Conversational Writing Style
Intro
When writing dialog for your digital assistant, imagine that you’re writing for a real person who has important tasks that they need to accomplish. The user might be frustrated or in a hurry to complete a work-related task. You’re having a conversation with your users and want to give them an answer that is quick, concise, and accurate. Don’t think about how you you’d write a statement for users, but how you’d say it to them.

Focus on user
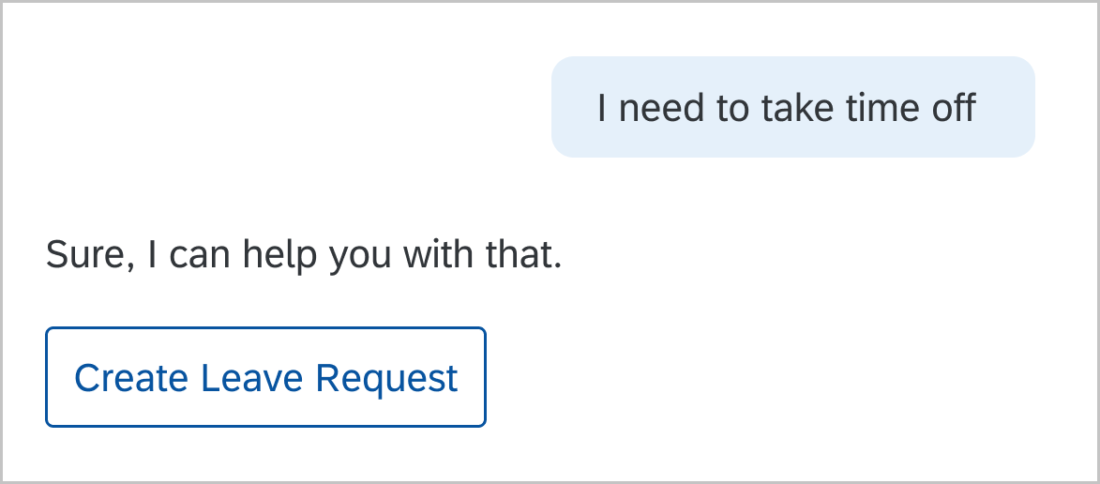
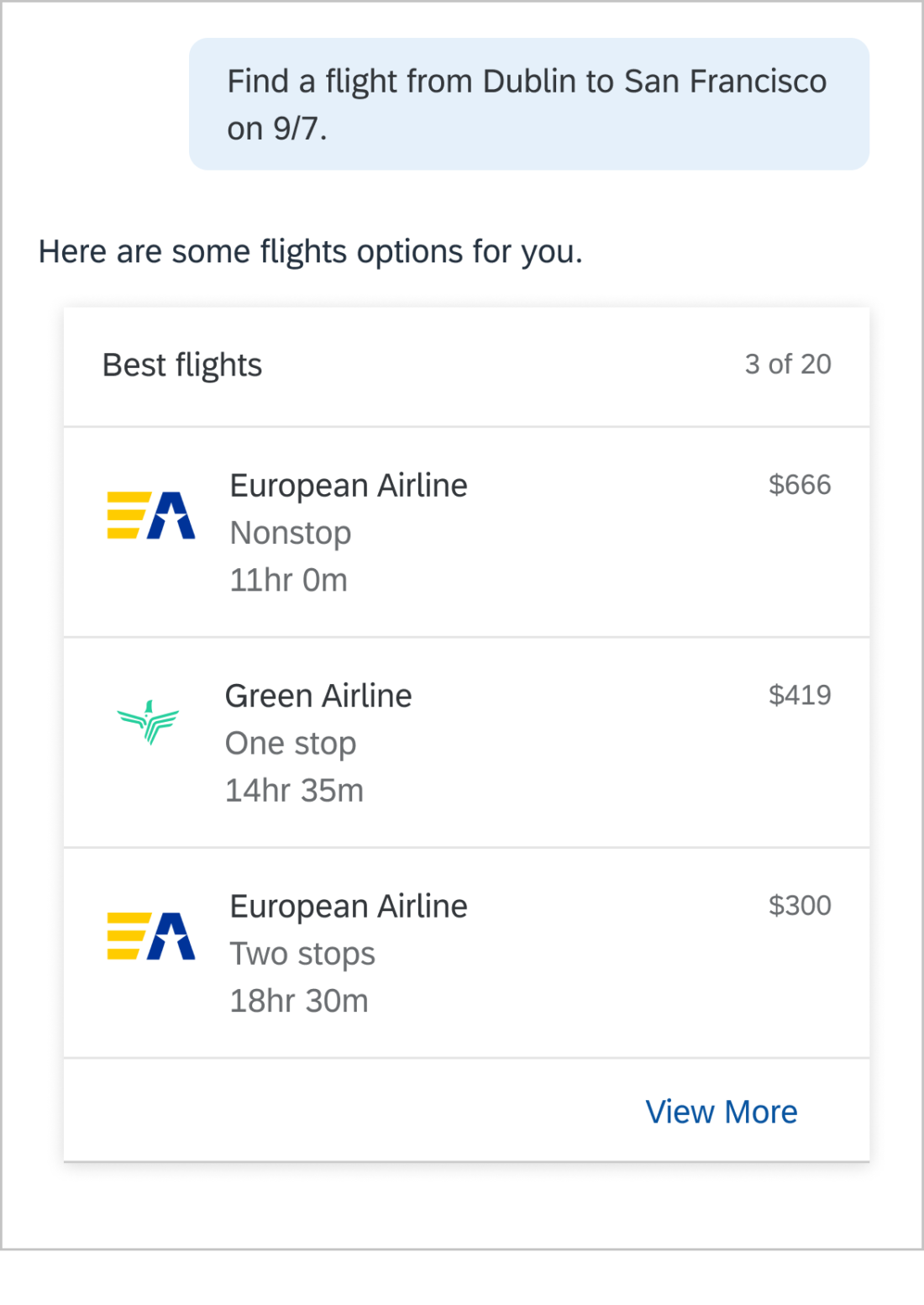
The user is the most important person in conversational design. Focus the conversational design on your users. Give users only the relevant information they need to complete their request. Don’t waste their time or frustrate them further.
Concise language
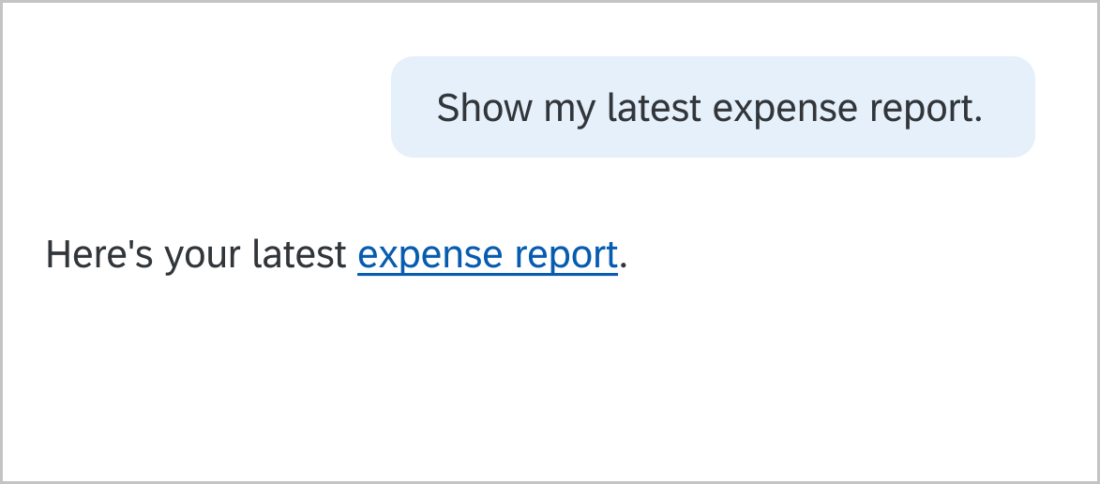
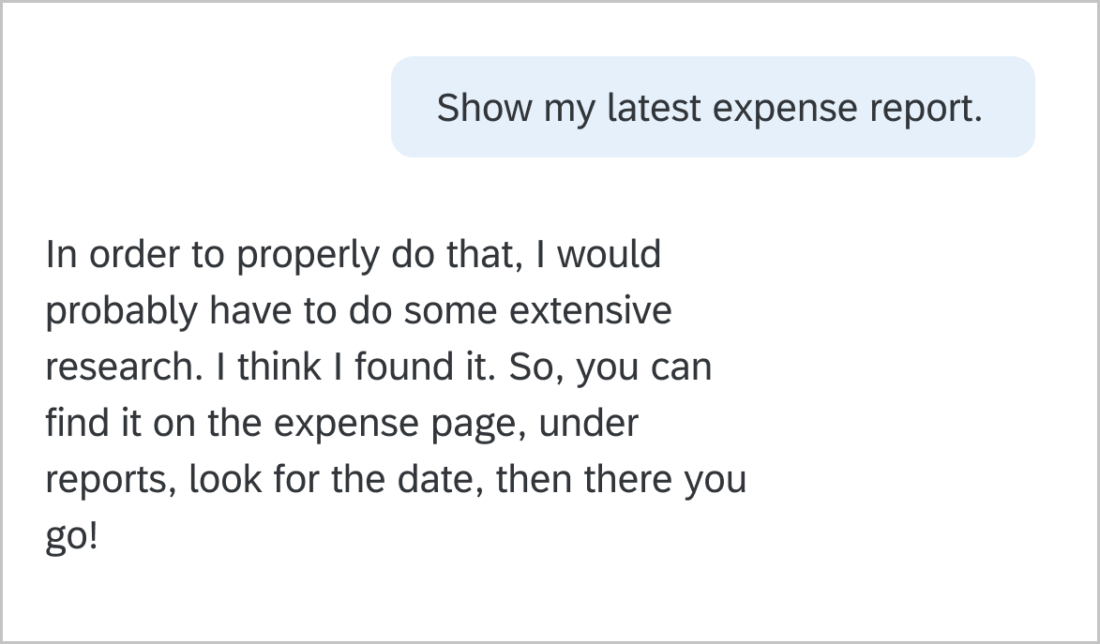
