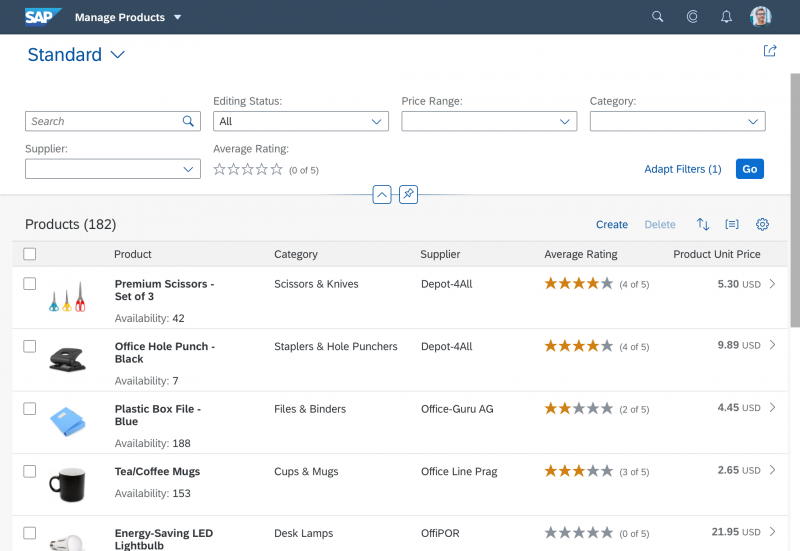
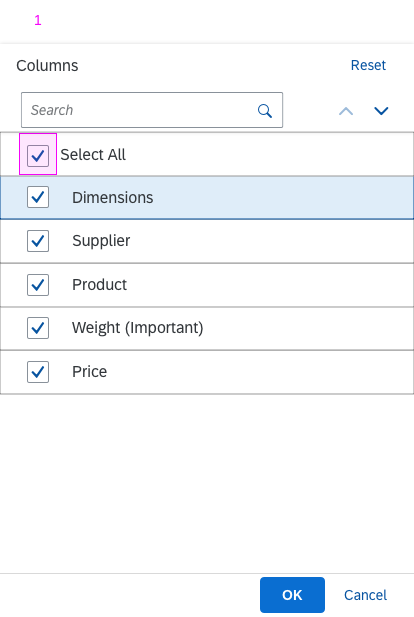
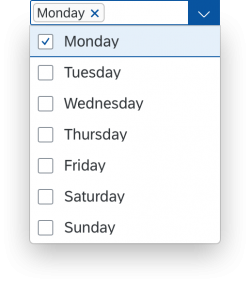
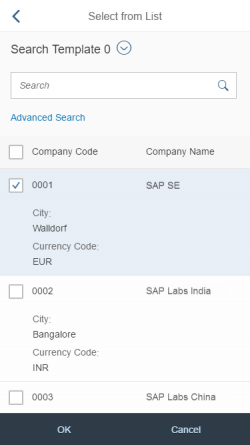
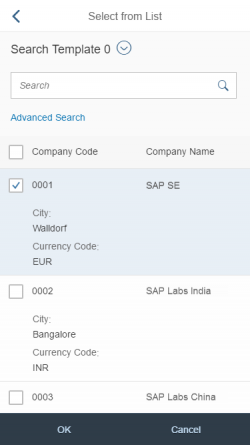
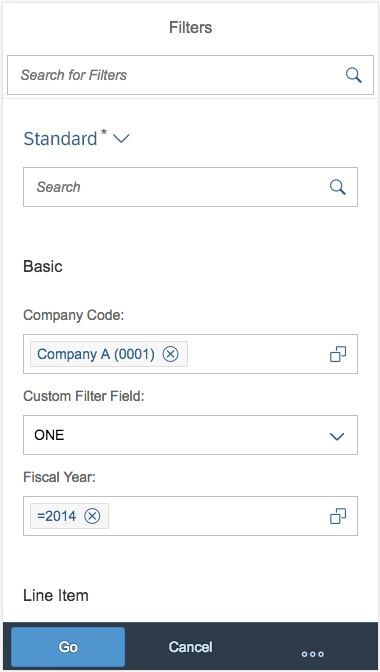
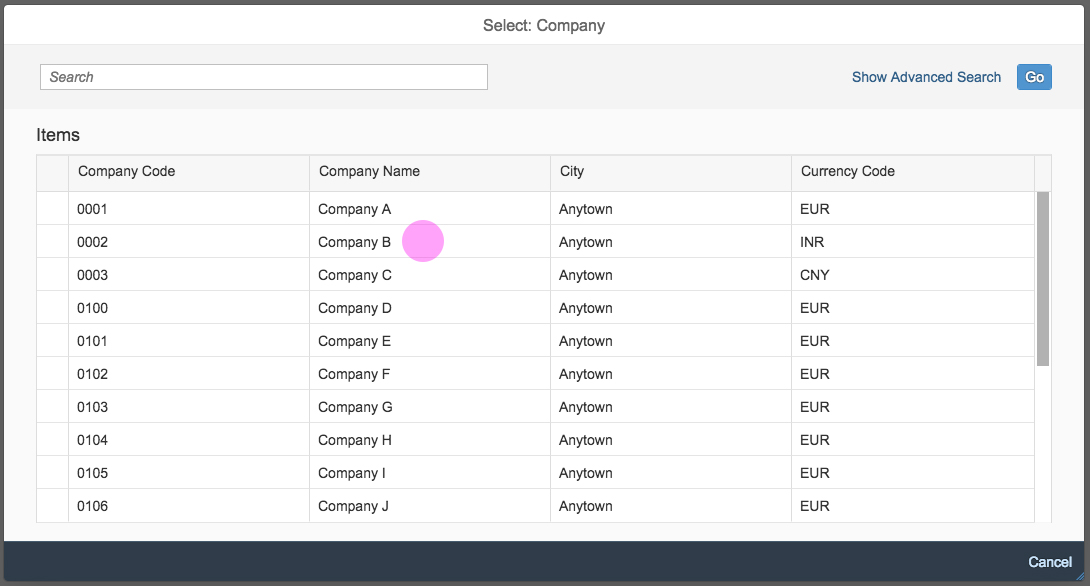
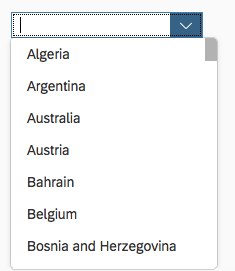
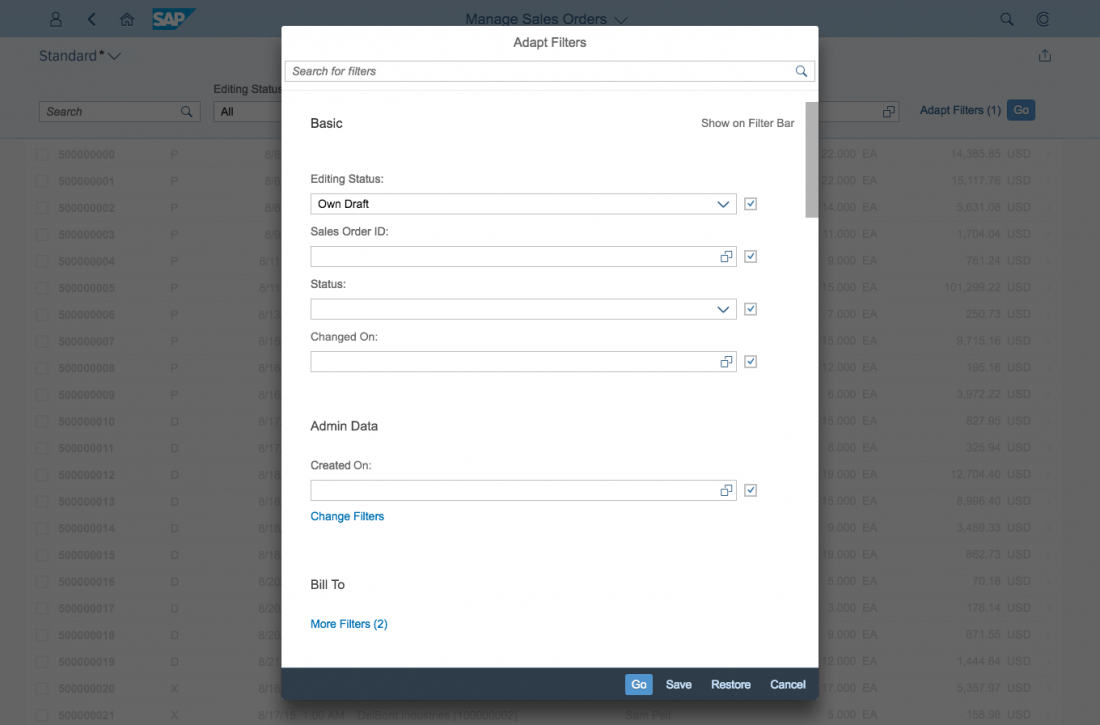
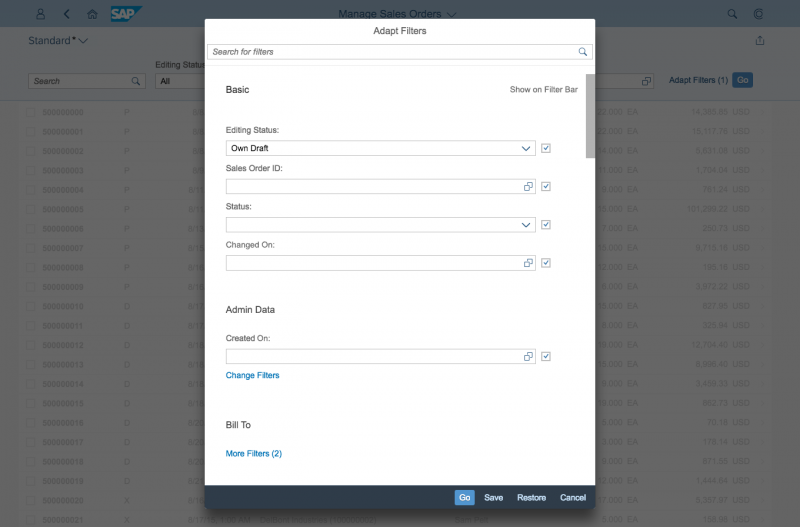
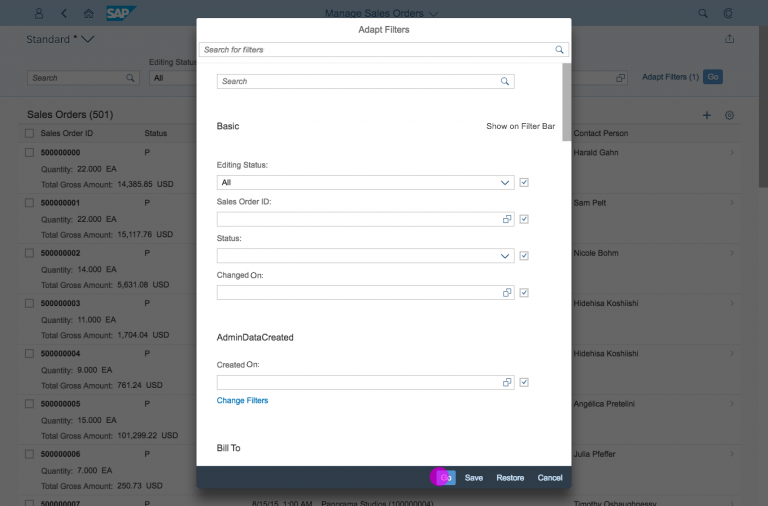
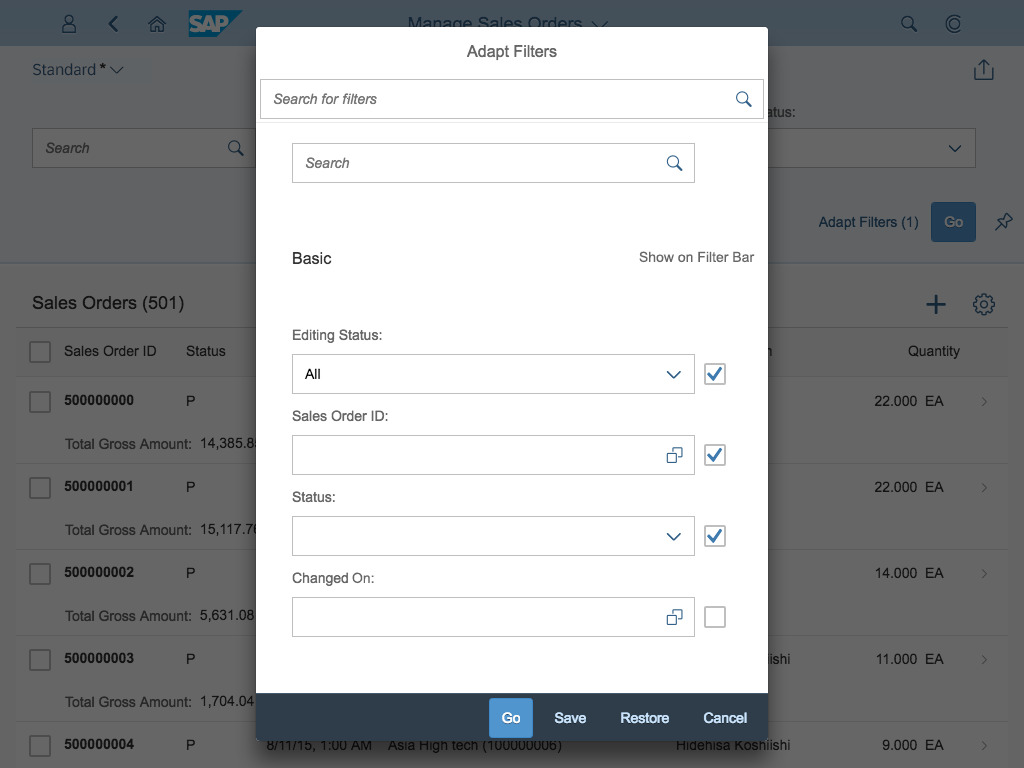
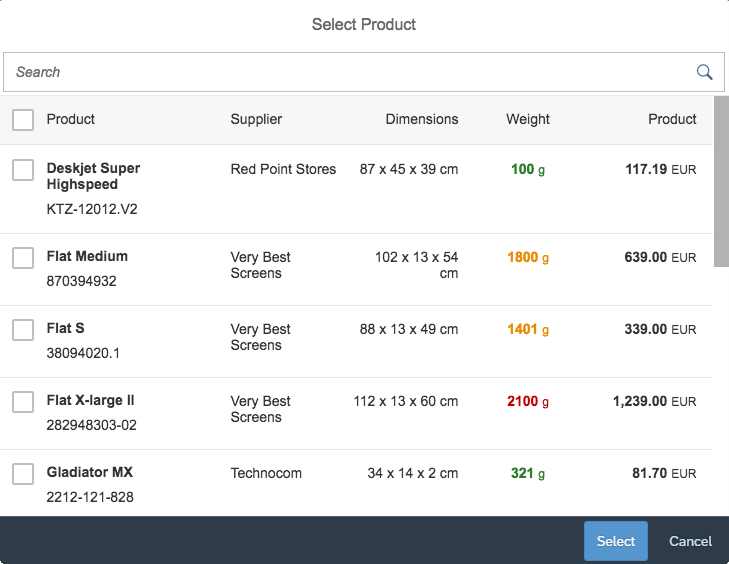
Select Dialog
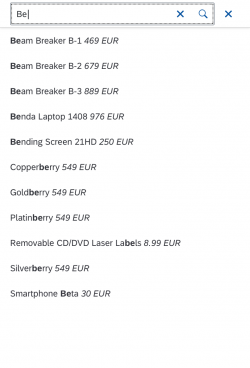
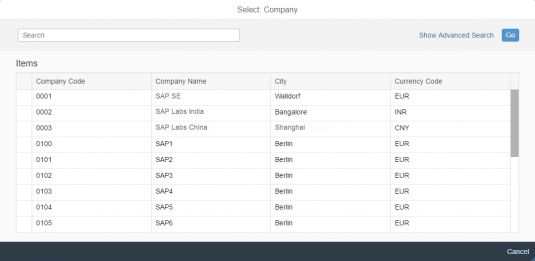
The select dialog enables users to select one or more items from a comprehensive list. The select dialog comes with a list of entries and a search field to filter the list.
