that he or she is responsible for in the role of quality manager.
The overview page uses cards. These cards display more (preview) information than tiles due to their sizes and properties. A further distinctive feature is that identical card types also could perform simple actions.
The overview page is always role-based. This means the user will find heterogeneous information related to a specific business context and the daily tasks of the specific role. This is not the case with the object page, which contains object-based, homogenous information.
Have a look at the tables below, which further describe the differences between the launchpad home page, the object page, and the overview page:
| Fiori Launchpad Home Page | Overview Pagge |
| Framework (given) | SAP Fiori application (optional) |
| “Birds-eye” view | “Street level” view |
| Single point of entry | Specific business context for a role |
| No actions | Micro actions |
| One SAP Fiori launchpad per user | Multiple overview pages per user possible |
| Overview Page | Object Page |
| Role-based | Object-based |
| “Street level” view | “Details” view |
| Heterogeneous information | Homogeneous information |
Role-Specific Overview Pages
Only provide an overview page for a role if it makes sense to do so. An overview page gathers information from different sources that support a specific task focus or information need. If a role or user has several such main tasks that require a specific set of information, the role or user might also have multiple overview pages. However, there is no fixed coupling (for example, one overview page per role).
Interaction Flow
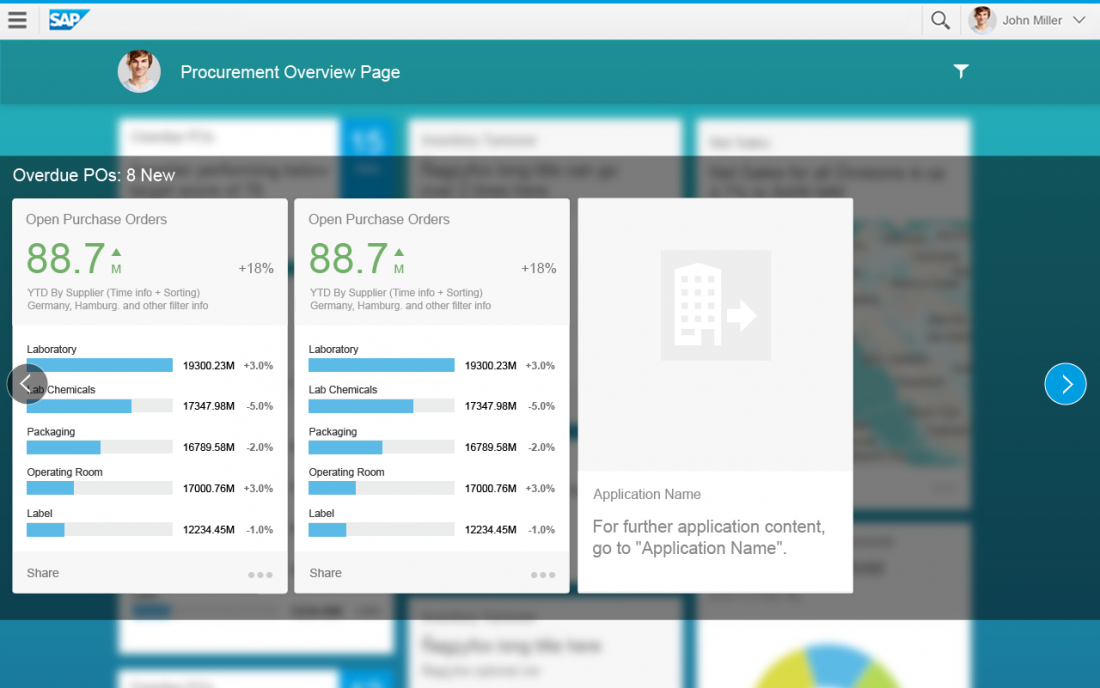
The overview page in SAP Fiori functions like a typical SAP Fiori app. This means that you can start it by clicking a tile on the SAP Fiori launchpad home page, or by bookmarking the direct link to the overview page in your browser to access it directly as you would any other app. The figure below illustrates the complete interaction flow.
