English Punctuation
Intro
Best Practices
Here are a few of the most important rules of the English language and grammar that let you craft simple and appropriate conversational dialog for your users. If you have a multi-lingual digital assistant, using proper grammar and punctuation make sure the translation software translates the dialog properly.
Colons
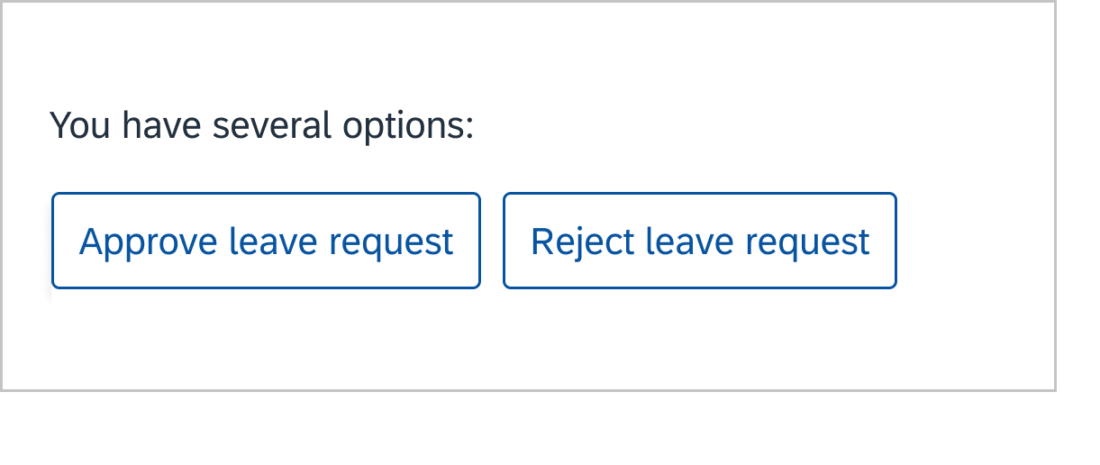
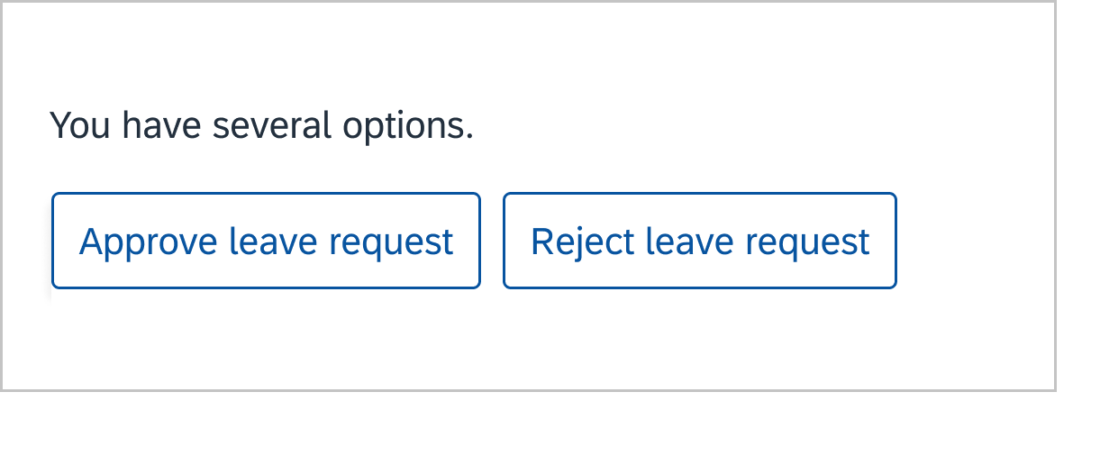
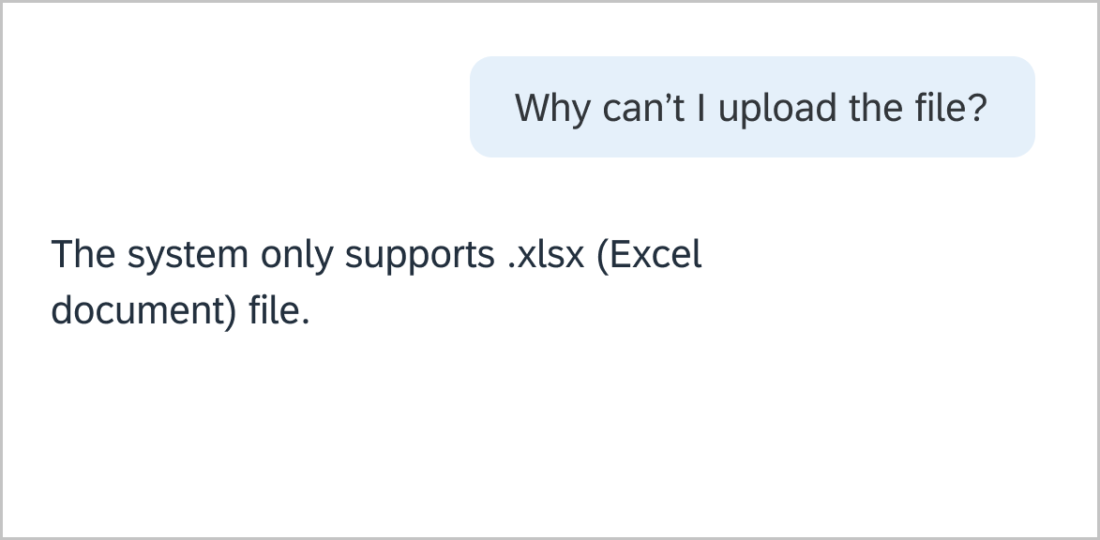
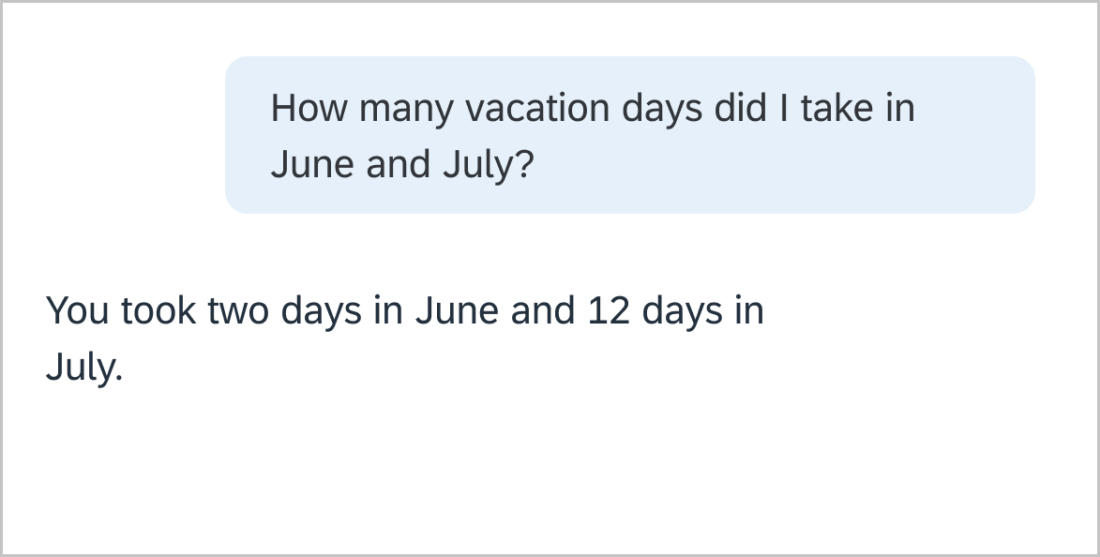
Use colons ( : ) when at the end of an introductory sentence for a list, table, or a graphic. If the colon is followed by a complete sentence, start the first word with an uppercase letter.
Example
Hyphens
Use a hyphen ( – ) to form a to link words or parts of words, if grammatically required. Some words in the English language are combined to form one word. These words are separated by a hyphen (the short dash) because they’re not really words in the English language. These words are language-specific (see the dash there). Some words have removed the hyphen, like “email”, but it can depend on your company style and branding.
Examples
- On-premise
- Self-service
- Web-enabled
- Other examples: sugar-free, camera-ready, computer-aided, custom-built, etc.
Contractions
Contractions combine two words using the apostrophe ( ‘ ) to combine the words. Contractions are useful in conversational design, as it makes the conversation a bit more casual as if someone would naturally speak to a friend or colleague. It’s a bit more casual, isn’t it?
Examples
Capitalization
Lots of words use capital (uppercase) letters. A few places to use capital letters to start a sentence and for the first letter of titles, headings, captions, and names, and product names. Don’t use all caps.