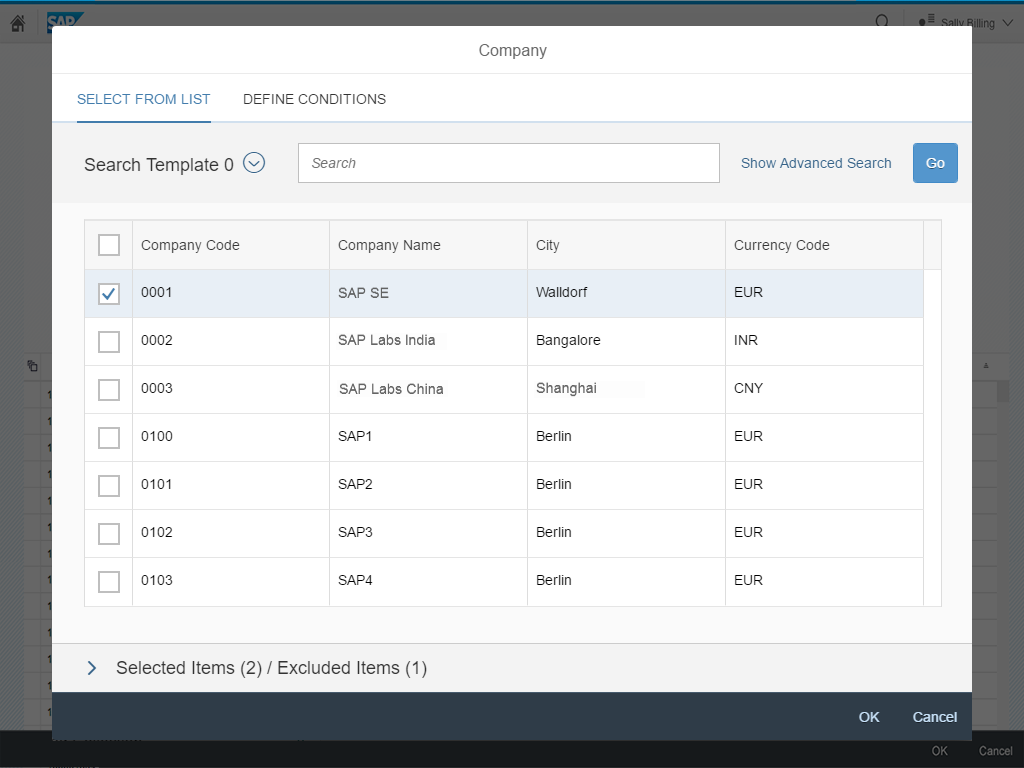
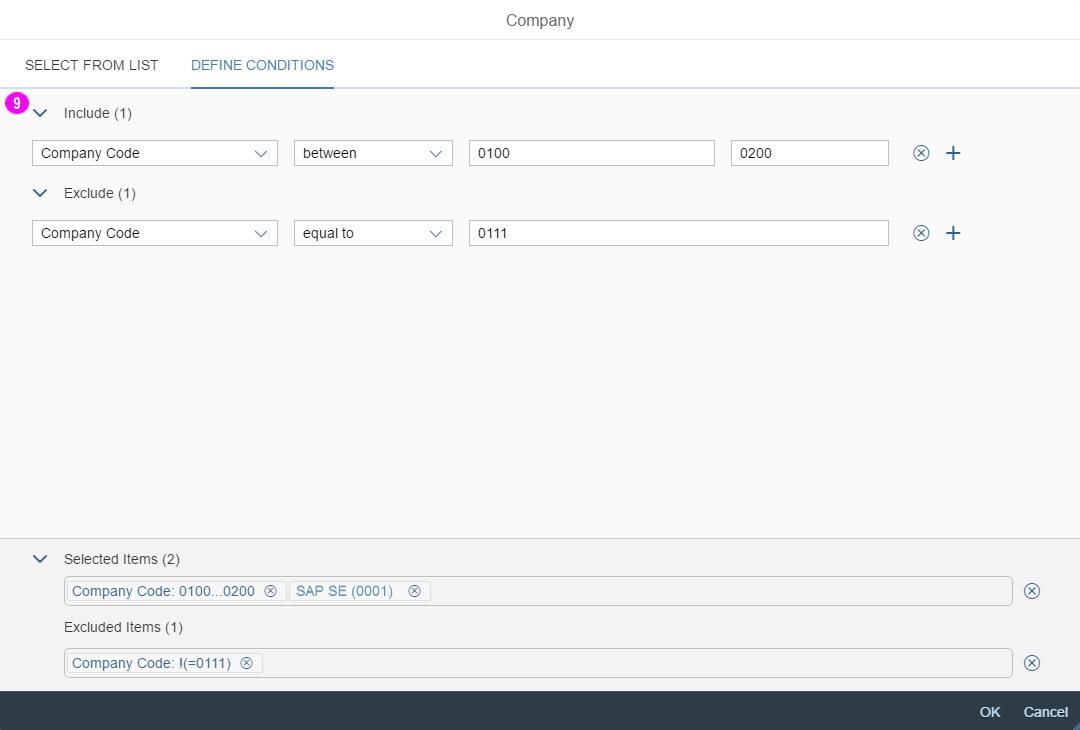
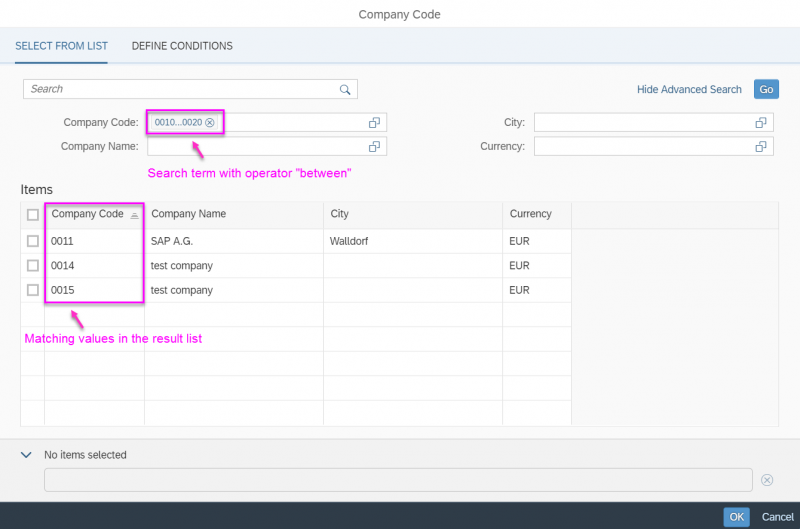
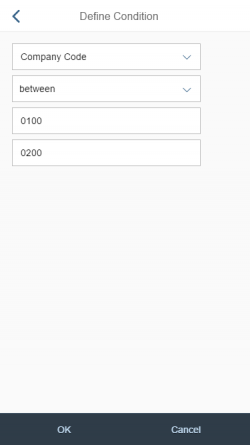
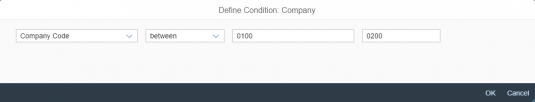
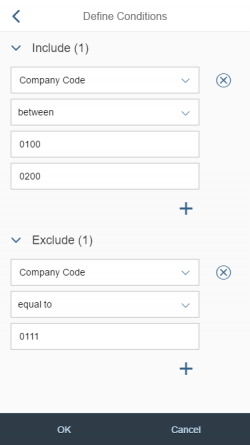
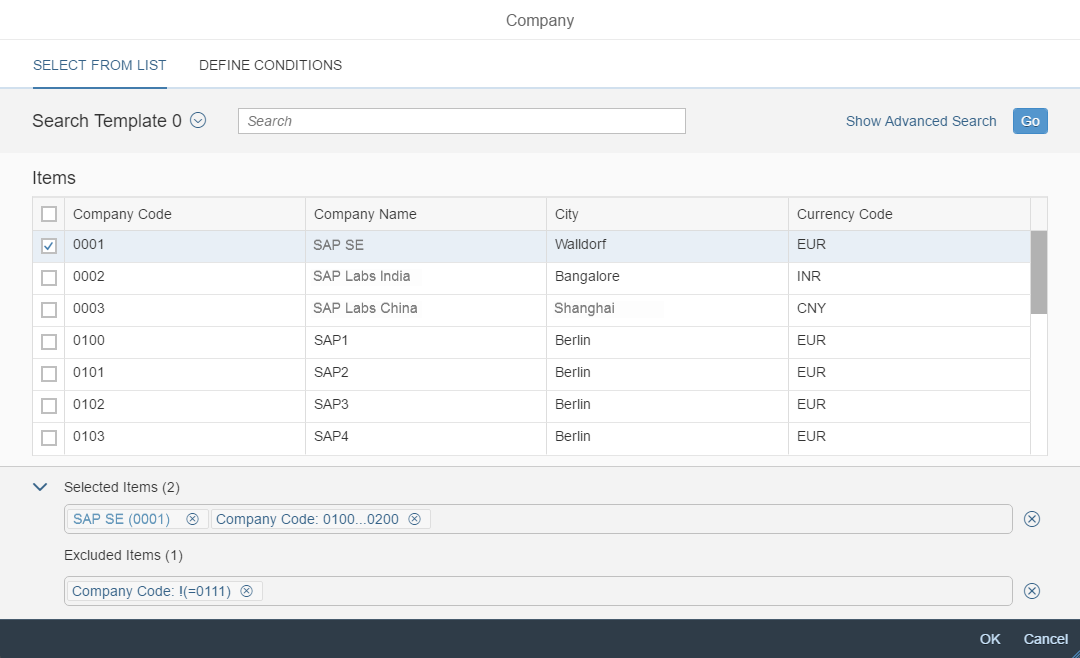
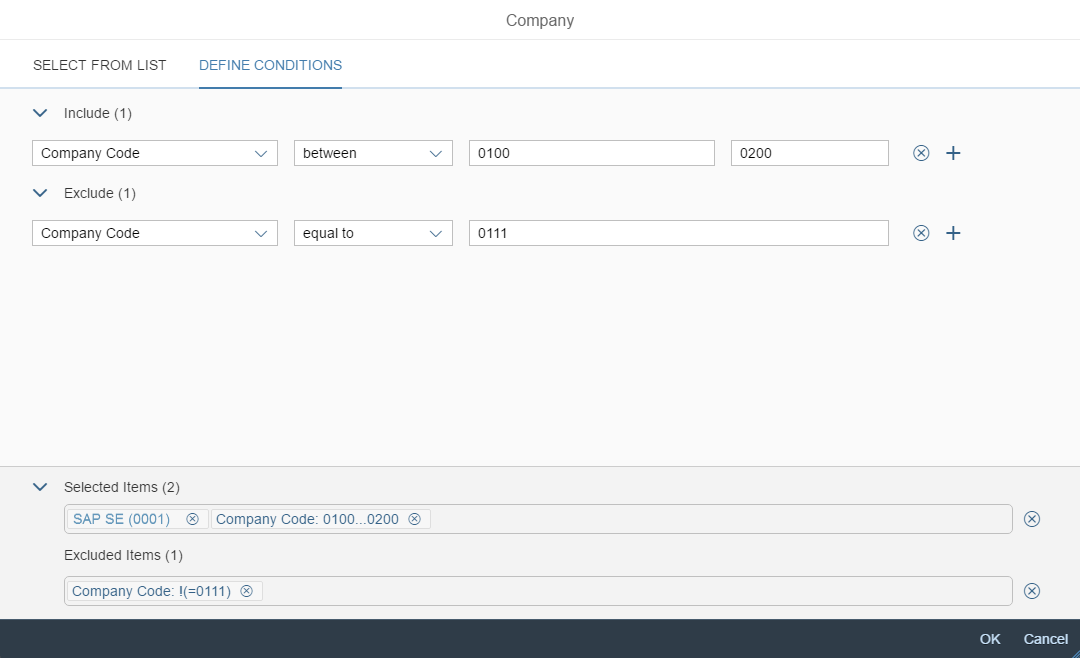
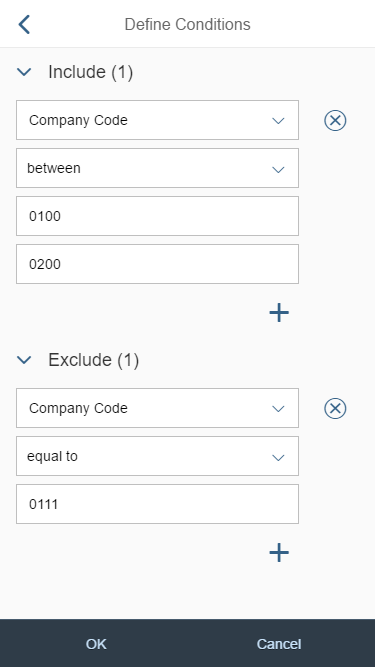
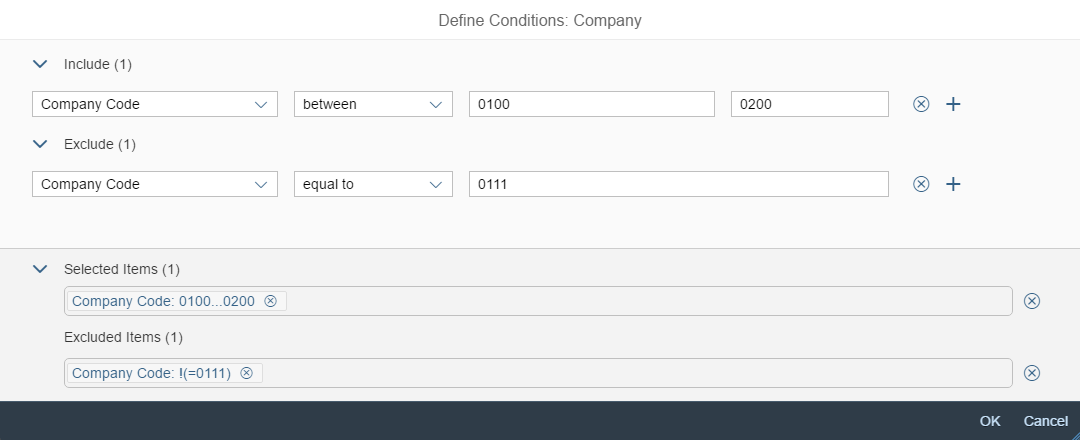
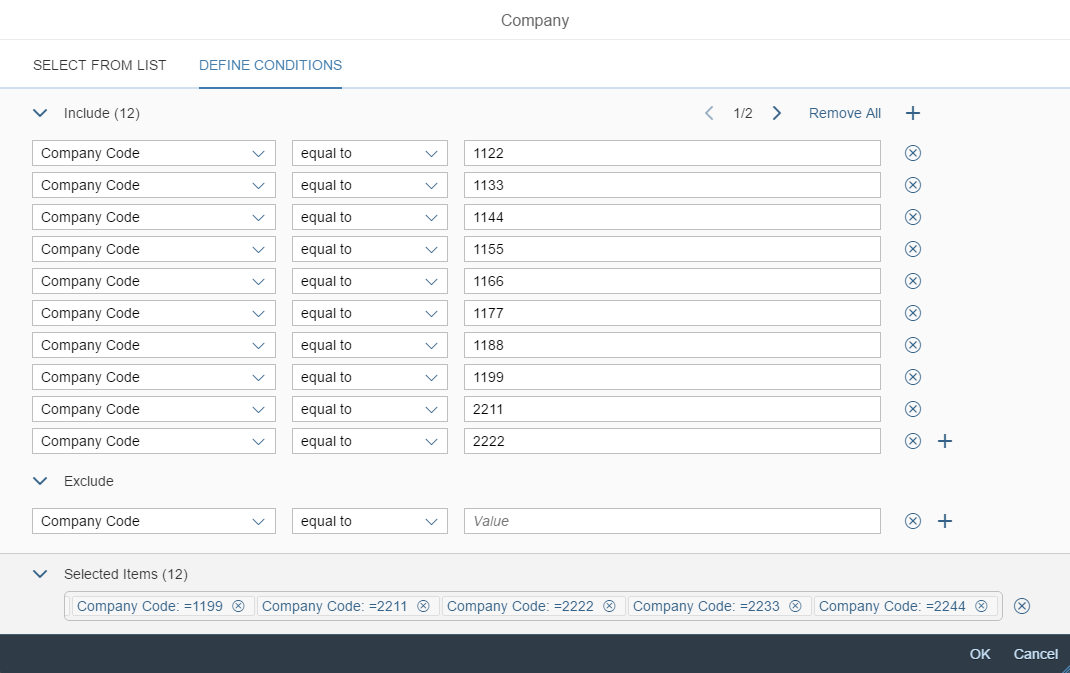
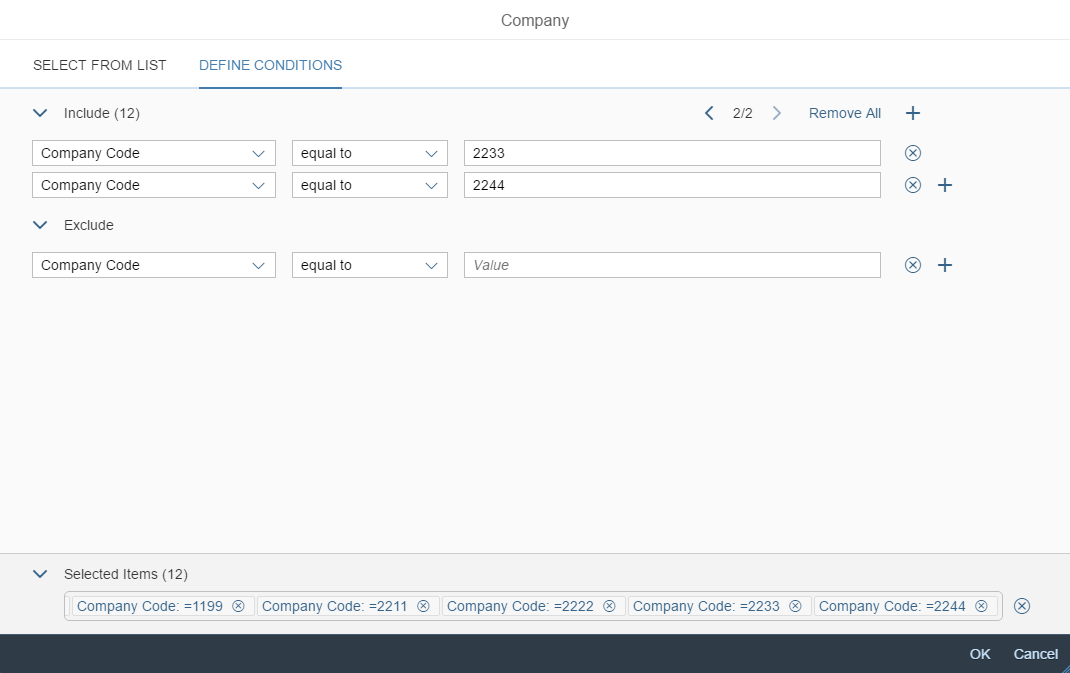
A more enhanced dialog for single selection and multiselection is the value help dialog as it offers range selection and excluding functions.
Usage
Use the select dialog if:
- Users need to select one or more entries from a comprehensive list that contains multiple attributes or values.
Do not use the select dialog if:
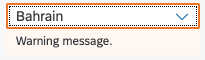
- Users need to pick one item from a predefined set of options that contains one attribute or value only such as languages. In this case, consider using the combo box or select instead.
- Your use case requires more enhanced functionalities such as a selection based on ranges. For the selection of values, consider using the value help dialog instead.
- Your use case requires tabs, filters, or an Add New functionality in the select dialog. In this case, use a standard dialog instead.