Responsiveness
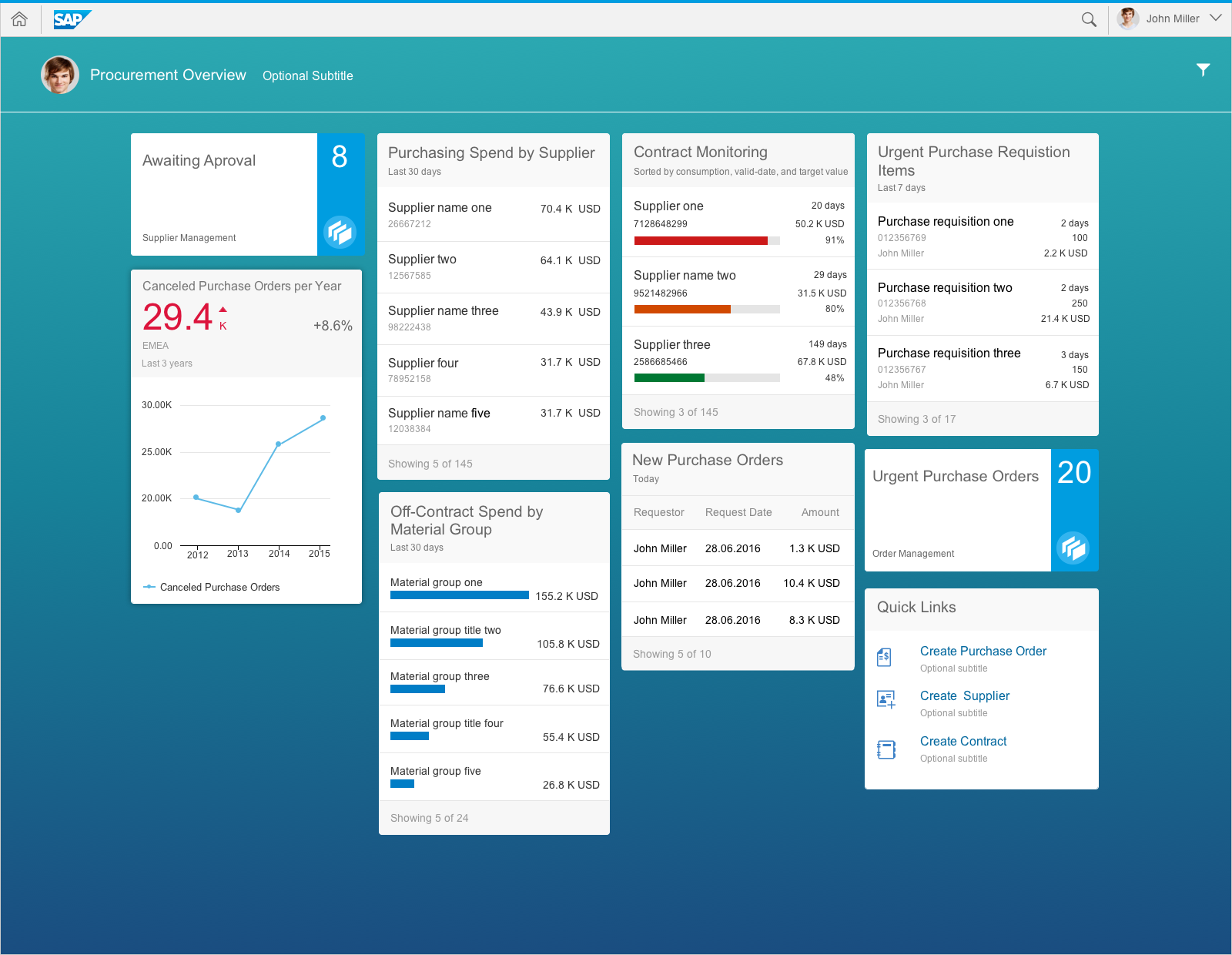
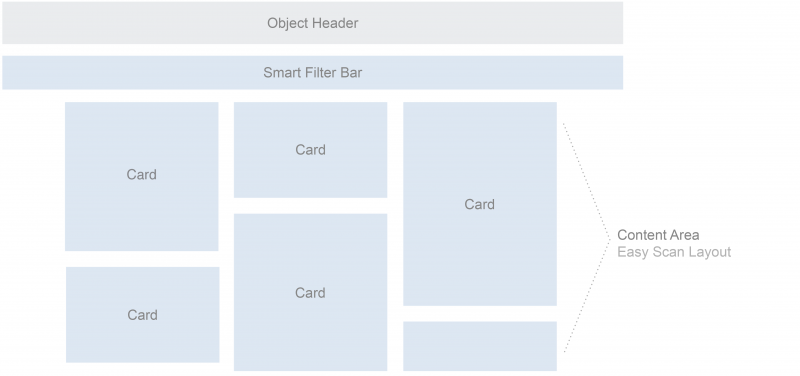
The entire SAP Fiori overview page floorplan is fully responsive and uses letterboxing. The flexible “easy scan” layout can accommodate typical laptop screens as well as larger desktop monitors, and features responsive (collapsible) “columns” of cards that can scale all the way down to tablet or phone screen sizes. The columns are of equal width and contain the cards in the following layout sizes:
- Small: one column
- Medium: two columns
- Large: three columns
- Extended: four to five columns for large desktop screen resolutions (maximum five columns)
The width of the cards changes depending on the screen size being used: either 20 or 25 rem is displayed. This process starts automatically and saves the responsiveness and readability of the cards to each device. This flexible width behavior applies to all card types.
