- Latest SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
- Latest SAPUI5 Version 1.120
- Version 1.118
- SAPUI5 Version 1.116
- SAPUI5 Version 1.114
- SAPUI5 Version 1.112
- SAPUI5 Version 1.110
- SAPUI5 Version 1.108
- SAPUI5 Version 1.106
- SAPUI5 Version 1.104
- SAPUI5 Version 1.102
- SAPUI5 Version 1.100
- SAPUI5 Version 1.98
- SAPUI5 Version 1.96
- SAPUI5 Version 1.94
- SAPUI5 Version 1.92
- SAPUI5 Version 1.90
- SAPUI5 Version 1.88
- SAPUI5 Version 1.86
- SAPUI5 Version 1.84
- SAPUI5 Version 1.82
- SAPUI5 Version 1.80
- SAPUI5 Version 1.78
- SAPUI5 Version 1.76
- SAPUI5 Version 1.74
- SAPUI5 Version 1.72
- SAPUI5 Version 1.70
- SAPUI5 Version 1.68
- SAPUI5 Version 1.66
- SAPUI5 Version 1.64
- SAPUI5 Version 1.62
- SAPUI5 Version 1.60
- SAPUI5 Version 1.58
- SAPUI5 Version 1.56
- SAPUI5 Version 1.54
- SAPUI5 Version 1.52
- SAPUI5 Version 1.50
- SAPUI5 Version 1.48
- SAPUI5 Version 1.46
- SAPUI5 Version 1.44
- SAPUI5 Version 1.42
- SAPUI5 Version 1.40
- SAPUI5 Version 1.38
- SAPUI5 Version 1.36
- SAPUI5 Version 1.34
- SAPUI5 Version 1.32
- SAPUI5 Version 1.30
- SAPUI5 Version 1.28
- SAPUI5 Version 1.26
Chart – Time Axis
Intro
The time axis is compatible with a number of charts and is designed to show the variation of values through time. It can display years, quarters, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
The time axis incorporates three valuable features:
- All the complexity involved with formatting the labels – including localization – is taken care of automatically
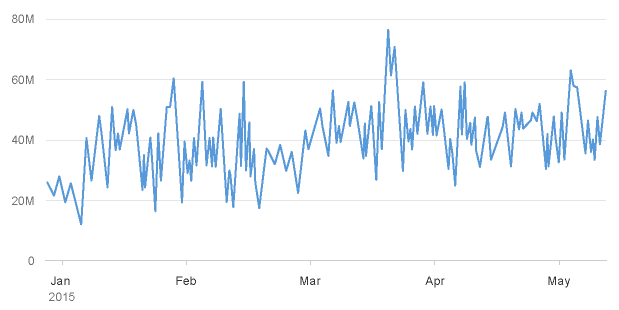
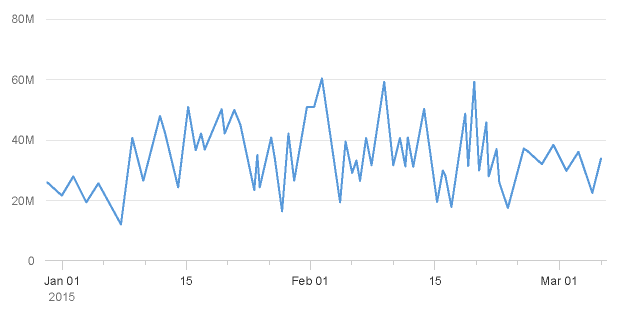
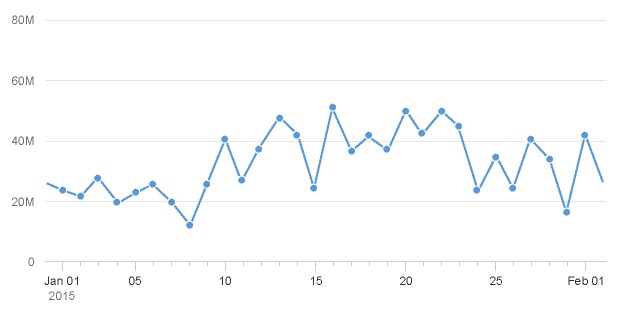
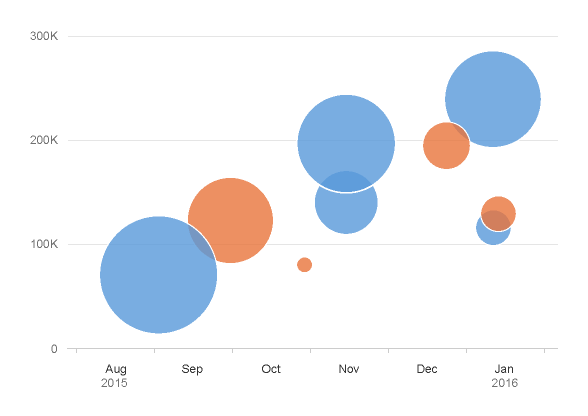
- The time unit labels behave responsively according to the zoom factor. As you can see below, the time unit labels in the top row change as the zoom increases, while the time unit label in the row below is only displayed once to prevent unnecessary repetition.