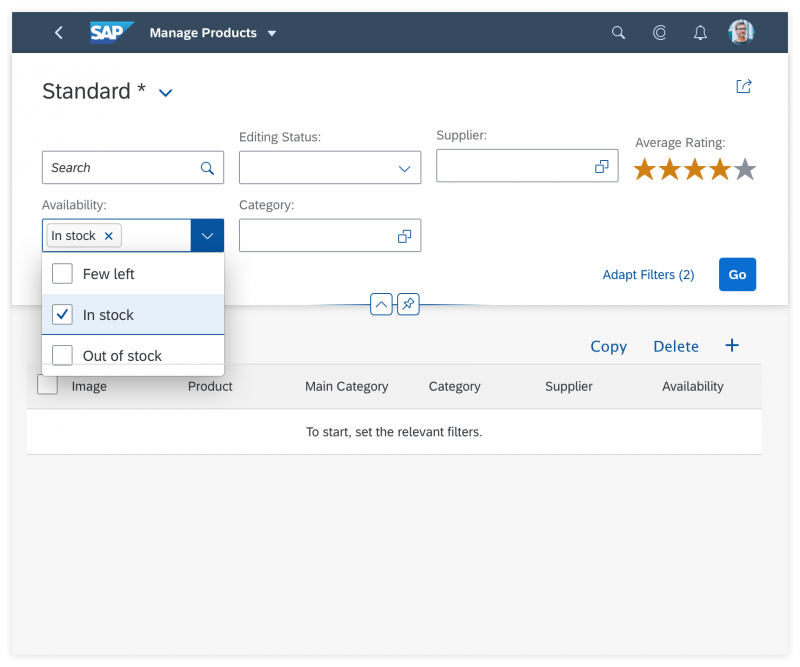
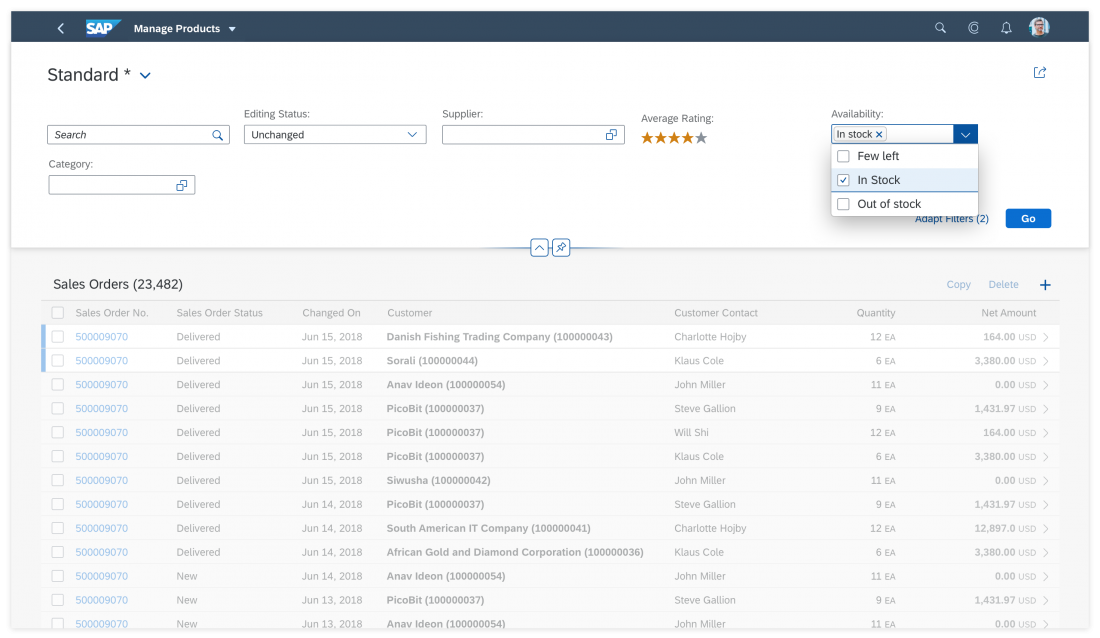
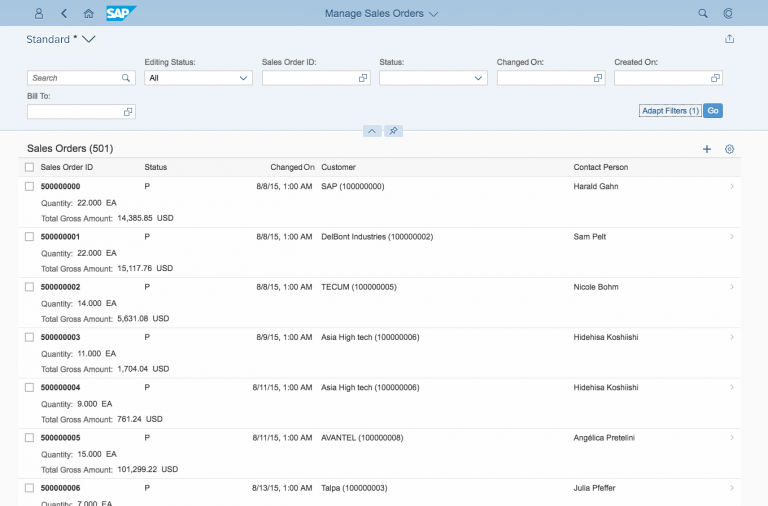
Responsiveness
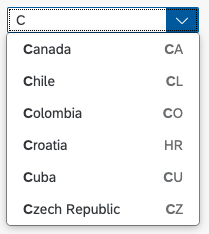
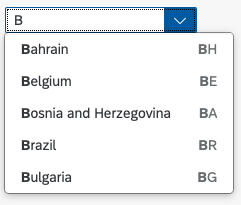
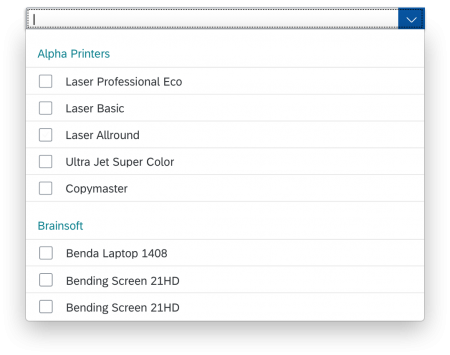
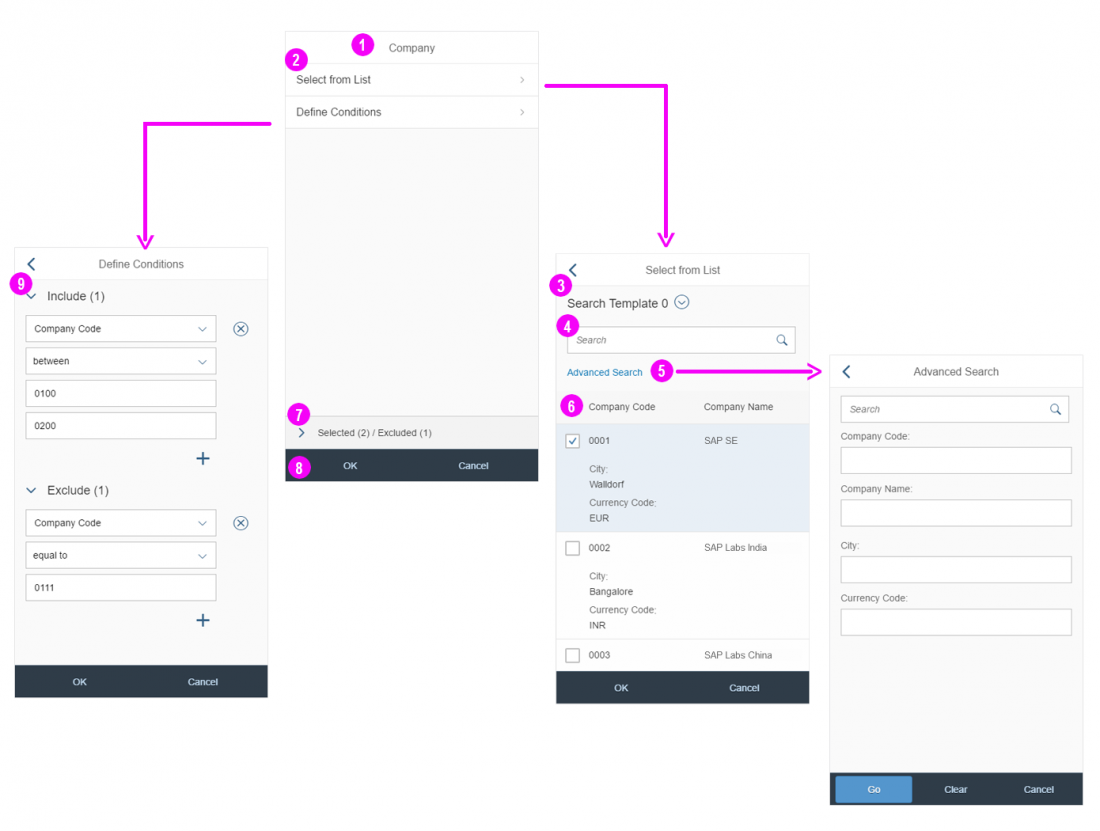
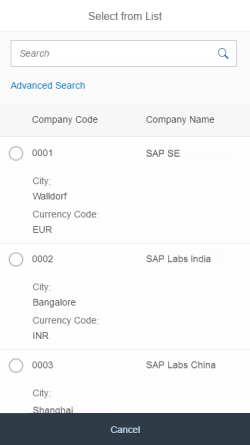
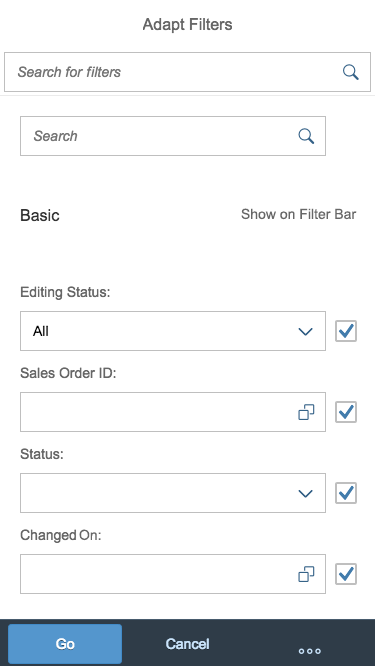
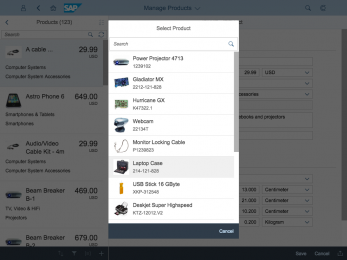
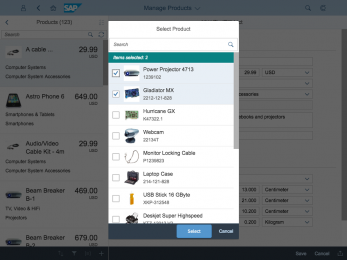
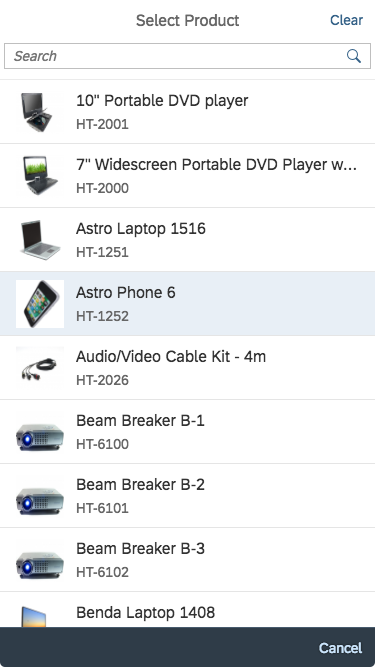
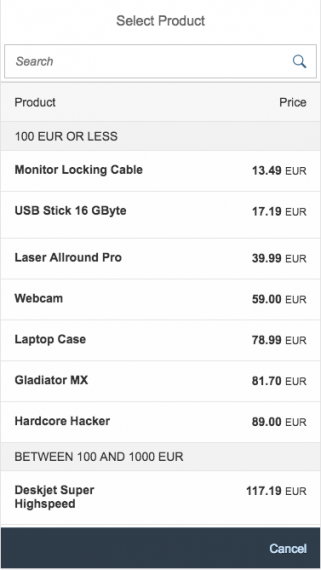
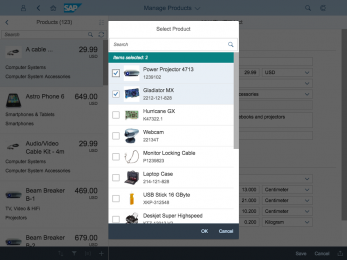
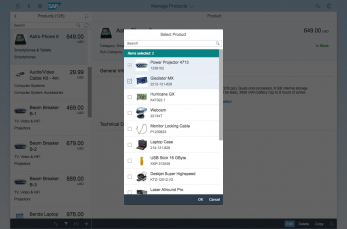
The display of the select control depends on the device. On phones, the selection list takes up the whole screen. On desktop and tablet devices it appears as a popover.
Size S
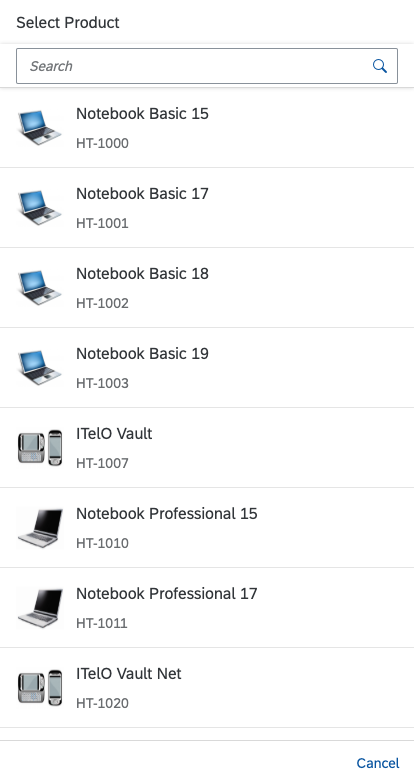
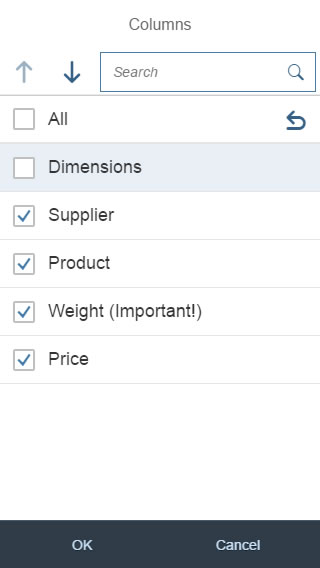
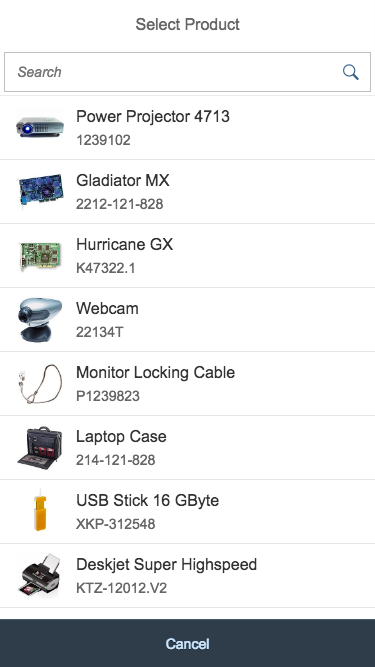
Single select dialog in full screen on smartphone