Structure
Components
Overview Page Header
The overview page uses the object page header for a page header. The header is the uppermost element in the floorplan. Its purpose is to provide the user with context and relevant information about the page it represents. The information allowed in the object page header of an overview page is limited to a title, subtitle (optional), and an icon button used to open the smart filter bar.
Smart Filter Bar
The smart filter bar is used “as is”, meaning that for the overview page, all existing functions and behaviors of the current UI5 control are available, including variant management. The smart filter bar filters all the content on the page and in the data base. A notable exception is that the smart filter bar is not visible when the page is first loaded; the user must select the filter icon from the object header to cause the smart filter bar to appear on the page. On a desktop, once the smart filter bar has been invoked, it is always displayed in extended mode. On mobile devices, once it has been invoked, the smart filter bar is always displayed as collapsed.
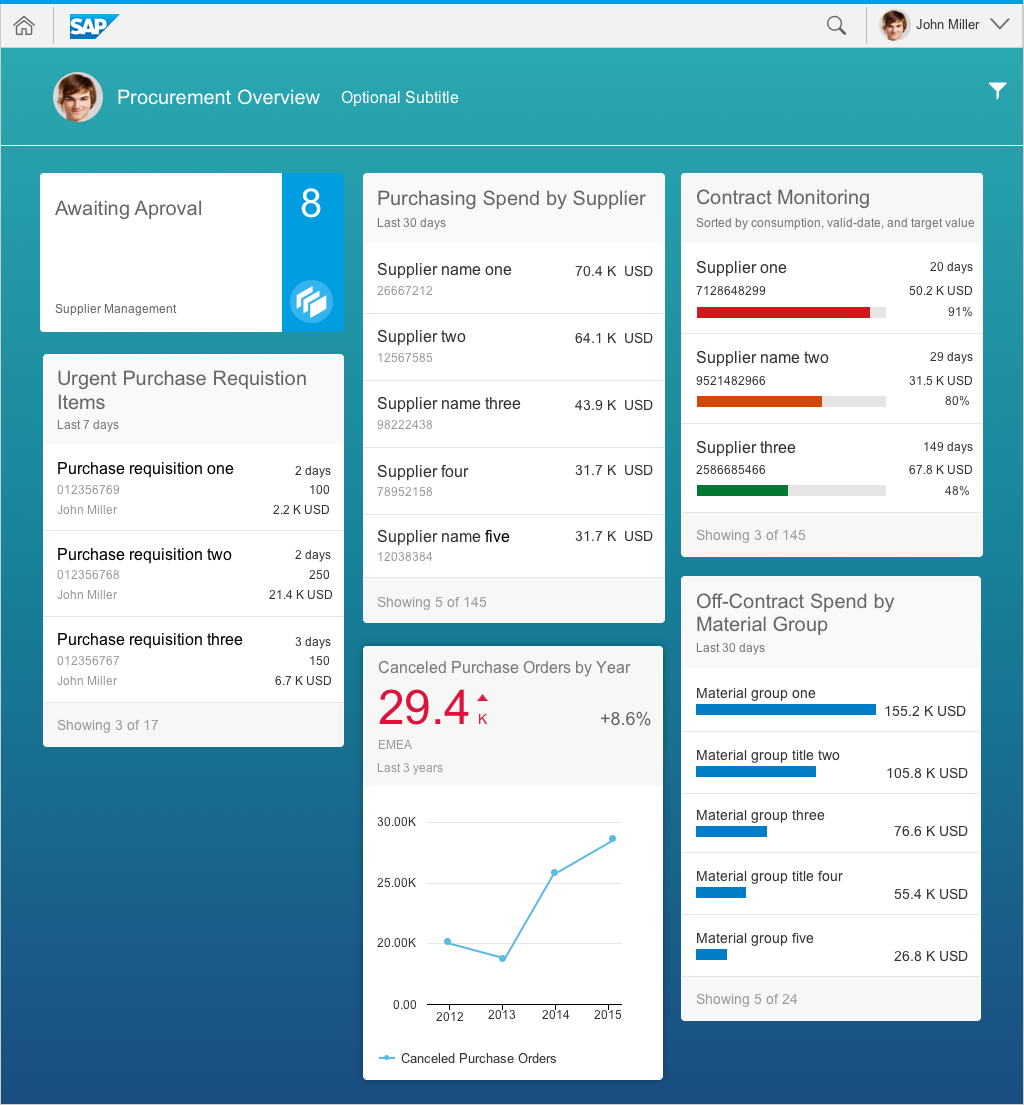
Content Area of the Overview Page
The content area contains responsive (collapsible) columns of cards. The content area of the overview page features what is referred to as the “easy scan” layout. Note that you cannot place tiles in the content area on the overview page. Like an operating system’s home screen, the home screen only