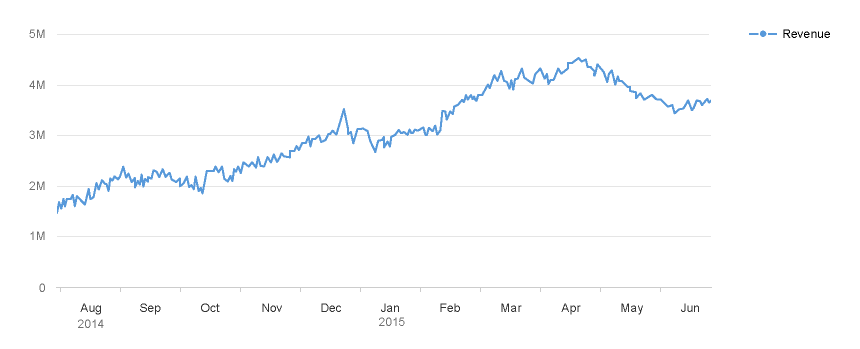
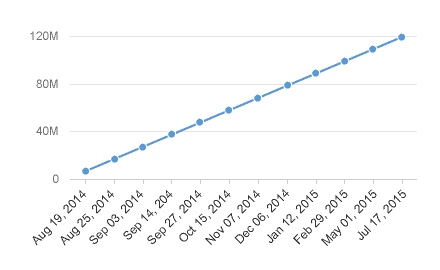
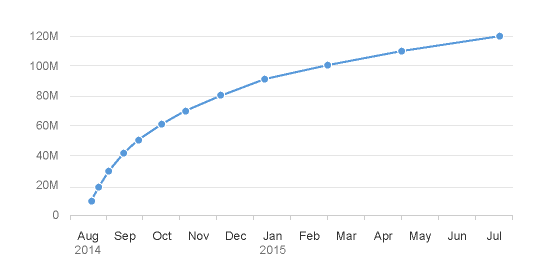
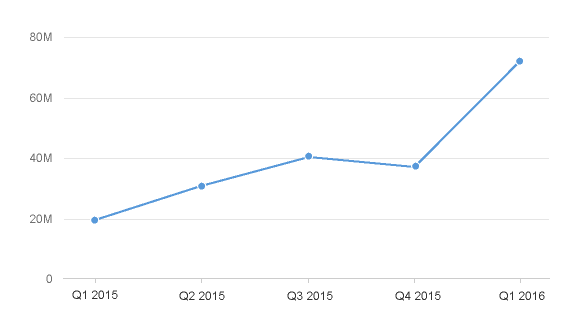
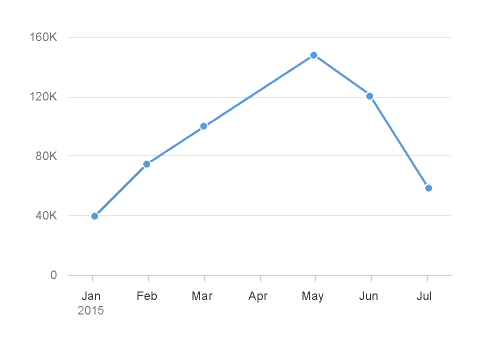
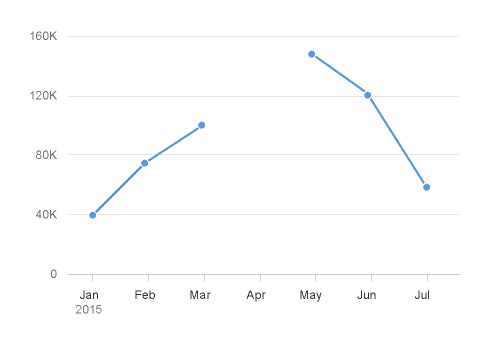
3. For certain chart types, the physical spacing between your data points accurately respects the time scale being displayed, as opposed to just rendering all your data points equidistantly. We can see what a difference this makes by comparing the charts below. The chart to the left uses the categorical axis and the chart to the right uses the time axis. Even though both charts were generated from exactly the same dataset; they tell completely different stories with respect to how the values have increased over time due to the high concentration of early data points.
Compatible Chart Types
A number of SAP Fiori charts can accommodate the time axis, such as the bubble chart, scatter chart, line chart, column chart, and more.
You can find the full list of charts that can accommodate the time axis in the chart types article.
Customization
Choosing Which Time Units are Displayed
By default, the time axis displays day, month, year. However, you can display different time units to suit your dataset using one of 18 recommended combinations:
- Second, minute, hour
- Second, minute, hour, day, month
- Second, minute, hour, day, month, year
- Minute, hour
- Minute, hour, day, month
- Minute, hour, day, month, year
- Day, month
- Day, month, quarter
- Day, month, year
- Week, year
- Week
- Month, year
- Month, quarter, year
- Month, quarter
- Month
- Quarter, year
- Quarter
- Year
Any other custom combinations will likely lead to undesirable results.
Define the Layout of Your Time Unit Labels
By default, your time unit labels will be displayed in one or two rows depending on the zoom factor that is applied to the time axis at any given time. You will notice below that the time unit labels are not repeated in the bottom row so there is no unnecessary repetition of time unit labels.