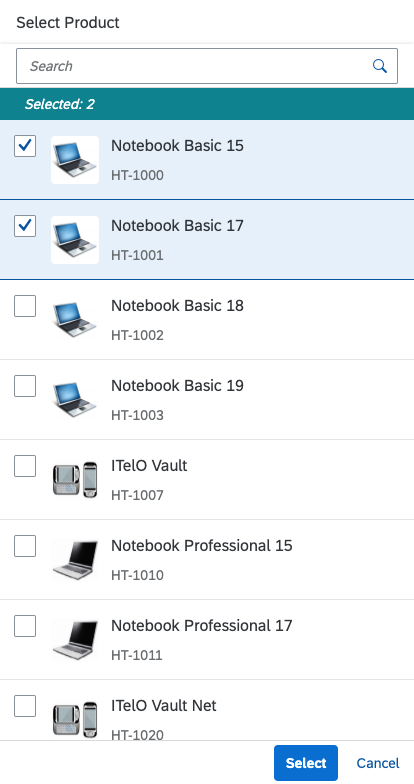
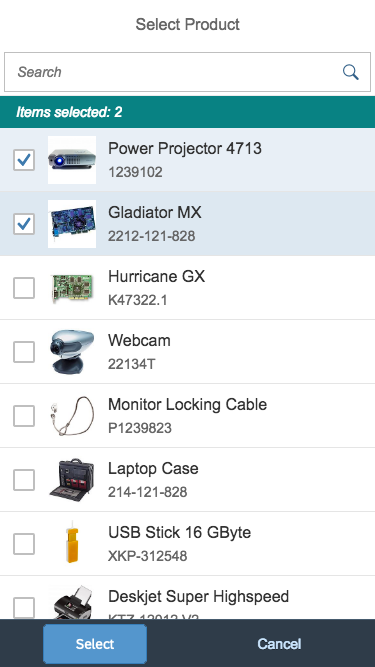
Multi-select dialog in full screen on smartphone
Components
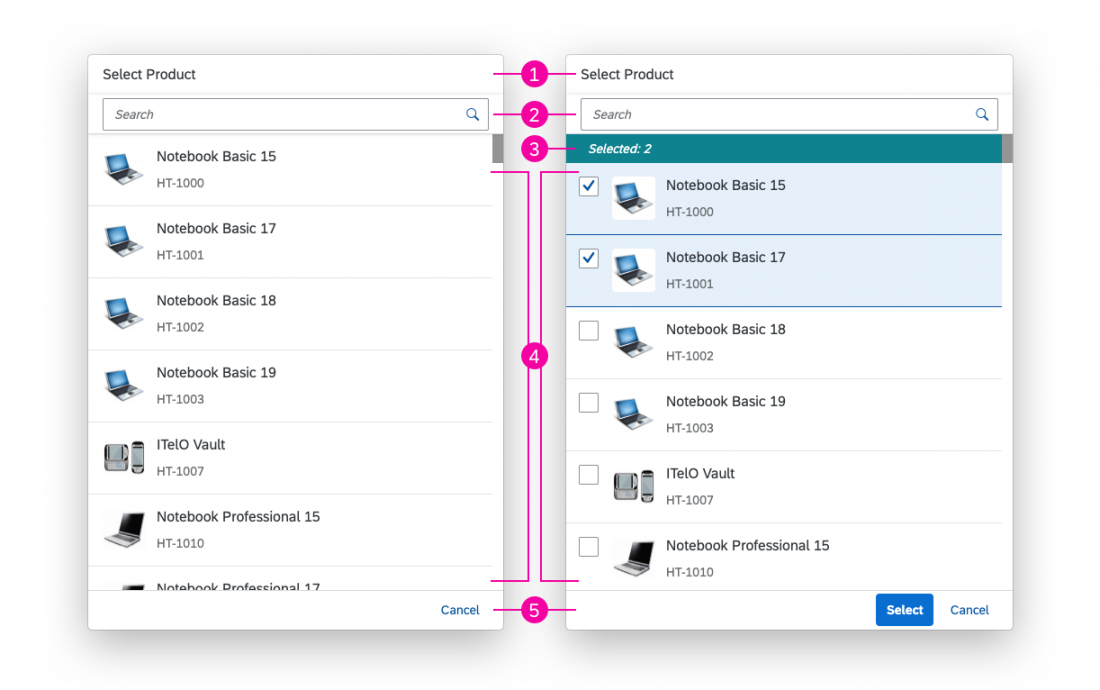
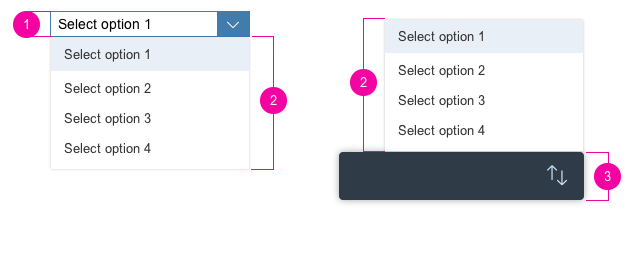
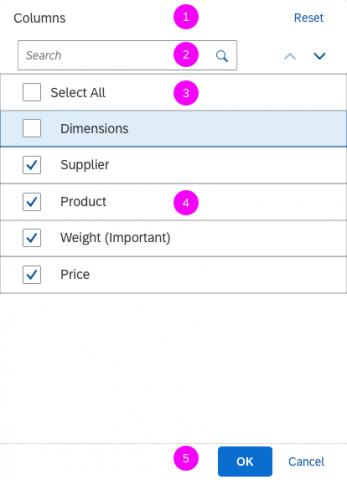
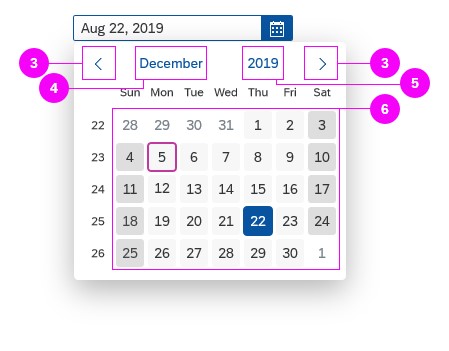
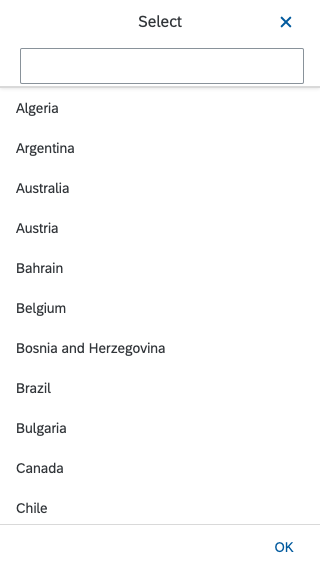
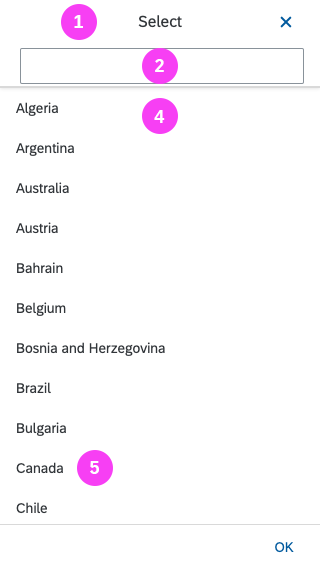
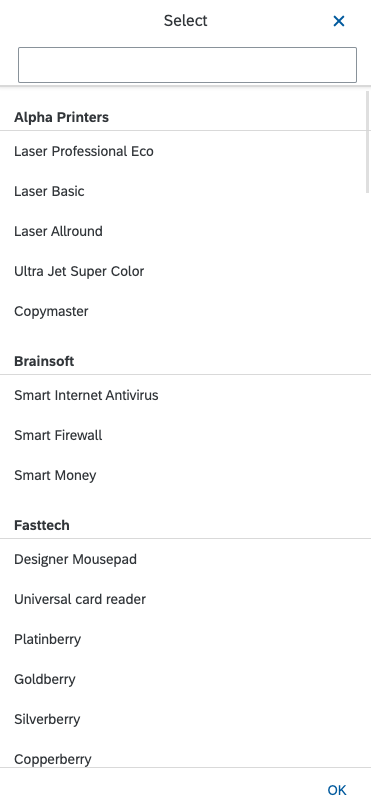
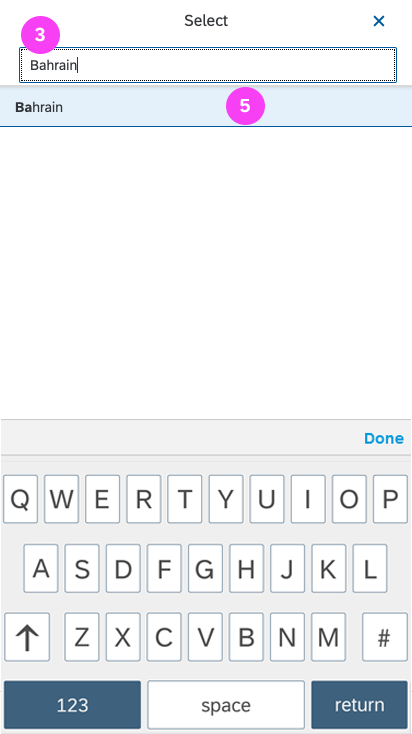
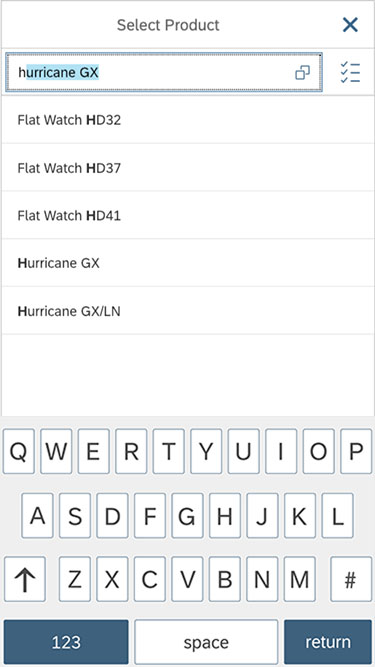
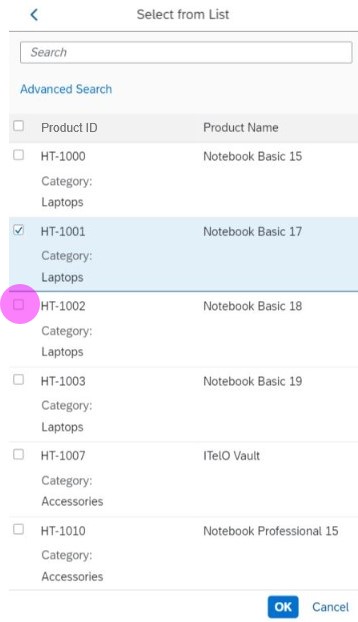
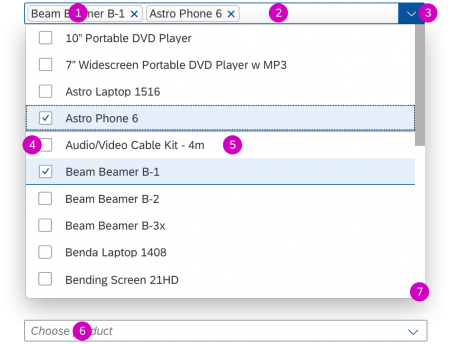
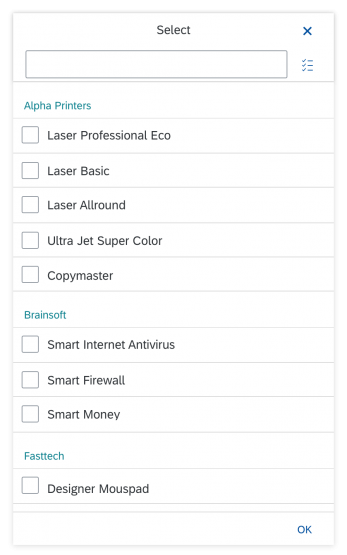
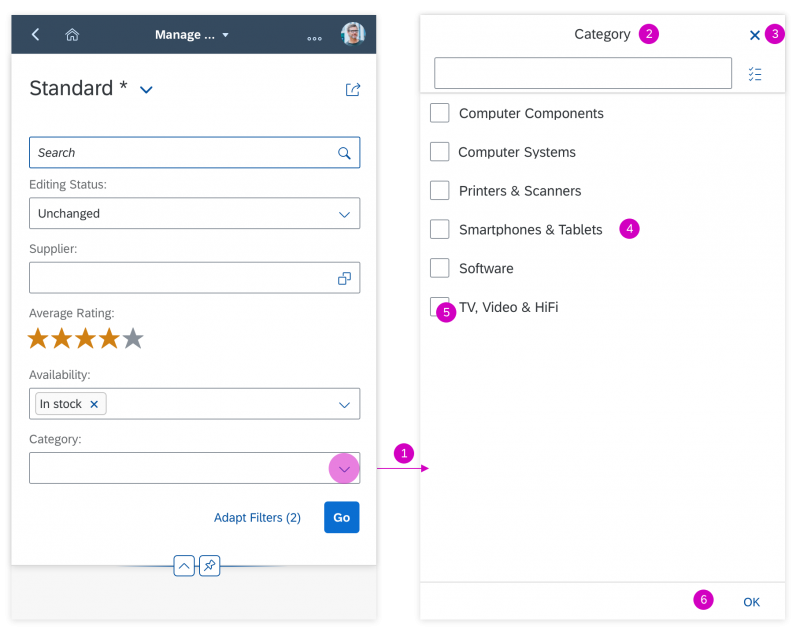
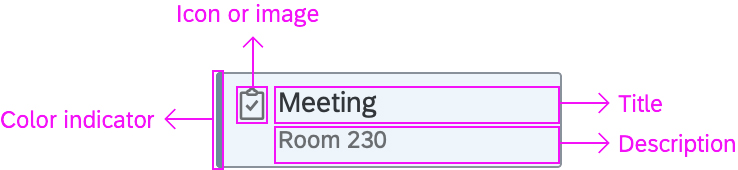
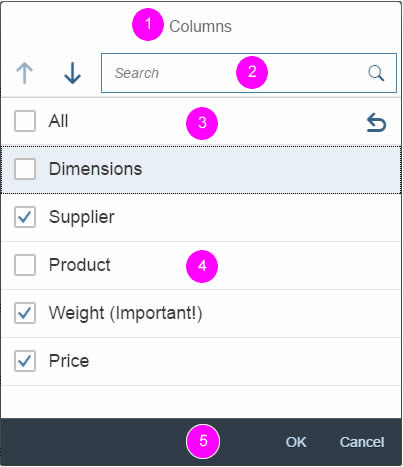
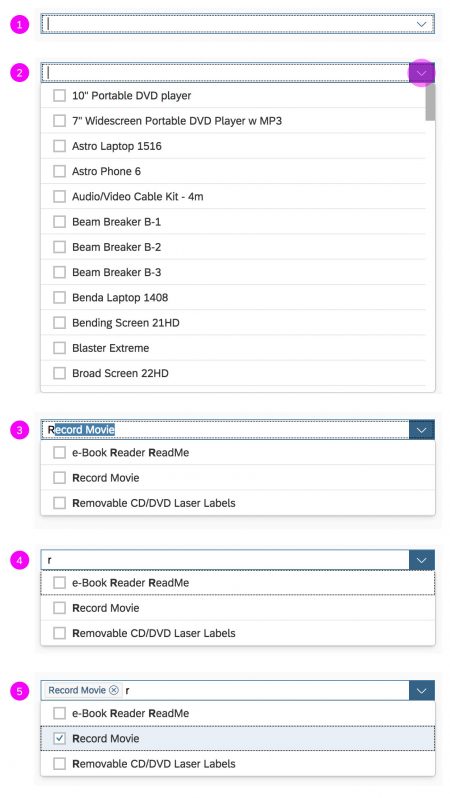
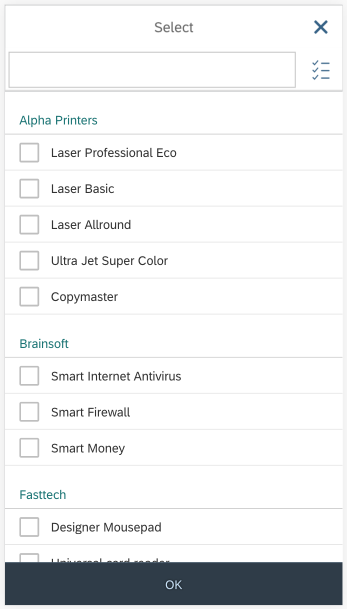
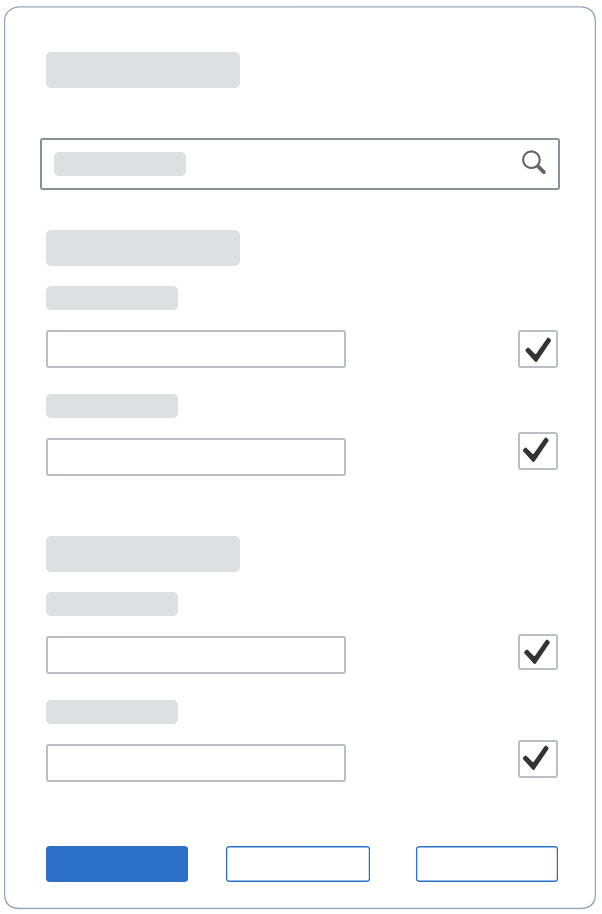
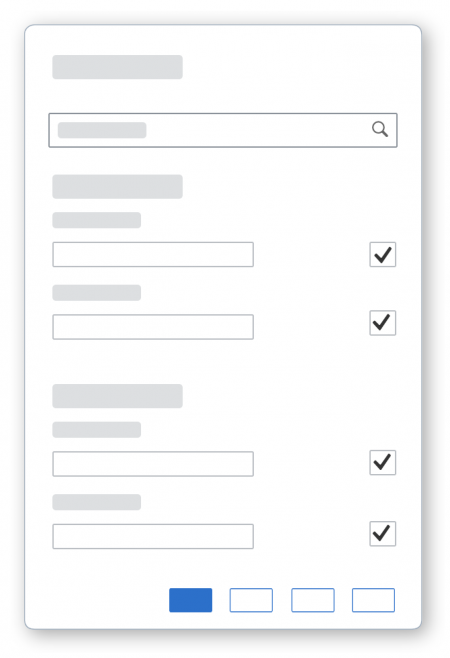
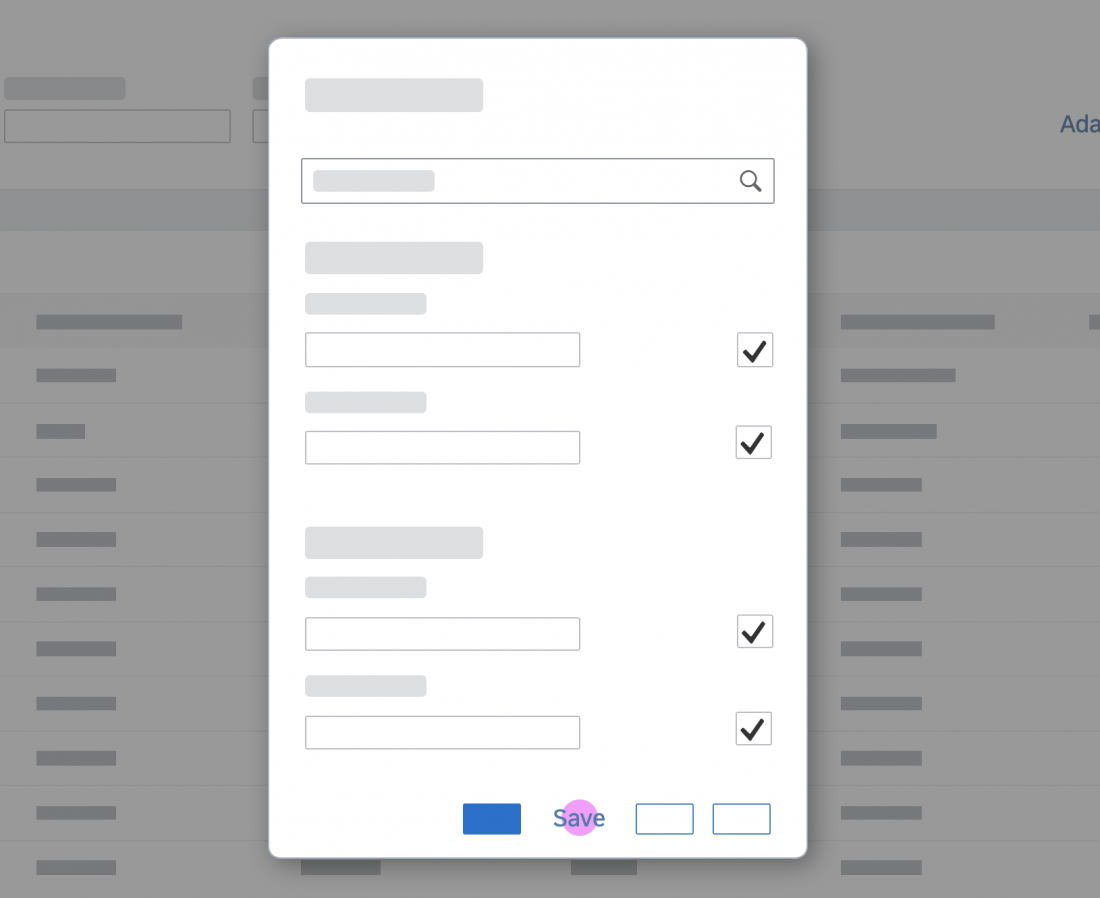
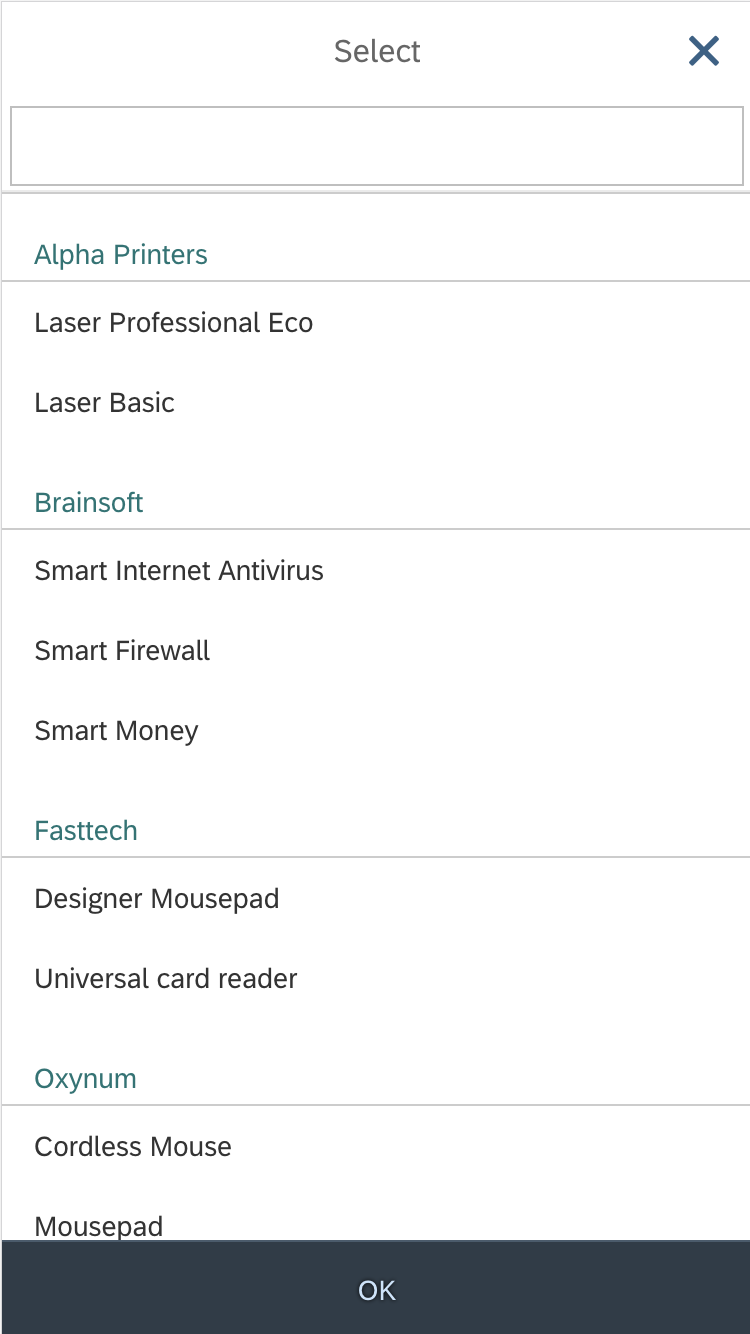