offers access to apps, but no further functionality for keeping the home page clean and usable. The overview page contains cards but no tiles. Cards have more than one interaction area and might even offer actions, thus making them much richer than tiles. Apps can be launched from an overview page through the header area of a card that is related to the specific app.
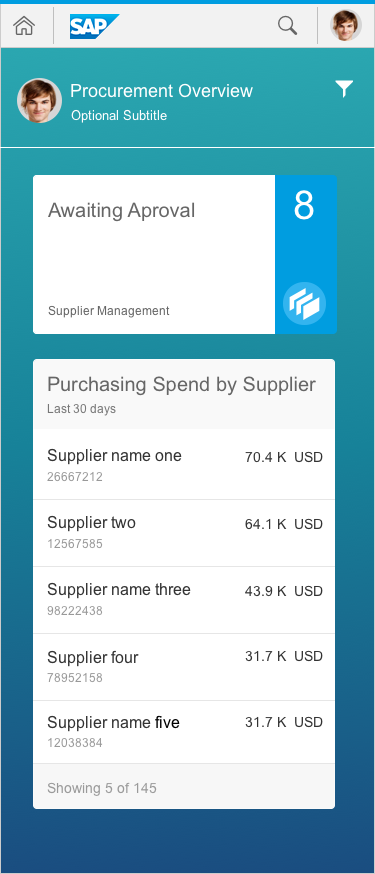
Cards, which are entirely new for the overview page, are containers of application content. A card is a smart component that uses UI annotation to render its content, and is bound to a single data source. Cards differ in the content they display. They can show a chart, a list of items, a table, informative text, or a combination of two elements. For example, an analytical card may show a KPI header and a chart.
Cards used for the “easy scan” layout always have a uniform horizontal width, but may vary in their vertical dimension based on the card type.
The vertical size (height) is determined by the card type and the embedded control.
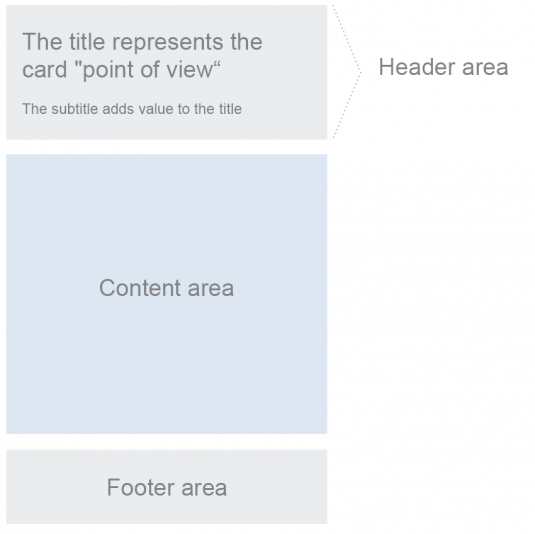
Card Components
Every card comprises three components: a header area, a content area, and a footer area. The header and content areas are mandatory. In some cases, the footer area is not needed (such as for the stack or analytical cards) and is therefore optional. Please have a look at the UI text guidelines for the overview page to ensure the correct usage of UI texts in the overview page.