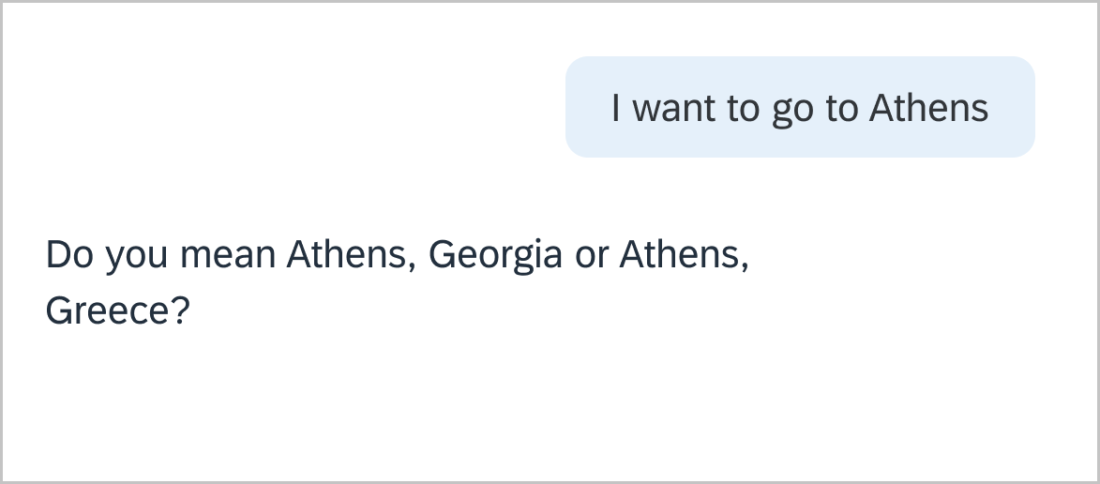
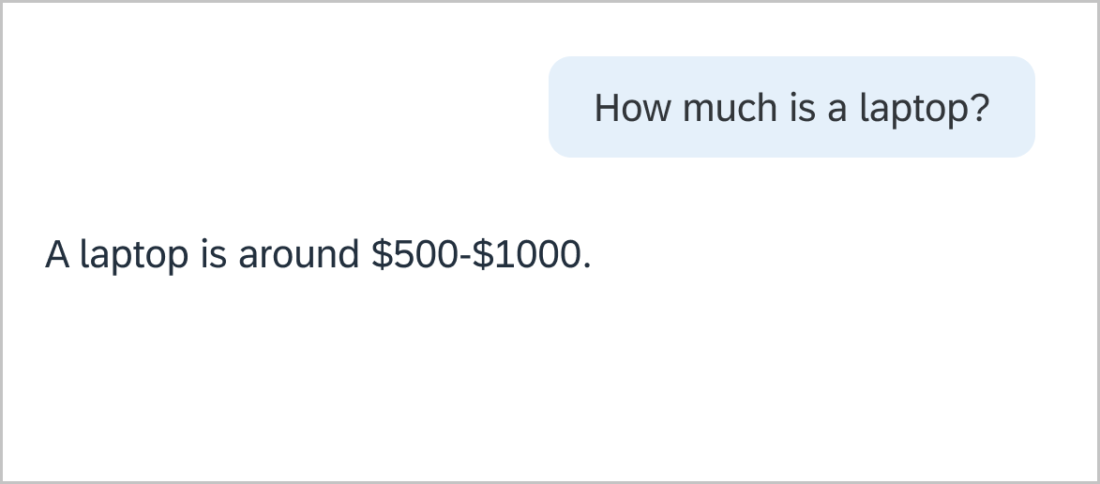
Use concise, natural, neutral language. Typical responses are between 60-90 characters. Keep it simple.
Active voice
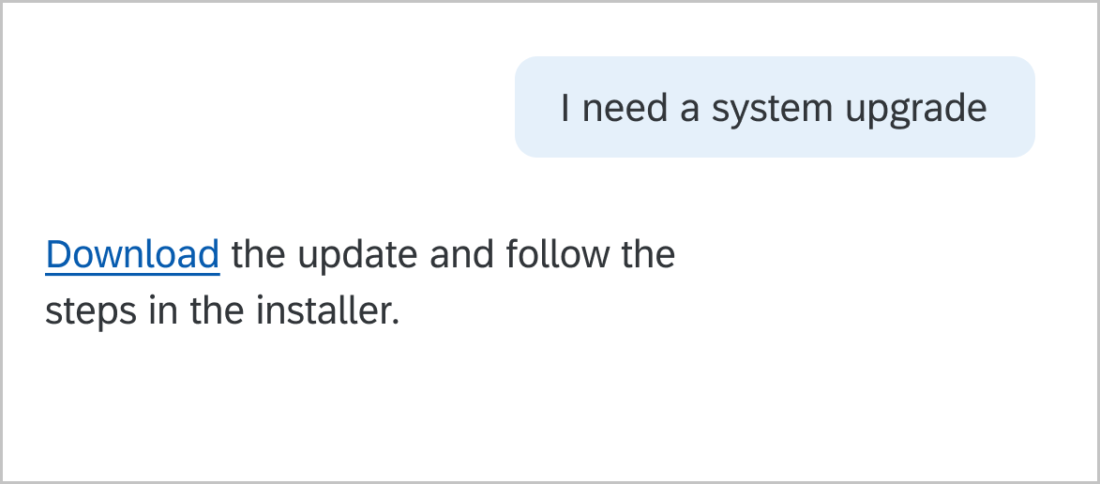
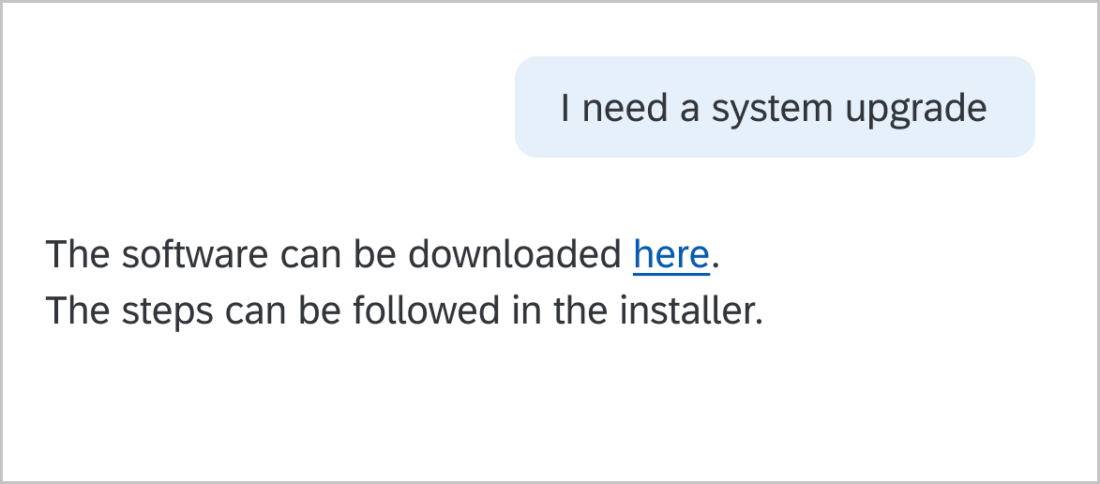
Basic active voice sentences are subject, verb, object. I love biking. Active voice is more understandable and direct. In the passive voice, the subject