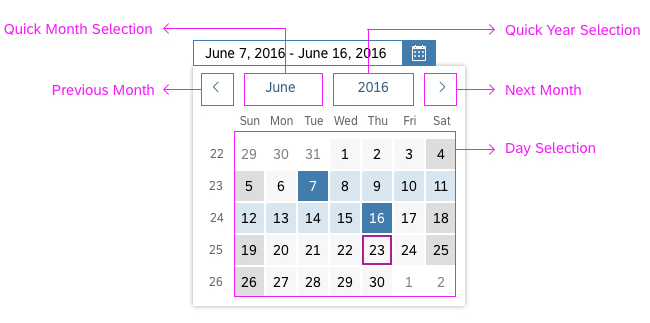
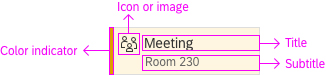
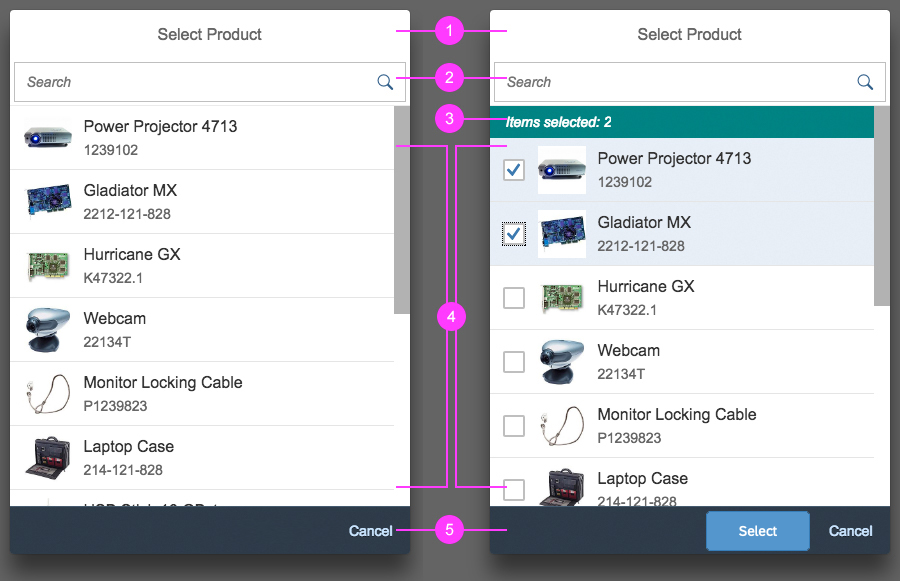
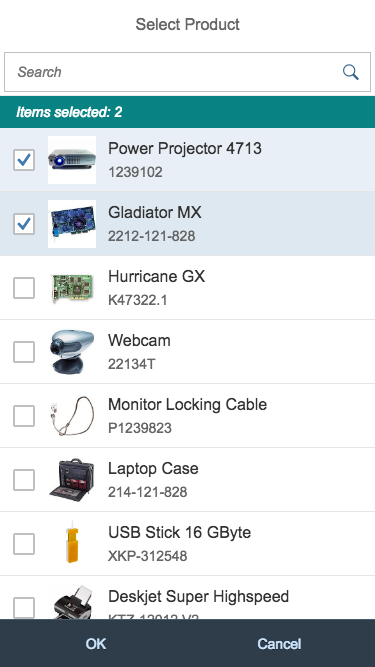
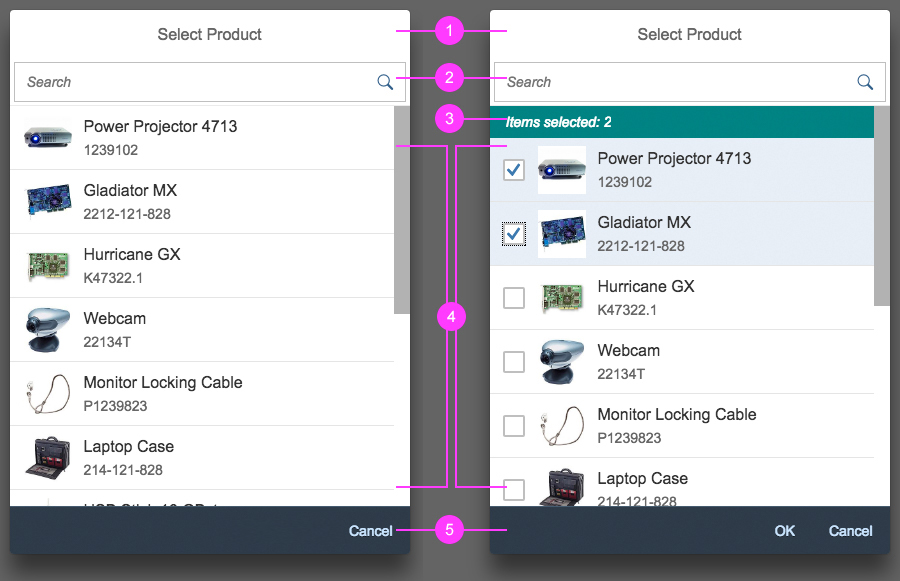
Dialog Header
You need to set the title of the dialog header (1). We recommend the following form:
Single selection
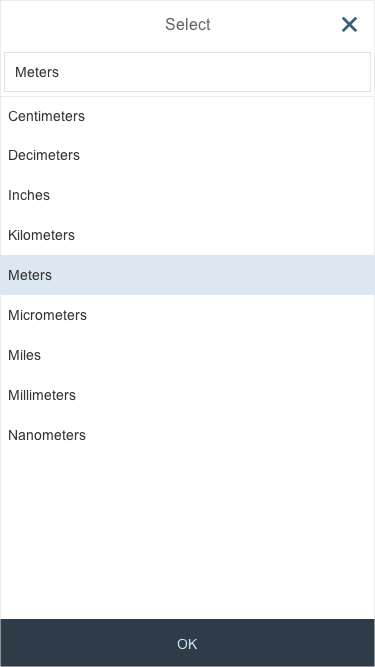
Select
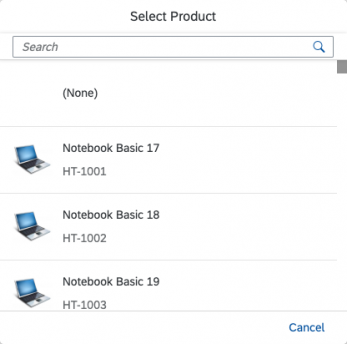
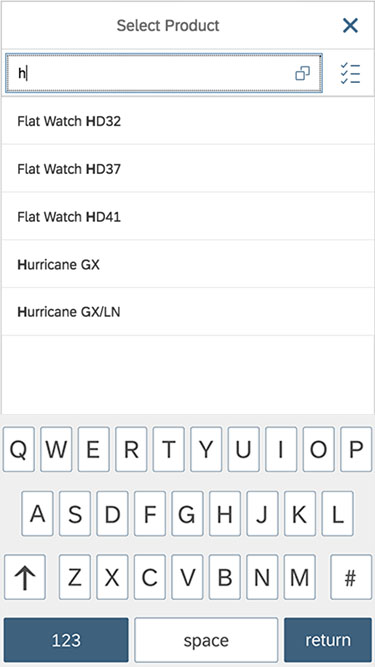
Example: Select Product
Multi-selection
Select
Example: Select Products
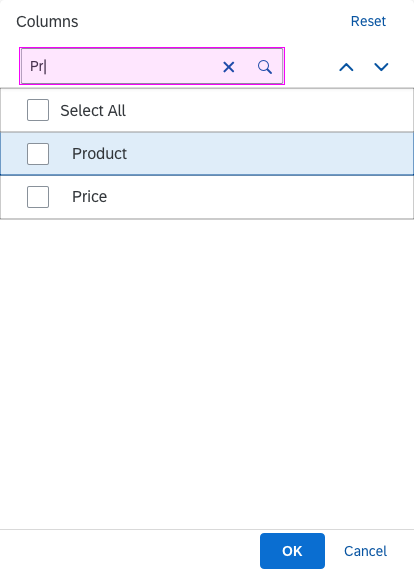
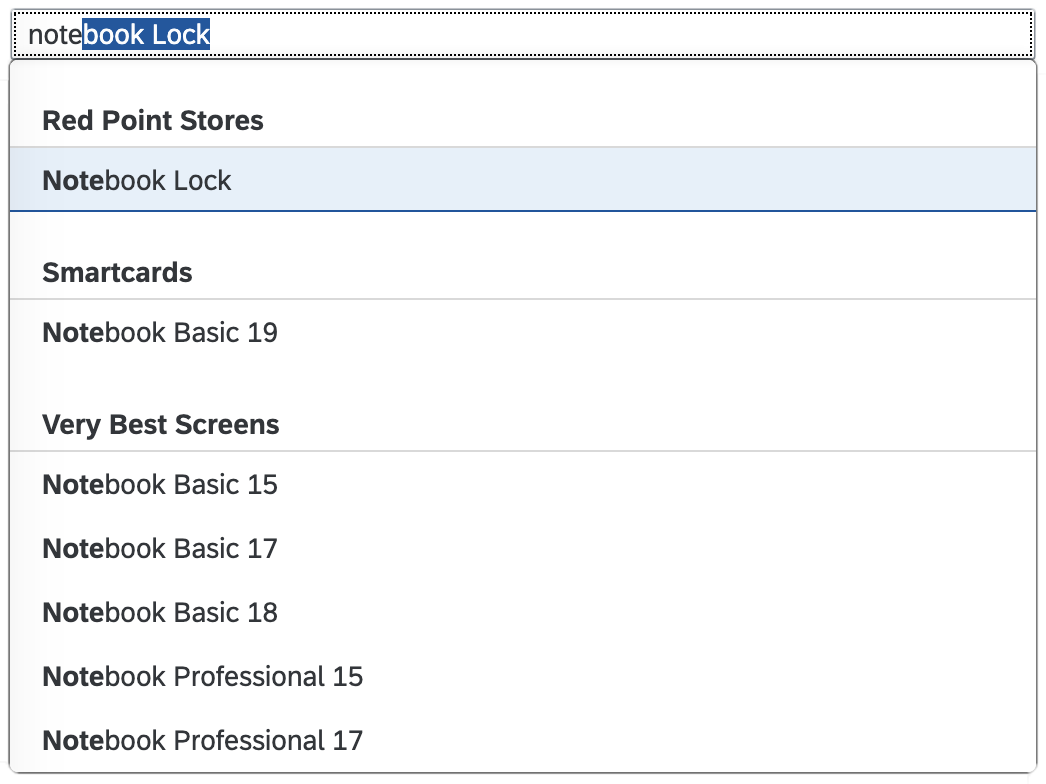
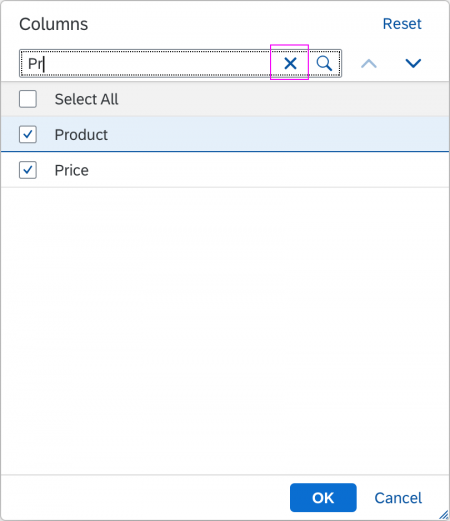
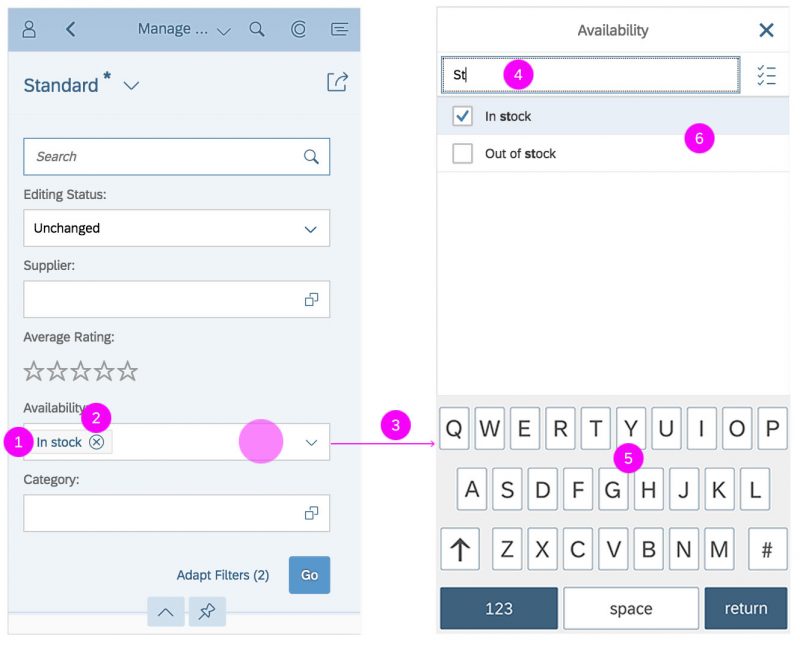
Search
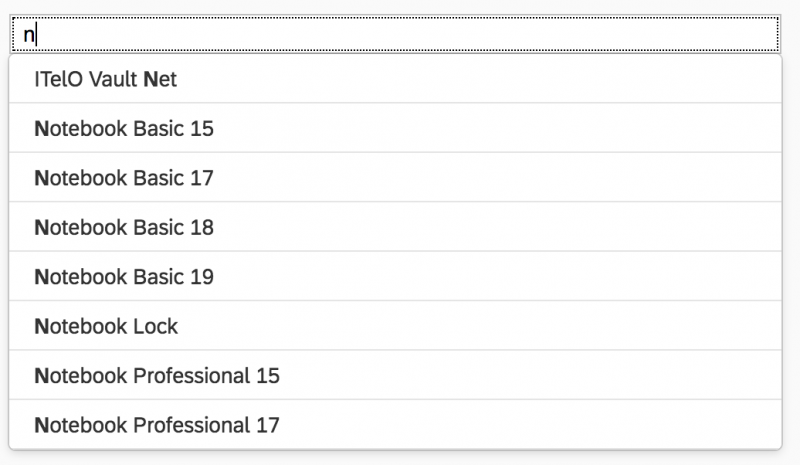
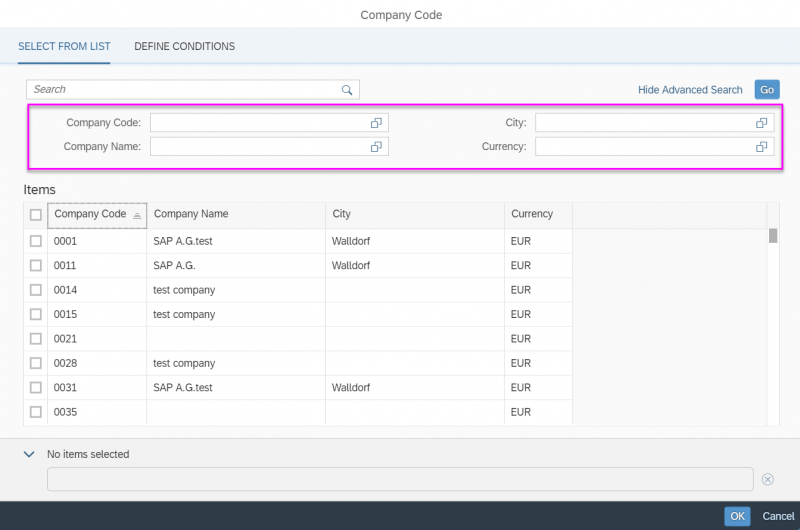
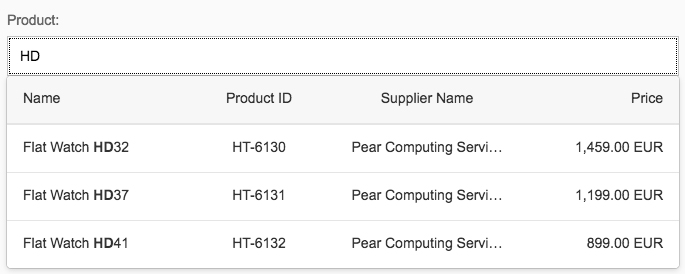
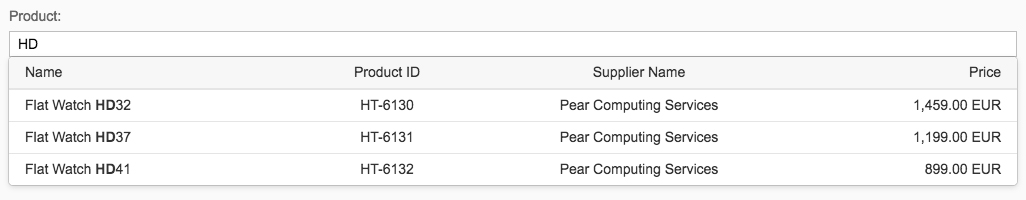
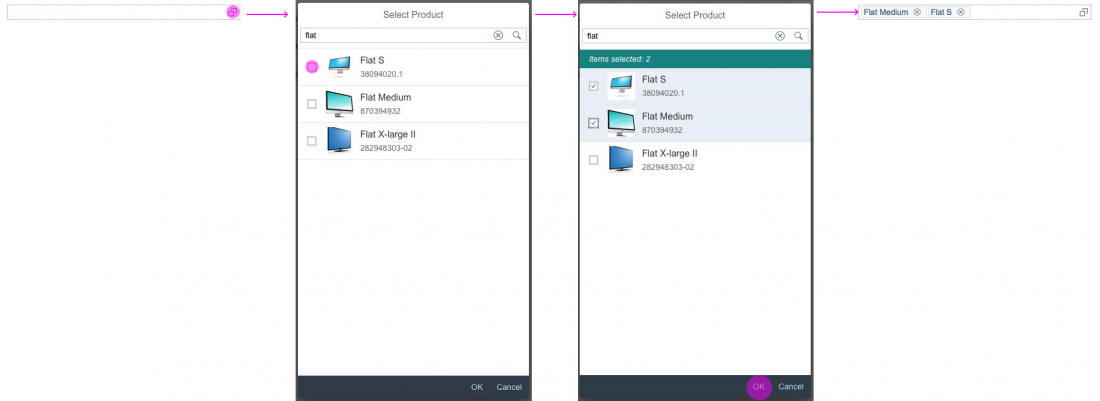
The first element in the dialog is a standard search field (2).