Header Area
The card header area is a required section of the card layout. It serves two purposes:
- It indicates what content the card contains.
- It functions as a navigation area. As the entire header is selectable, the user can navigate to the specific app or view from which the card content originates. We recommend that you continuously use a navigation functionality on all cards (exception: link list cards).
The height of the header area is variable; it expands vertically to contain the text. The header area is mandatory and can contain up to two text fields for descriptive purposes: title and subtitle. At least the title must be used in the header area as a required element. The subtitle is still optional.
The primary purpose of the header area is to identify the content source and present the reason why it is important to look at the card (title), to show any relevant parameters (subtitle), and to provide navigation to the content source (application).
Title
The headline represents the card’s “point of view”. In one or two words, it explains why this card exists and why a user might want to use it. It is a natural language reflection of the annotated view and should express the results of the setting.
Subtitle
You can use it to qualify the title, offer an explanation, or show a status. The use of the subtitle can differ, depending on the card type.
Content Area of Cards
The content area is mandatory and reserved for application content. Content is currently displayed in a card by embedding a UI5 control that specifies the properties and data format to be displayed. For example, an embedded UI5 standard list control provides formatting (such as row height, font sizes, and number of text blocks).
Footer Area
The footer area has a fixed height. It is also optional as, in some cases, a footer area is not needed (such as for stack or analytical cards). It serves two purposes:
- For cards that display information about a single object or data point, the footer area is used to display actions associated to the content of the card. This only applies to the quick view card. For more information, see the section on Behavior and Interaction in this article. For this case, the overflow toolbar control is used.
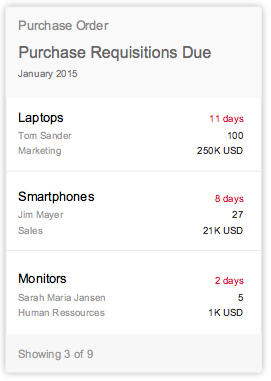
- For cards that display links to a group of multiple objects (such as list or table cards), the footer is informational and contains no actions. It provides a summary text label which describes how many items are shown on the card in respect to all items returned for the particular annotated view. For example: Showing 3 of 10. If there aren’t any items, the following text should be displayed: No items found.
Card Types
Single-Object Cards
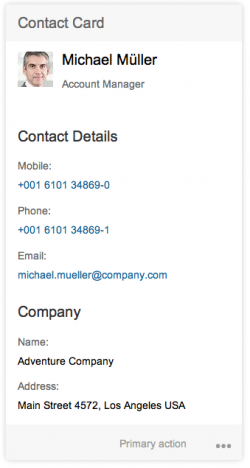
Cards that feature content with a single focal point, detail, or entity are called single-object cards. An example is a business card with information about a particular contact. The quick view card and the analytical card are single-object cards.
Object Group Cards
Cards that feature a subset of items grouped together by relation to a common topic are called object group cards. A typical example would be a list of sales orders grouped by amount, status, or most recent status. They do not have actions, but are designed in such a way that each row or list item is selectable, thus providing direct navigation to the detailed object within the parent application. Object group cards include all types of list cards and table cards.
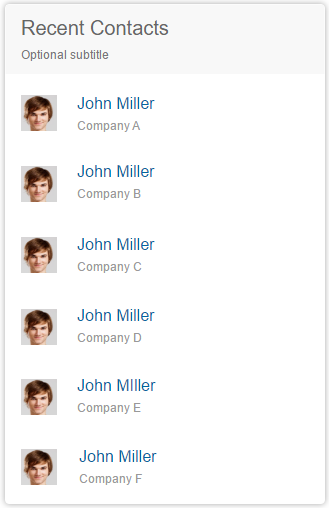
The quick view card displays basic details about a single object, such as a contact with name, address, and telephone numbers. A small picture can also be added. Clicking on the header area of a card opens the corresponding app. The quick view card inherits the UI5 element sap.m.QuickView. It is only available inside the object stream; you cannot position it on the overview page itself. Only the footer area of the quick view card can currently provide actions.