It is technically possible to force the labels so that they are displayed in just one row as illustrated below, although this will only work in a satisfactory way for two time unit combinations: “year, month” and “quarter, year”.
If your chart is going to be displayed in a small space, you can choose to display the first date and the last date in your dataset as illustrated below.
Formatting the Time Units
By default, the date unit labels follow SAP UI5 medium date formats which localizes the order of the time unit labels e.g. “7 Aug, 2016” (British) or “Aug 7, 2016” (American). However, three combinations will always be displayed in the same order: “year, quarter”, “year, week” and “quarter, week”. This is because these combinations are not supported by CLDR (Common Local Data Repository) localization standards.
You can use any of the other formats available in SAPUI5 such as “August”, “A” and “08”. However, due to the responsive behavior of the time axis, the zoom factor will affect the way that your time units are displayed. Therefore, you must create and register a format for all potential permutations. For example; if you want to display ‘year, month, day’ you need to create and register separate formats for “year, month, day”, “month, day” and “year”.
Defining the Initial View
By default, the time axis will render your chart from your first data point, with a scrollbar if necessary. However, you can decide which data points (or a specific time period) is initially displayed.
Managing Null or Missing Values in a Line Chart
If there are going to be null or missing values in your dataset, you can connect the available data points, or create a clear break between them.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.

 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.