Info Toolbar
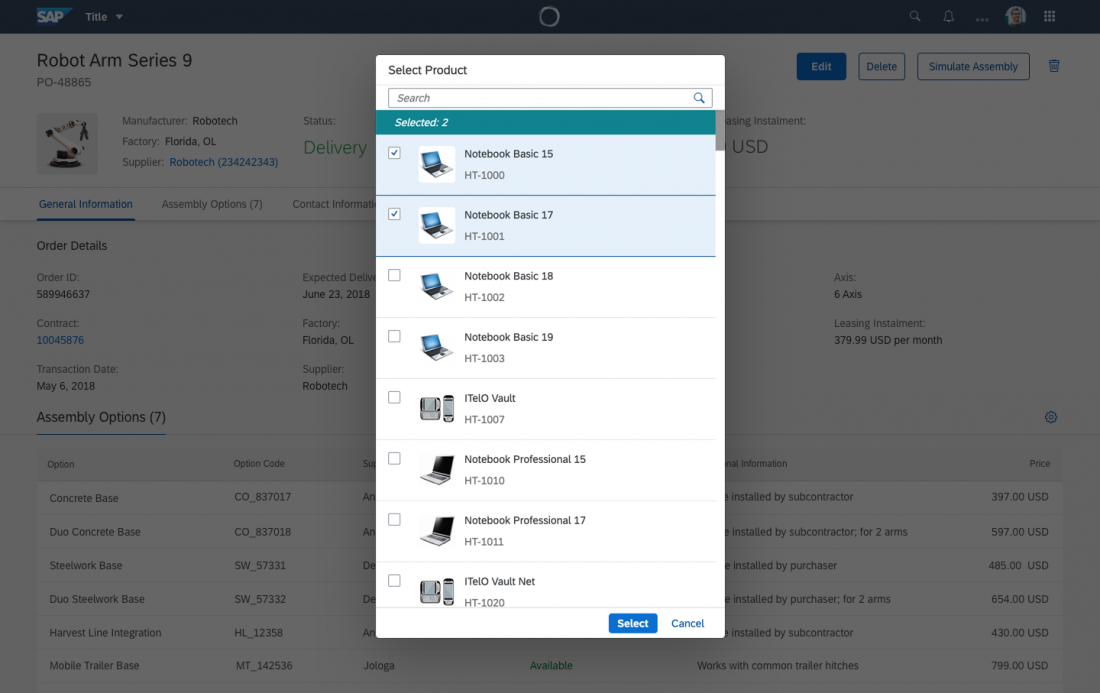
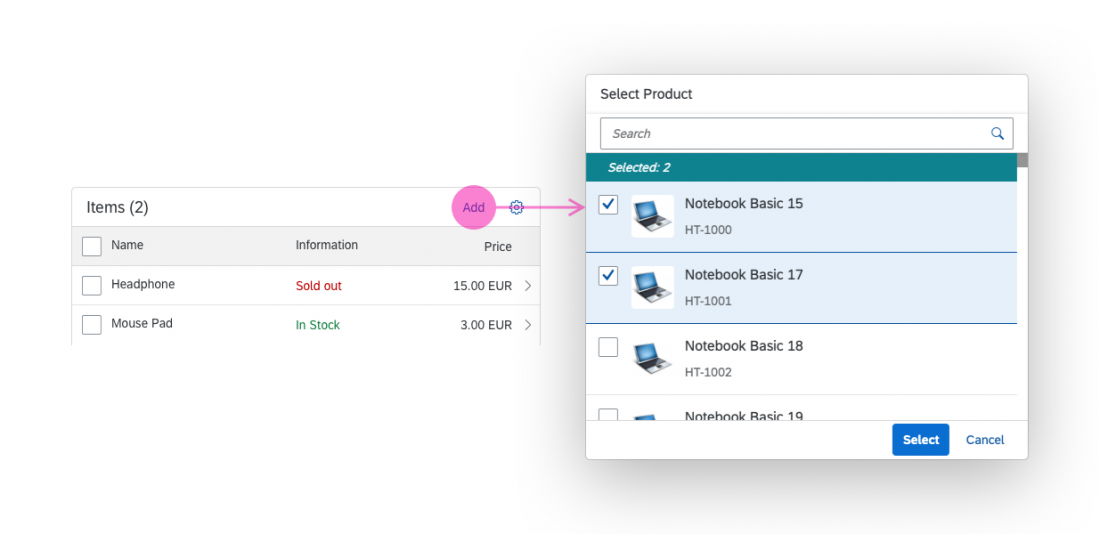
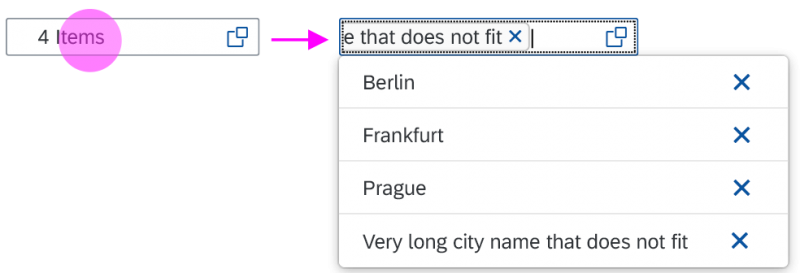
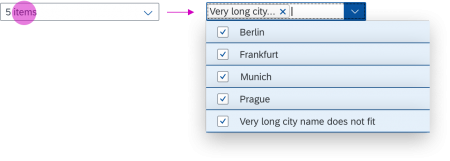
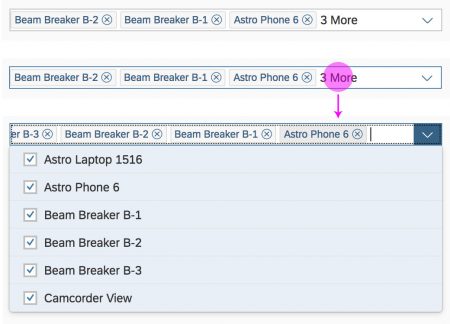
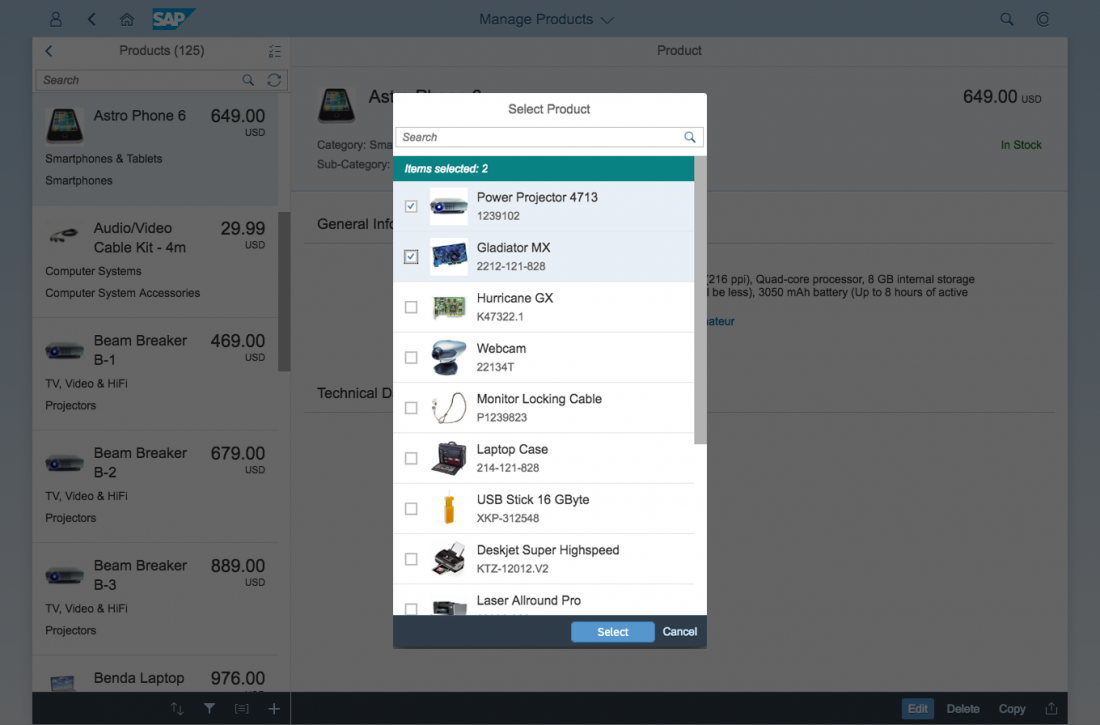
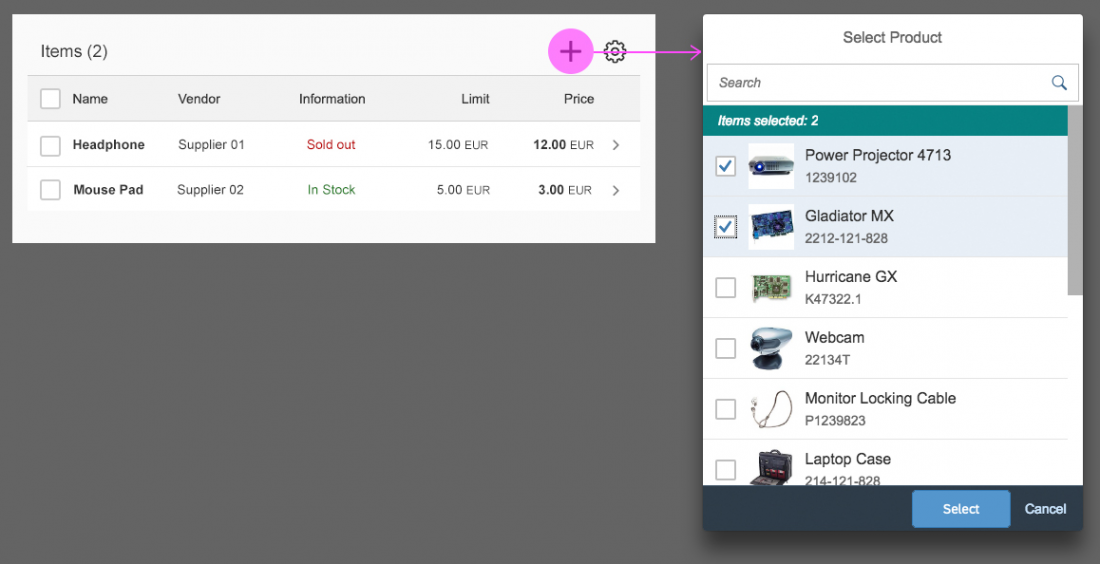
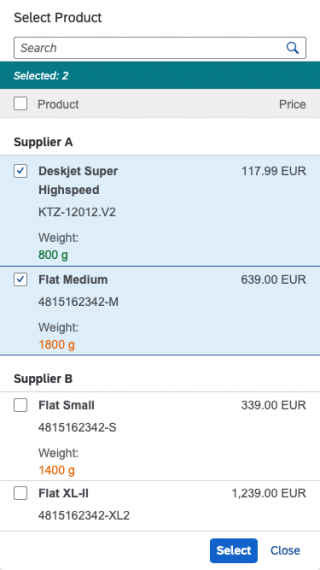
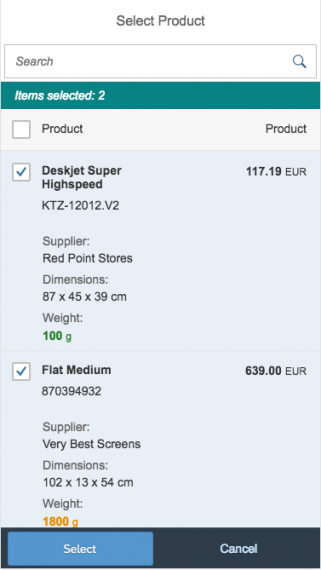
The info toolbar (3) is only available in multi-selection mode. It shows the number of selected items in the following form:
Selected :
Example: Selected Products: 2
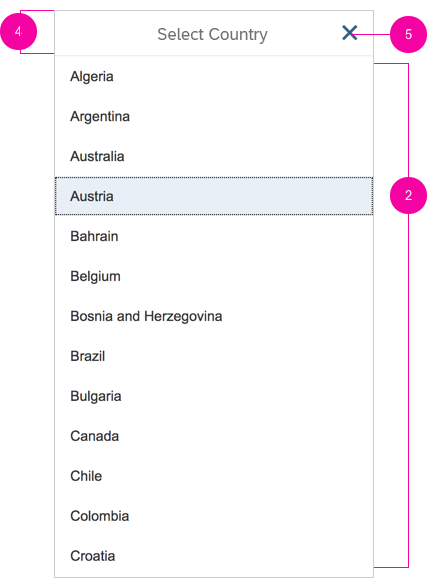
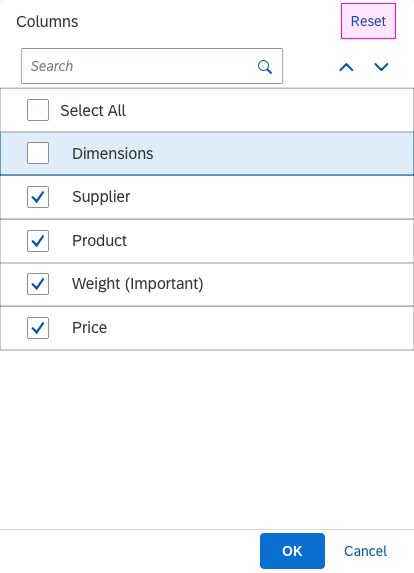
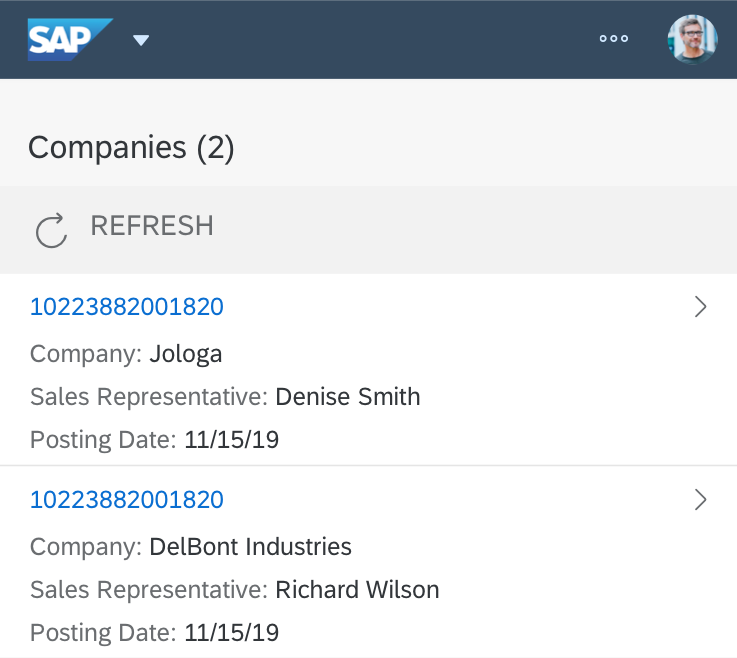
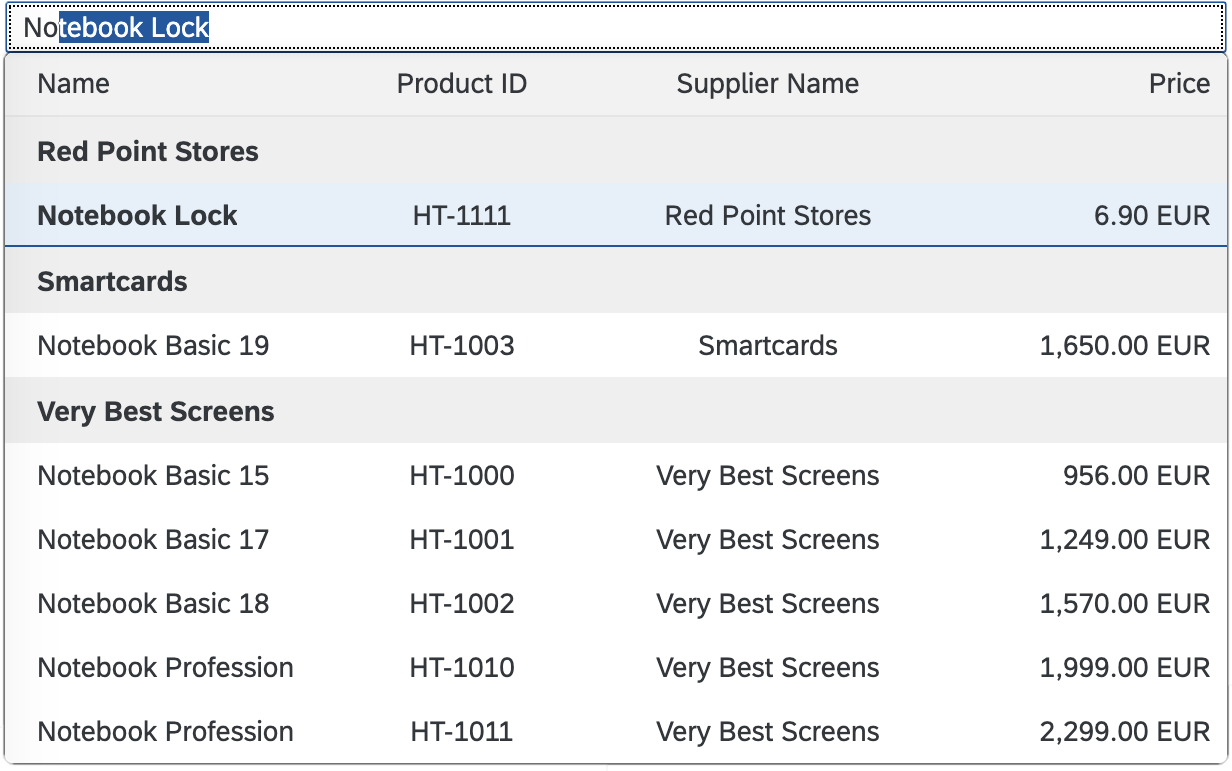
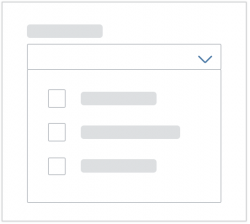
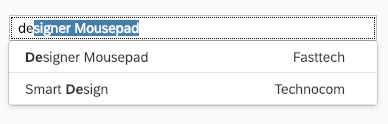
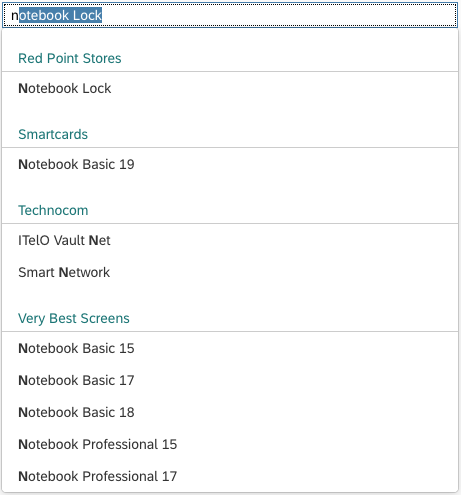
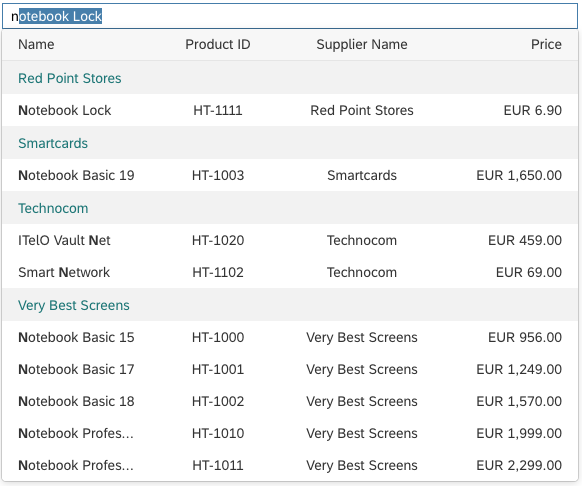
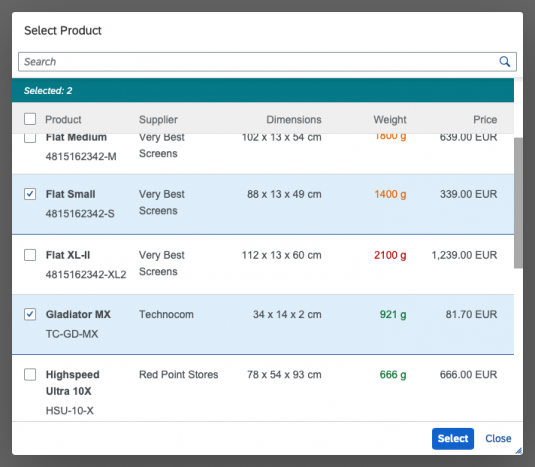
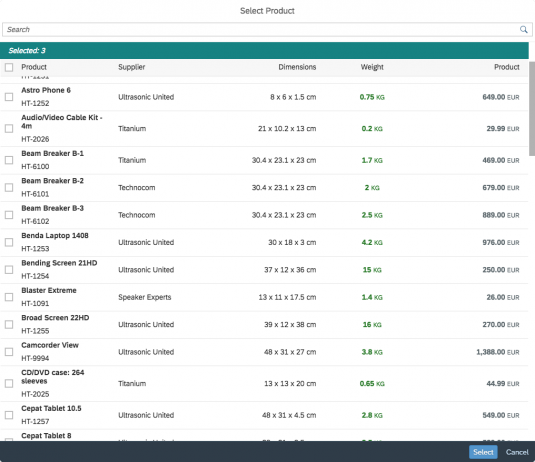
Content
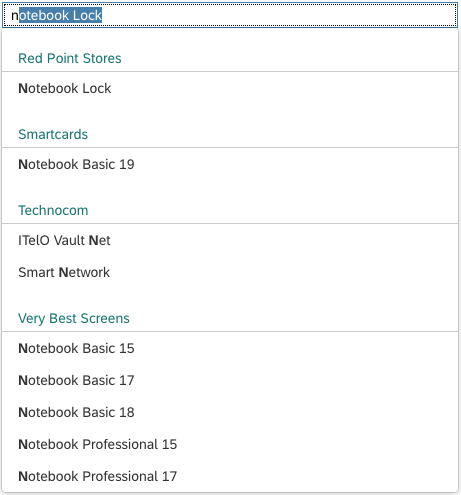
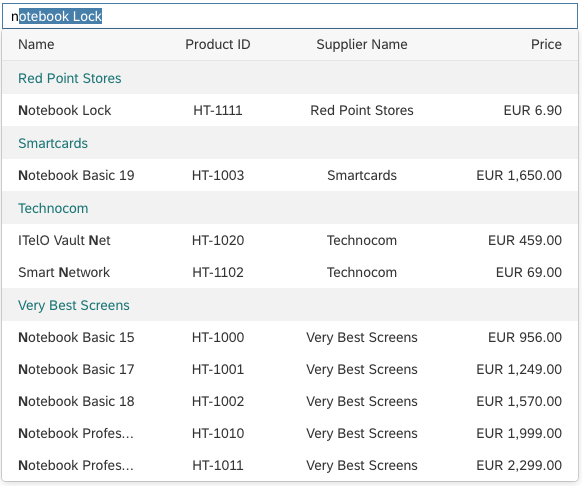
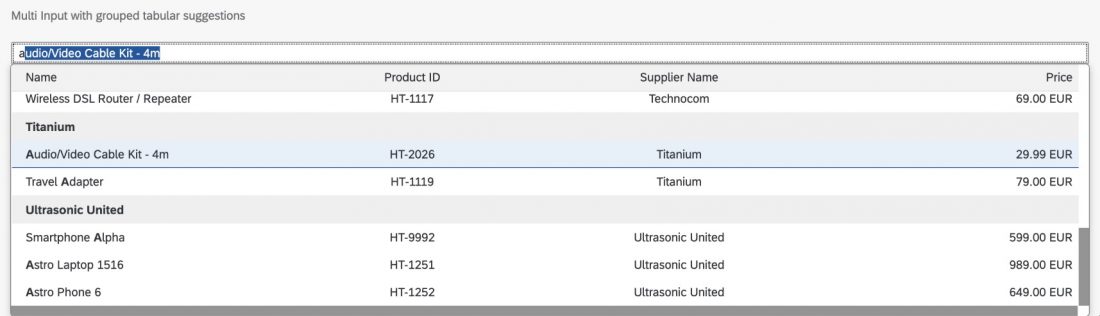