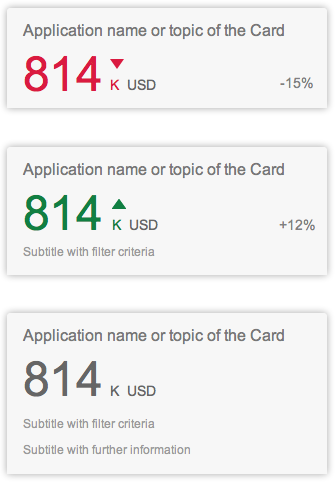
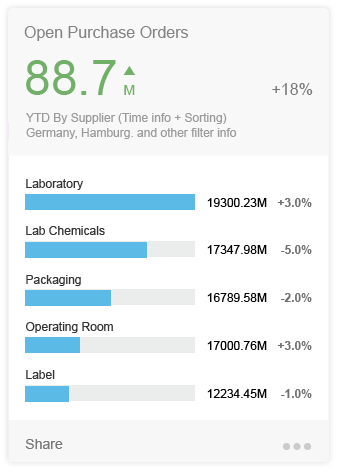
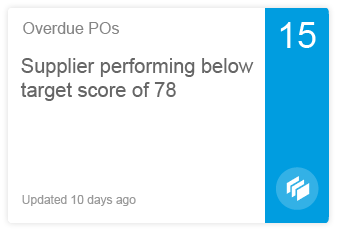
Analytical cards are used for data visualization. They are single-object cards that consist of two areas: a header area that displays the aggregated value of a key measure (KPI), and a chart area that displays a representation of data in graphical format. Analytical cards do not contain a footer area.
The KPI header is mandatory for the overview page. The KPI header includes the title (mandatory), the KPI with the respective unit (mandatory), and a subtitle (optional). The subtitle can show the filter criteria used for the chart, and can contain up to two lines of text. The KPI itself adopts the semantic colors red (negative), green (positive), or gray (neutral). The announcement of the percentage (optional) and the triangle indicator (optional, showing an upward or downward trend) can also be displayed.
The following charts (VizFrame) are currently available for use in the overview page:
- Line chart
- Bubble chart
- Donut chart
- Column chart
- Stacked column chart
- Vertical bullet chart
For more information, see analytical card.
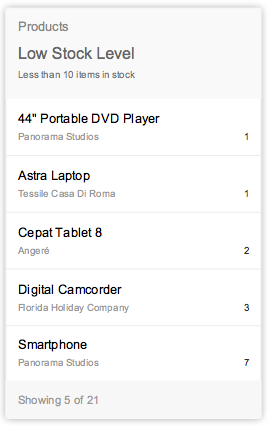
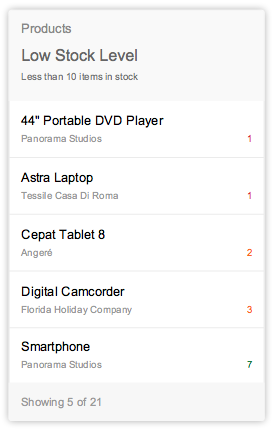
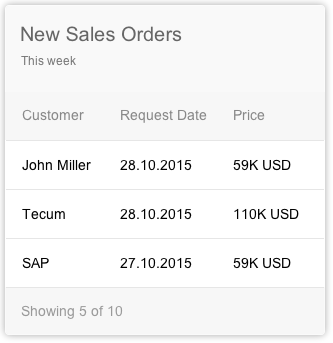
List cards are a type of object group card, and display a set of items in a vertical list. The list card uses the sap.m.List container in the content area. Clicking the header area of a list card opens the parent application, which uses the same filter as the annotated card, and shows a list of all the returned ResultSet objects. Clicking on a list item (row) on the card opens the detail view for that specific item in the same parent application.
Two different line item types are available: “condensed list item” and “extended list item”. However, you can only use one type of list item on any given card. The condensed list item shows minimal information – two lines of text and a number – and contains the same properties as the SAPUI5 control sap.m.StandardListItem. The extended list item displays more information – three lines of text and three numbers – and contains the same properties as the SAPUI5 control sap.m.ObjectListItem.
Size
The size of list cards displaying multiple objects adjusts depending on the amount content available. The height can vary depending on the number of text fields. However, there are rules for the fixed number of list items: You should show no more than 5 condensed list items and no more than 3 extended list items in one list card. The user should expect to navigate to the full app to see a list of all possible items or the result set.