Examples
Special characters or symbols
There are tons of other punctuation marks, special characters, or symbols you can use, but you should first determine if it’s really necessary. Make sure your target users are familiar with the special character or symbol. You can use common symbols such as the percentage sign (%). Symbols are also hard to translate. There might not be language-specific equivalents in the target languages. Use them only if they are a widely accepted standard in the business area.
Keep in mind…
Some special characters like ampersand ( & ) or dollar sign ( $ ) are used in programming language where the software or user interface is developed. Use “and” instead of “&” when writing a sentence in conversational design. Use the 3-letter codes for currencies. Use “USD” instead of ( $ ), “EUR”, instead of ( € ).
Examples
Good to know
Here are a few more little tips for writing conversational dialog.
Abbreviations
Spell out any abbreviations or acronyms the first time you use them and put the acronym in parentheses after the term. The next time you use the term, you can then use the acronym. Abbreviations are difficult for translation. Don’t assume users know all the acronyms you use. Each industry or country can have its own meaning for the same acronym. Spell it out or it can confuse users.
Examples
Numbers
As a rule, spell out numbers one through nine, but use numerals for 10 and higher. Use numbers if you’re referencing steps, figures, ages, times, years, and dates.
Examples
Product names and other approved names
Refer to your company’s branding site for approved names for products, services, programs, abbreviations, and more.