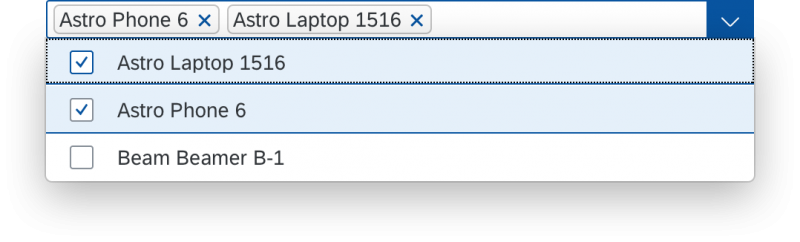
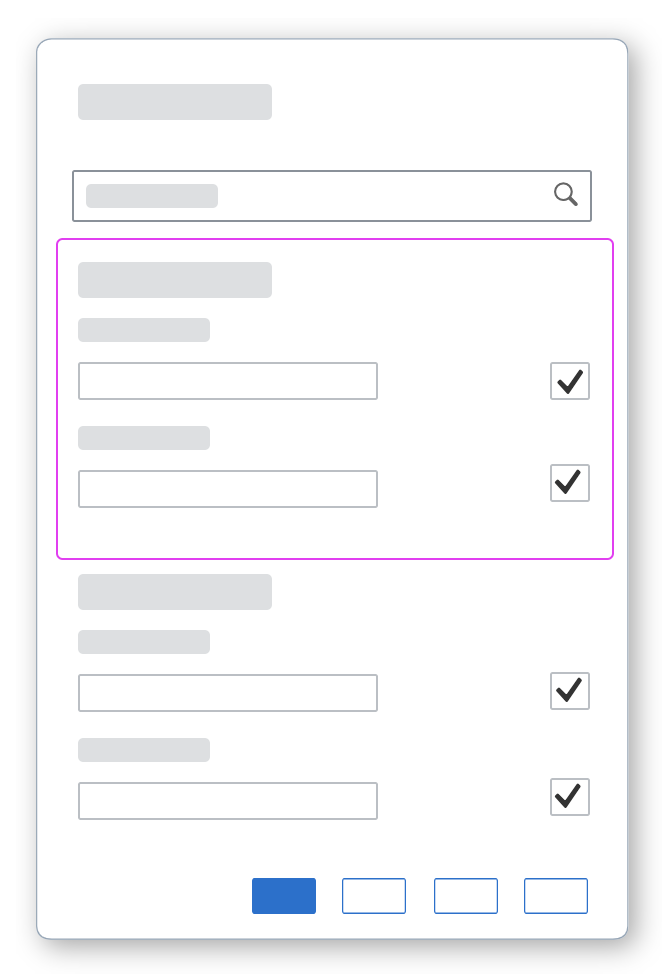
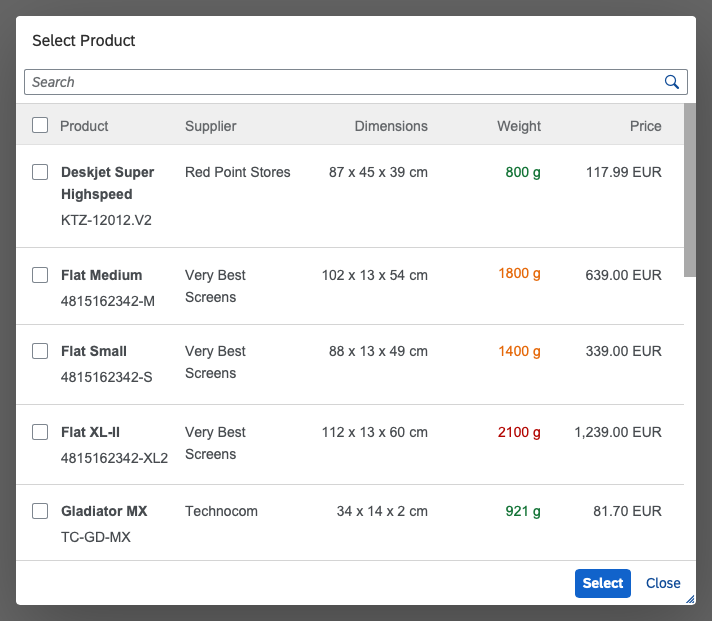
The content area (4) can be filled with any list content inherited from the list item base, such as standard list items, display list items, and feed list items. You can set the content to be displayed as grouped.
Button Toolbar
Behavior and Interaction
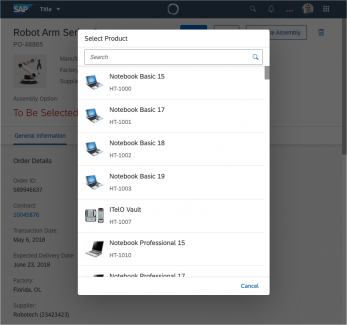
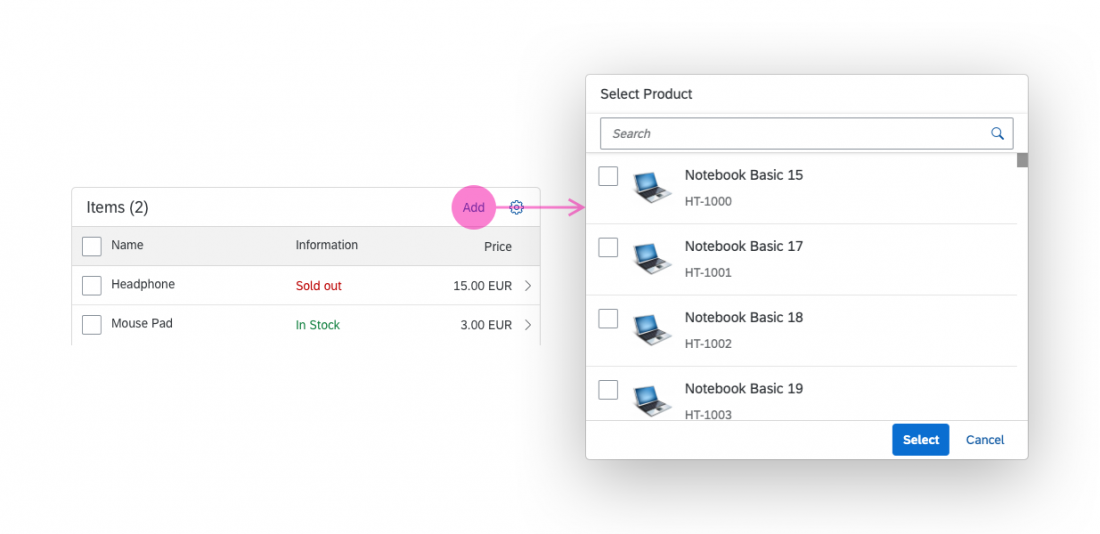
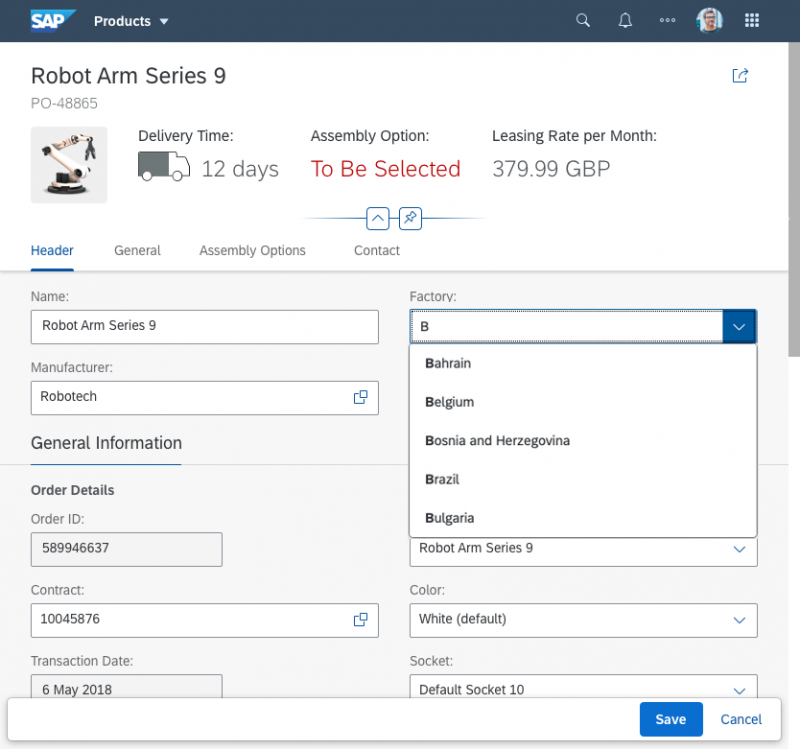
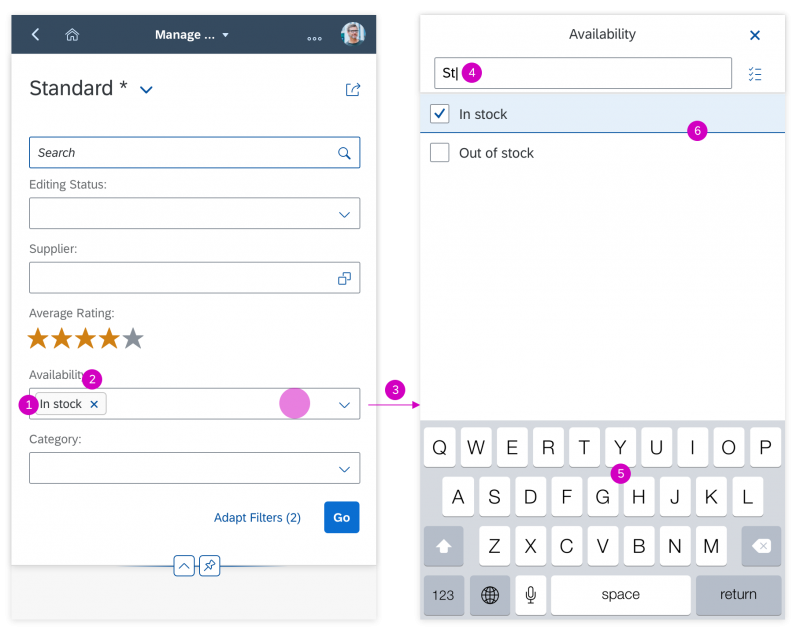
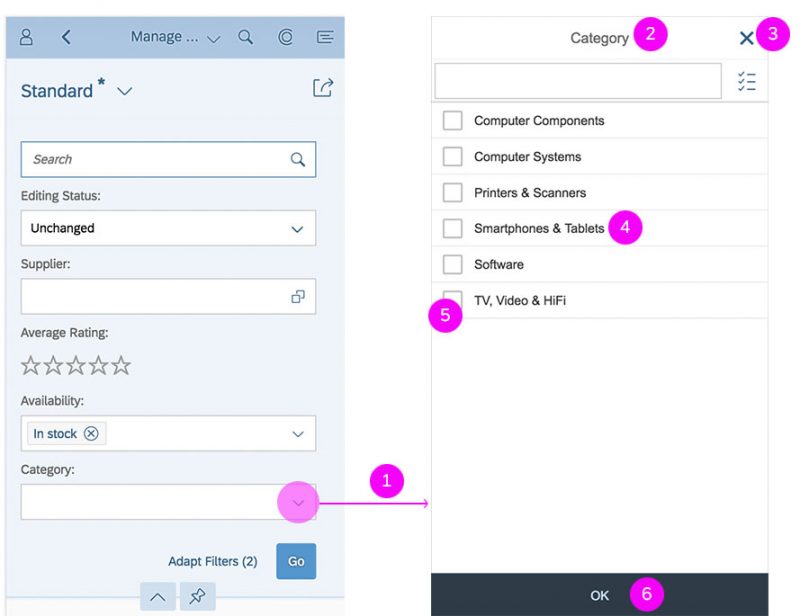
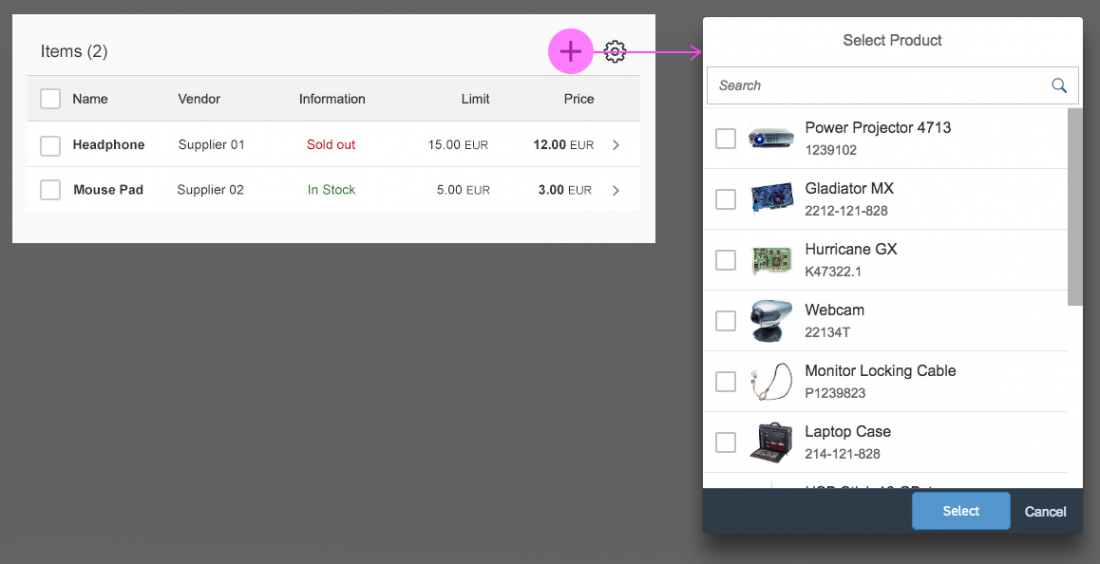
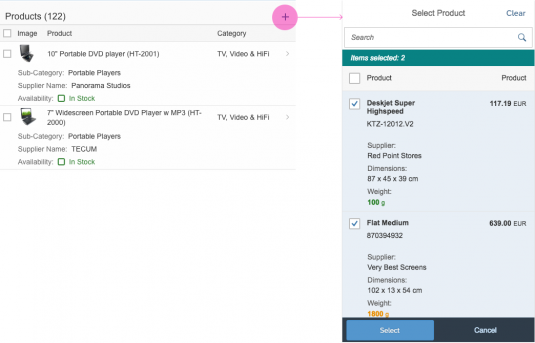
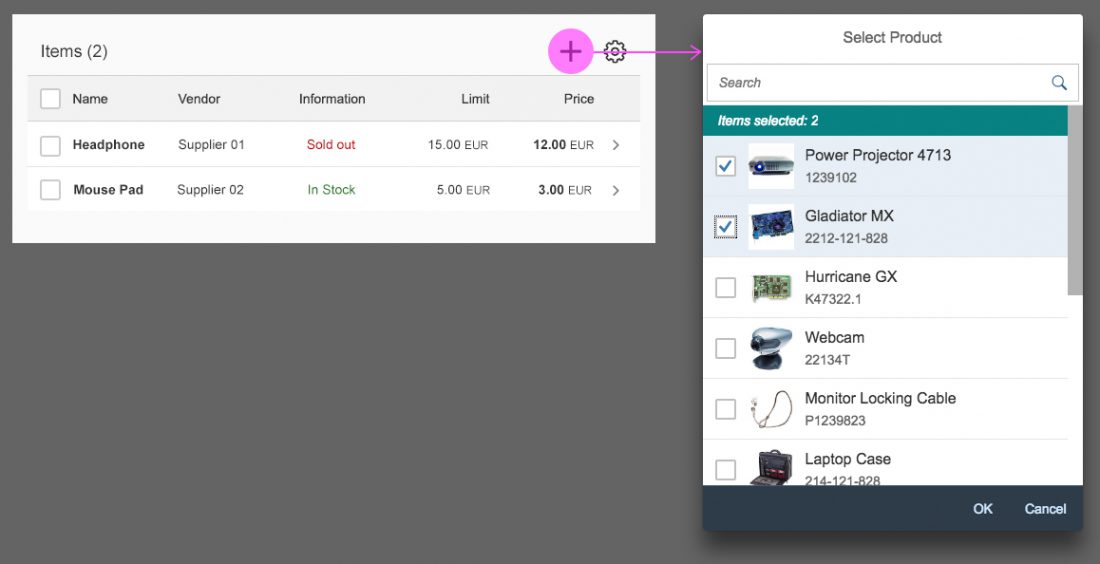
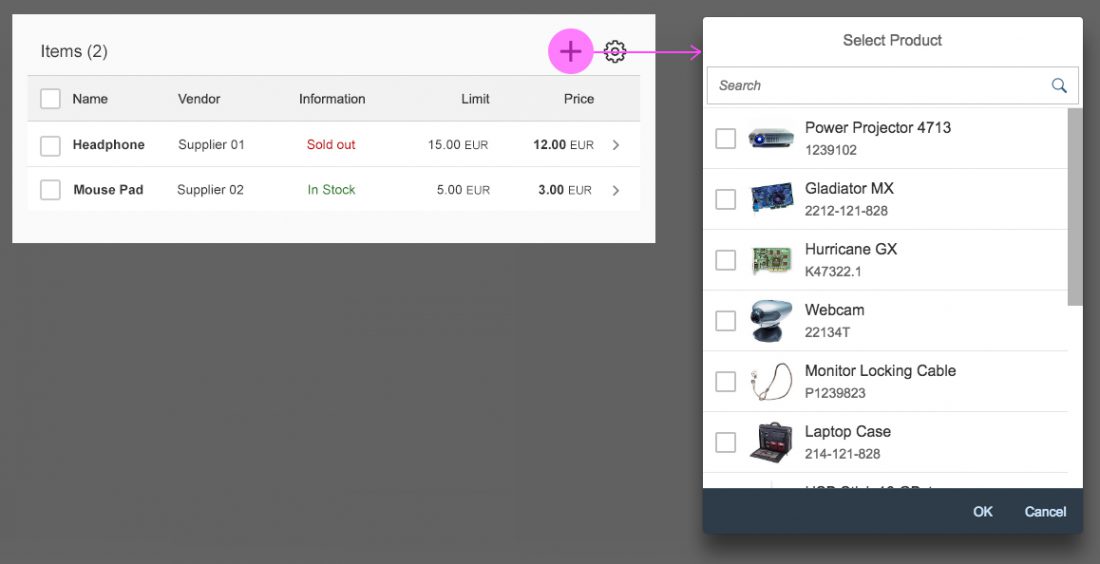
The select dialog can be called up from any control. The most common trigger is an input field with selection icon, also known as a “value help field”, or F4. Alternative triggers are buttons or icons, which add items to an existing list or the infobar in the master list in order to apply a contextual filter.