The bar chart list card adds a chart component to a list. You can embed a progress indicator in either a condensed or extended list format.
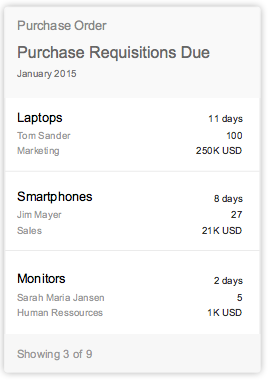
Table cards are a type of object group card, and display a set of items in a table format. Table cards use the responsive SAPUI5 control sap.m.Table. Clicking on the header area of a table card opens the parent application with the same filter applied as for the annotated card with access to a table of all the returned ResultSet objects. In contrast, clicking on a table row inside the card opens that specific object detail screen within an app. The card limit the width of the table to three columns and no row should display more than three lines of text The first and second column show a data field and the last column a data point. The height of the card reflects its content. If one or more items are returned, show the items in the footer area with a summary text “Showing x of x”.
Size
The size of list cards displaying multiple objects adjusts depending on the amount content available. The height can vary depending on the number of text fields. However, there are rules for the fixed number of list items: You should show no more than 5 condensed list items and no more than 3 extended list items in one list card. The user should expect to navigate to the full app to see a list of all possible items or the result set.
If no items are found, the card should only display the header and footer information. The only selectable area would be the header for navigation to the corresponding app.
If one or more items are returned, show the items in the list/table format with a footer area for summary text. The height of the card depends on the amount of content.
Link List Card
Link list cards allow you to display a collection of links or images that can reference both internal and external targets. Links and images are handled as two separate variants:
Variant Type List
The variant type list shows a collection of links which navigate to a target, or which open a popover to show additional information. You may optionally add a subtitle or additional information below each link. Maximum one line of text for each link and each subtitle is allowed. You may also display an icon or an image in front of each link. If icons are added to the link list, each link must show an icon. This is also the case for images. If an image is not available, you can use a placeholder instead.
Example use cases for the variant type list include a list of links with navigation to the most used apps for a specific user role, or a list showing recently used contacts.
Variant Type Image
The variant type image uses the sap.m.Carousel control to display one or more images for different use cases. If the user hovers over the image with the mouse, forward and backward icons and the paging indicator appear. If there is only one image in the carousel, these will not be visibile. The link and an optional subtitle are displayed above the carousel. Maximum one line of text for the link, and one line for the subtitle, is allowed.
Stack Card
The stack card cover contains the following components:
Title Area
The title should be one line of text and can be the name of an app or a topic.
Stack Content Count
Stack card covers should always display the total number of cards contained within the stack. The maximum number of cards in a stack is 20.
Headline Area
The headline in a stack card can have up to two lines of text. Subtitles are not available. The headline should be used to explain the contents of the stack, and to highlight what is new or has changed since the last visit.
Status Area
Every stack card should display a single line of text to indicate a status. This can be the time of the last update, an indication of urgency, or the last time the user opened the stack.
Navigation
The stack card cover contains two clickable areas for navigation: the left area navigates to the parent application, and the right area triggers the opening of the object stream (see below), which contains the scrollable collection of cards in an overlay.
The object stream is a scrollable, open stack of cards that appears on the surface of the OVP in a modeless overlay. Cards in the object stream should be ordered chronologically, with the most recent items appearing first by default. However, app developers can also define the best object stream sorting option for their own needs and custom content.
Object Stream Components
The modeless overlay serves as a container or layer for other controls and functionality. Clicking on the stack card cover opens the overlay. When invoked, it should be bound to the card object that launched it. The opened overlay should appear centered vertically to the entire screen window.
Once invoked, the modeless overlay should expand to contain whatever content is provided by the object stream. If more cards are available than fit in the available overlay window space, the area becomes scrollable, and the user can scroll or swipe to see more cards. An arrow icon appears, indicating that the object stream contains more cards.
The overlay should contain a single-line label for text and a Close button. Clicking outside the overlay surface also closes the overlay.
If the stack card contains no cards, the stack link is not active and the overlay cannot be opened. The stack count number displays 0. If only one card is in the stack, an object stream opens containing just a single card.