is acted on by the verb. Biking is loved by me. This can be unclear or too wordy. Write dialog as if you are having a conversation with a friend or coworker. If you say it aloud and it sounds strange, try to reword it.
Guide users
Users don’t know what they need. That’s why they’re asking for help. Find out what they need and give them options and next steps to help them complete their task. Keep earlier information in mind when responding. Give users a call-to-action to complete their task.
Slang and jargon
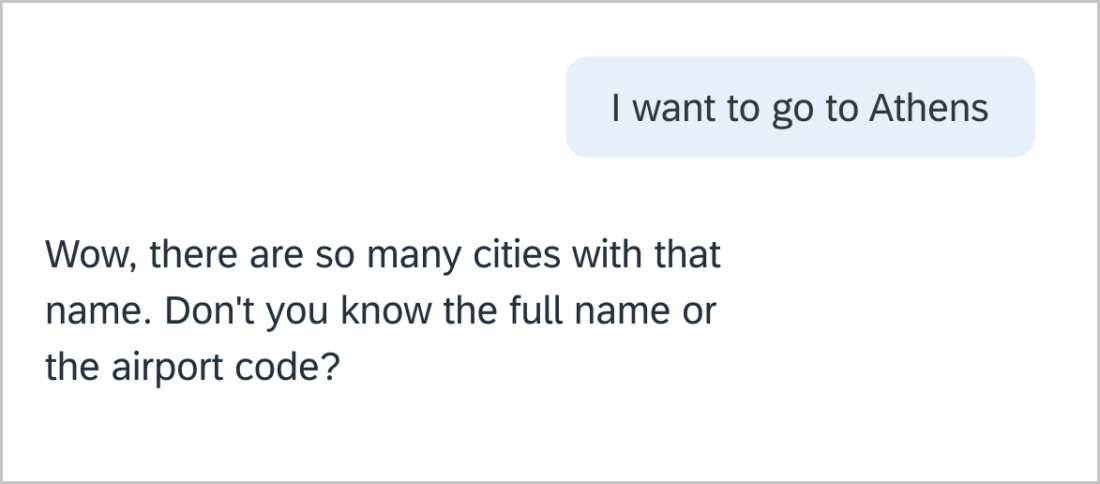
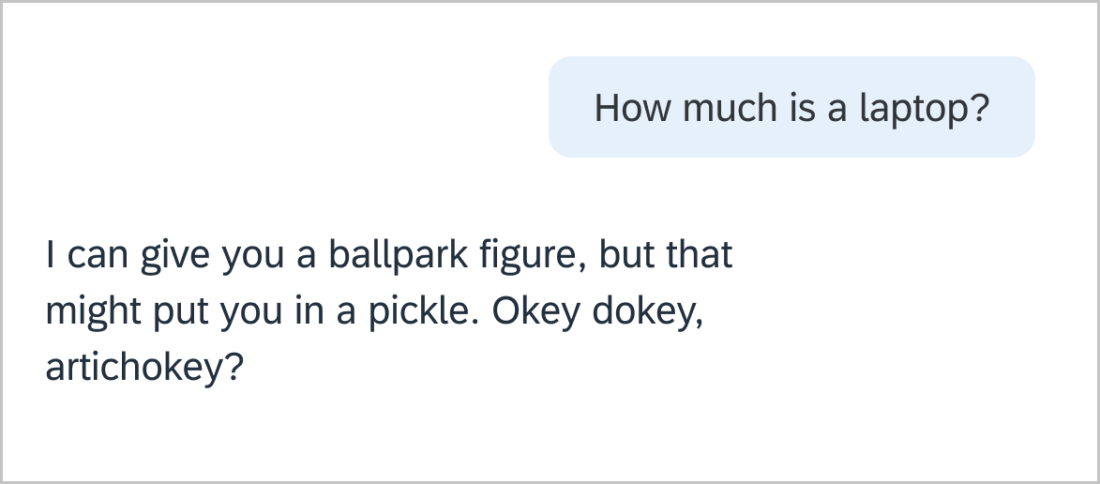
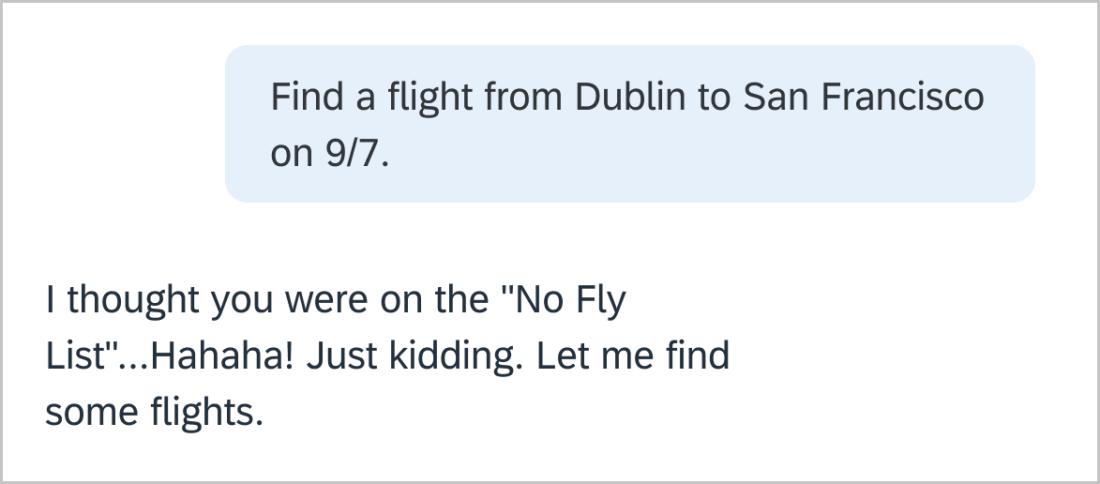
We want our users to know that we take them and their concerns seriously. Slang (very informal language) and colloquialisms (local or regional expressions) don’t translate well. Indian English, Australian English, and US English often have very different ways of saying things. What is said in English can be insulting or disrespectful in another language. Stick to basic, professional language.
Emotions and Humor
It’s best to stay away from using emotions, emojis and emoticons when communicating online. These don’t always translate well from one culture to another. Certain emojis, like a hand gesture, can be offensive in some cultures. Humor is subjective and can be interpreted differently.