Tablet Version
On tablet devices, the modeless overlay should expand horizontally to display three cards in landscape mode and two in portrait mode. It should also expand vertically to contain the card height plus room for an area at the top of the control where the stack card title and a button can be provided allowing the user to close the overlay. The overlay should be vertically centered in the entire screen window.
Smartphone Version
On a smartphone, tapping on the right navigation area opens the object stream in a new window that fills the screen at the top of the OVP page. Here, the user can swipe through cards in the stack and take micro actions. Tapping the Close button closes the stack card and returns the user to the main OVP page.
Arrow Indicators (Scrolling)
Arrows appear only in the desktop version. If all cards in a stream are displayed on the screen, no arrows are visible. If there are more cards in the stream than fit in the visible area, the arrow icon appears on the right side when hovering over anywhere on the object stream. Hovering the mouse anywhere over the arrow button area causes the cards to advance.
Once the first card begins to move out of the viewable overlay area, a second arrow button indicator appears on the left. Once the last card has come completely into view, the right arrow indicator disappears.
Placeholder Card
The object stream can display up to 20 cards. A placeholder card occupies the last card position in any object stream. It marks the end point of the object stream and provides a quick navigation point for jumping to the app or apps that have card content in the stream. The placeholder is not included in the number of cards shown to the user on the stack card cover.
The entire card is navigable and should direct the user to the app that the stack card represents, or should display links to the apps corresponding to the cards in the stack.
Behavior and Interaction
The layout of the overview page consists a scrollable page of cards for each device, making it easy to scan through quickly.
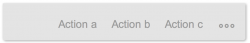
Only quick view cards can have actions in the footer area (inside the object stream). Through the usage of the overflow toolbar control the primary and secondary are lapsed.
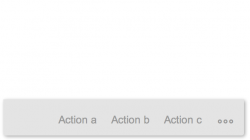
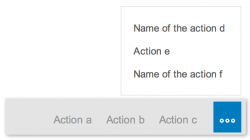
All actions are right-aligned. If there are more actions to be displayed than is allowed by the space in the footer area, the additional actions move into the overflow. This icon is represented by the three dots (…) and is used as a place to consolidate all other actions. Clicking on the overflow invokes the appearance of an action sheet, which displays the list of additional actions. Clicking on an action starts it and dismisses the action sheet. A maximum of six actions are allowed in the footer area. We recommend using only those actions which are actually necessary for the user.
There are two possible types of action: navigation and function import. Any combination of navigation and function import actions is allowed. Any error or confirmation would be displayed directly on the overview page with message handling.
Navigate
Navigation is “intent-based” and takes the user to a different SAP Fiori app that specializes in executing an action. Navigation actions are always multiple-click (meaning they can be repeated over and over). If we take the example of an SAP Fiori detail view that supports operations for the intended action, the intended destination screen would open in the same browser window, and any errors or task confirmation toast messages would be handled by the supporting application, not the overview page. If another application is open, the object stream should remain as is until the user returns to the overview page.
Import Function
The import function is a term to describe how actions are named in OData. It has two purposes:
- An action requires some input parameters. These would be handled on the overview page screen without further navigation. When an action choice is made (through user selection), the card should change to a dialog, and the input or selection action can be carried out.
- An action can have no parameters, and in such a case, the action request is sent immediately. Once the action has been completed, the card disappears from the object stream.
Action on Smartphone
Action behavior on a smartphone is very similar to that on a desktop or tablet. The main difference is that whenever an action on a card requires an input dialog box, the default option should be to use a full screen version for the smartphone’s form factor.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about the SAP Fiori Overview Page.
Elements and Controls
- Introduction to Smart Templates (guidelines)
- List (guidelines)
- Standard List Item (guidelines)
- Responsive Table (guidelines)
- Progress Indicator (guidelines)
- Chart (guidelines) (guidelines)
- Analytical Card (guidelines)
- Toolbar Overview (guidelines)
- Dialog (guidelines)
- Message Handling (guidelines)
Implementation
- List (SAPUI5 samples)
- Standard List Item (SAPUI5 samples)
- Responsive Table (SAPUI5 samples)
- Progress Indicator (SAPUI5 samples)
- Chart (SAPUI5 samples)
- Overflow Toolbar (SAPUI5 samples)
- Dialog (SAPUI5 samples)
- Message Handling (SAPUI5 samples)
- Chart (SAPUI5 API reference)



 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.