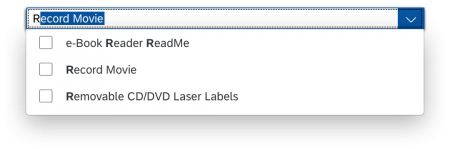
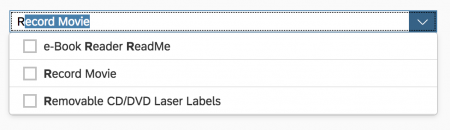
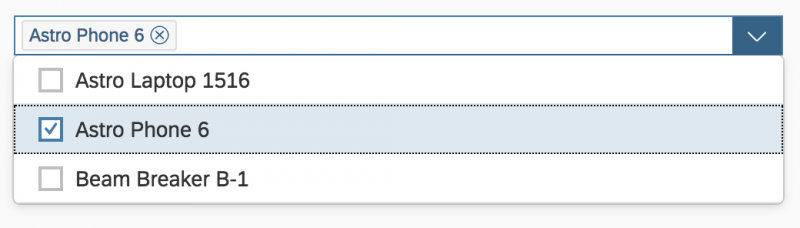
Single Select
Once users select an entry, the select dialog is closed and the selected entry is taken over. If applicable, the entry is displayed in the field from which the dialog was triggered.
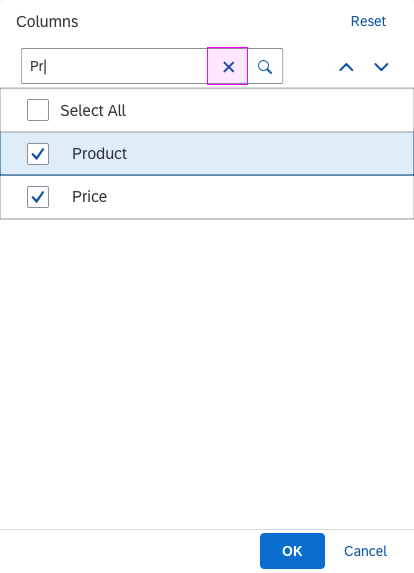
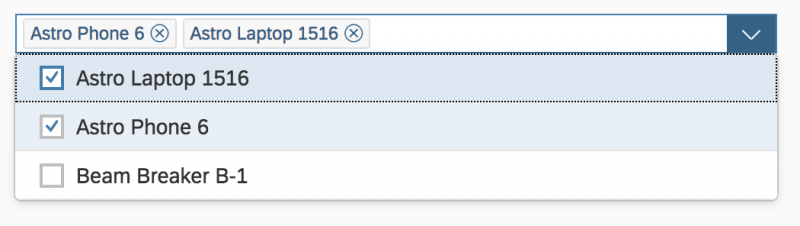
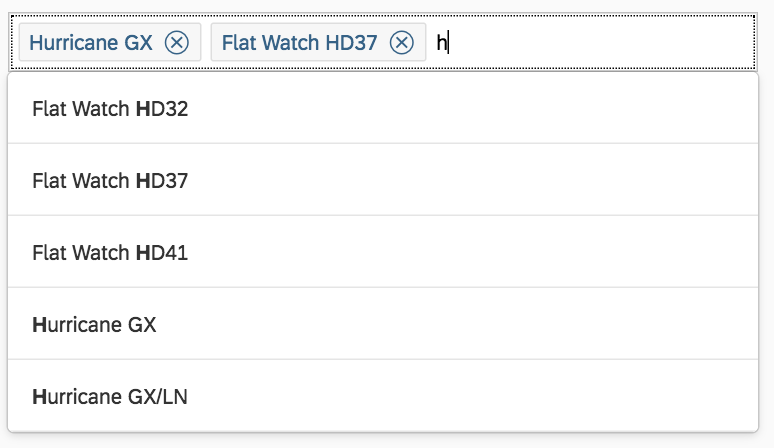
Multi-Select
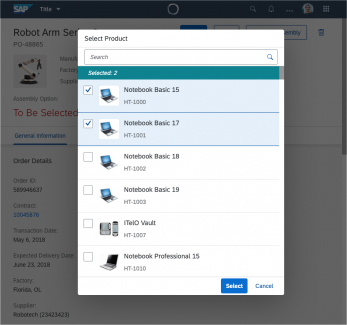
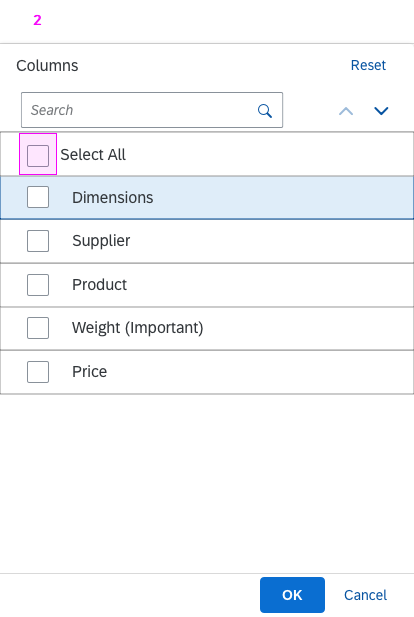
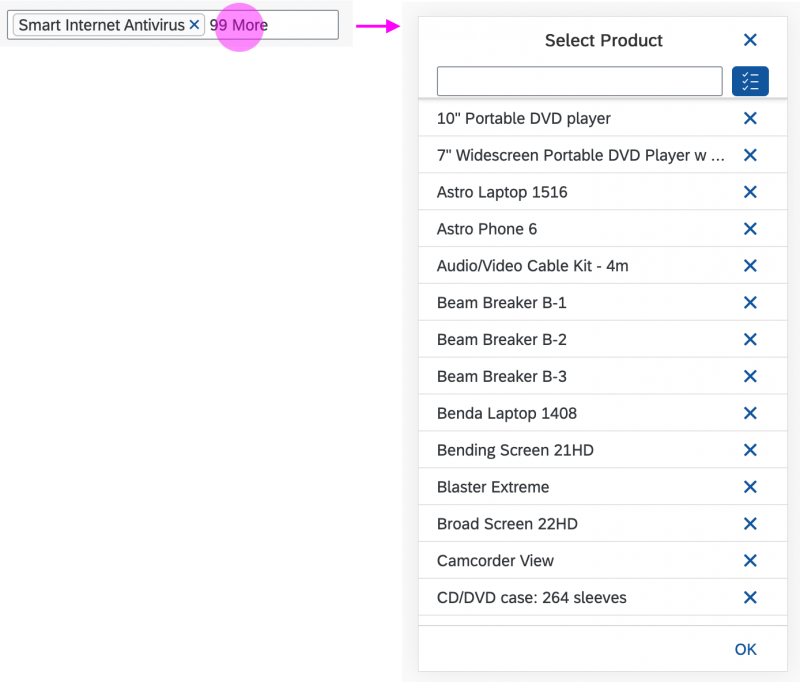
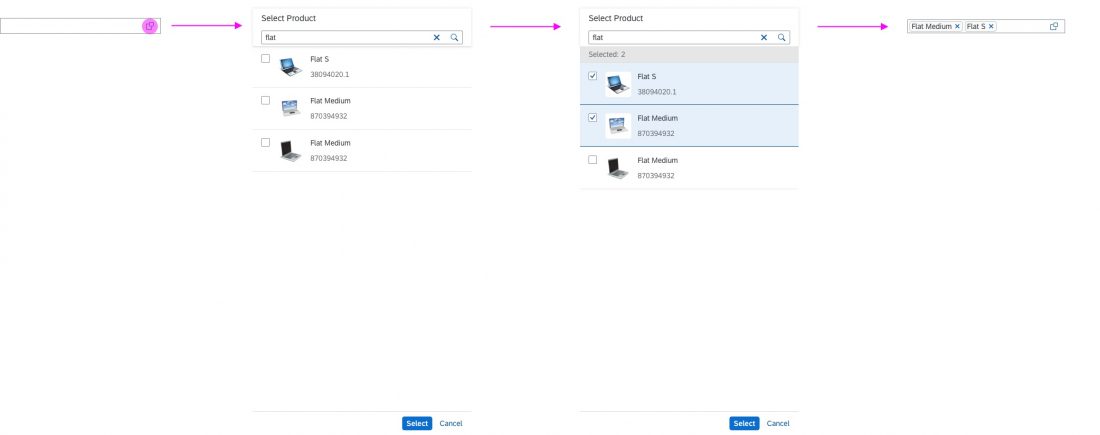
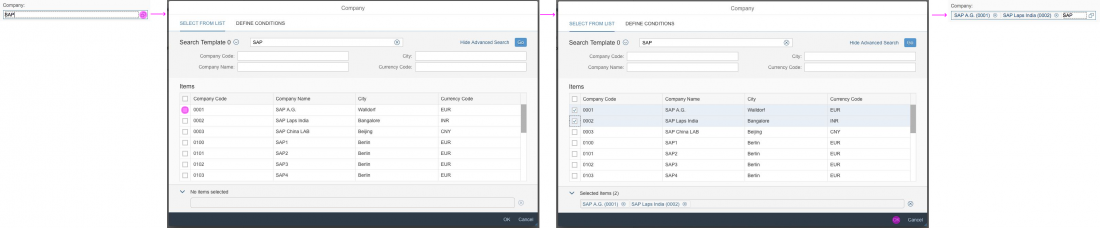
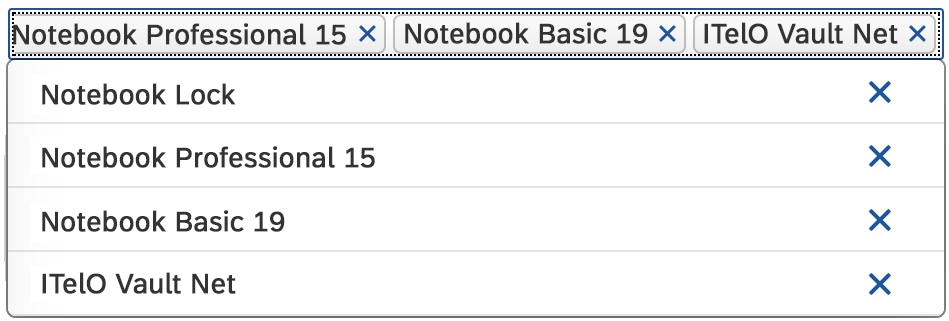
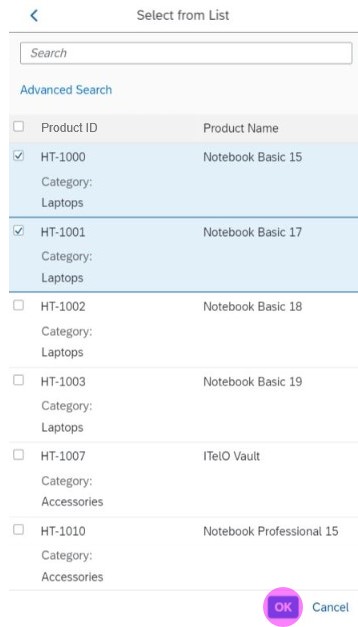
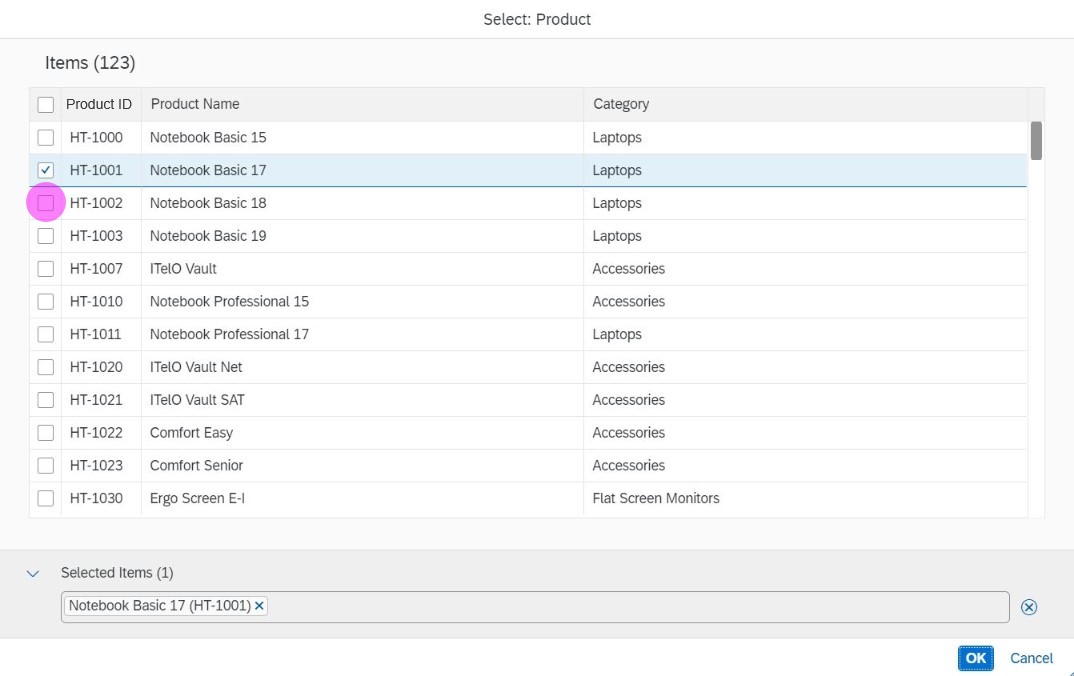
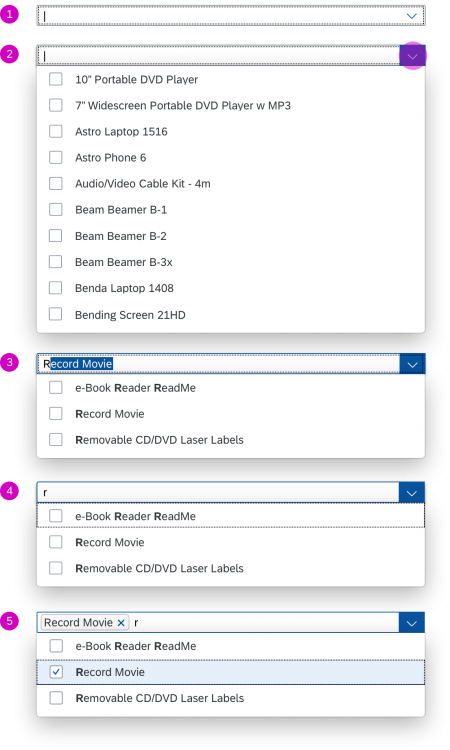
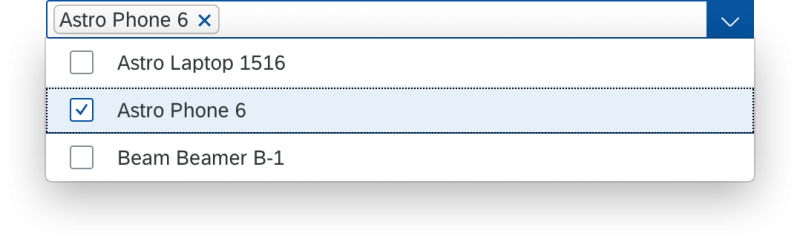
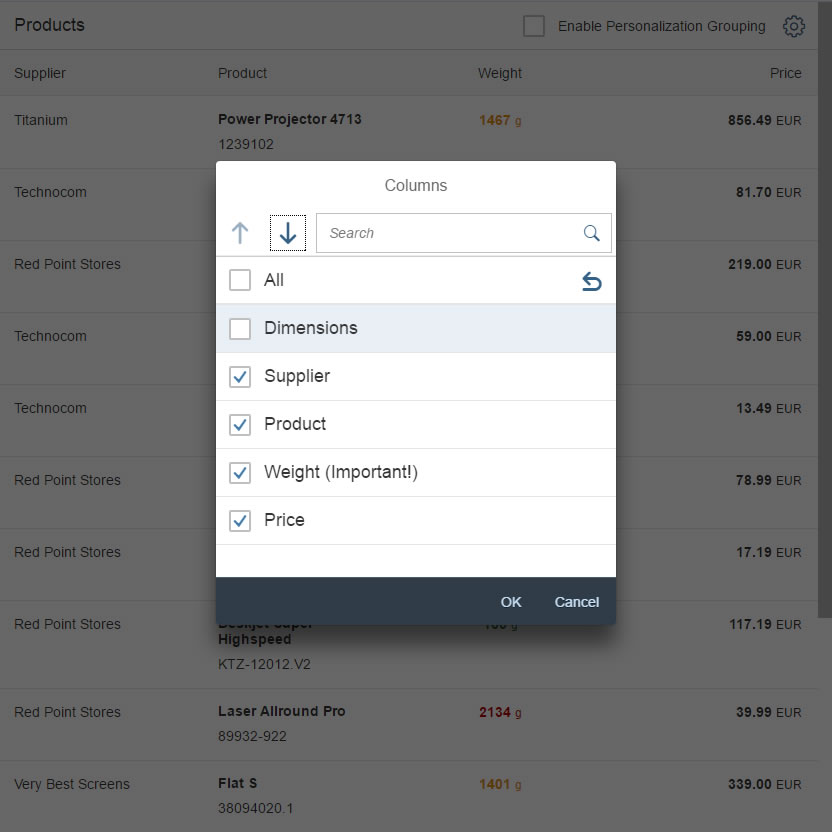
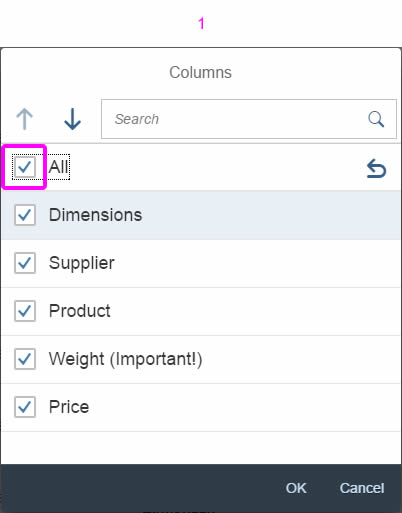
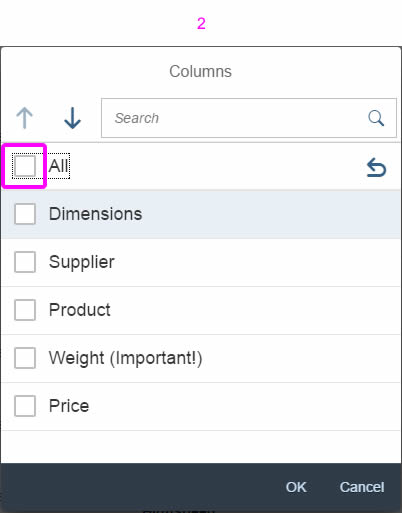
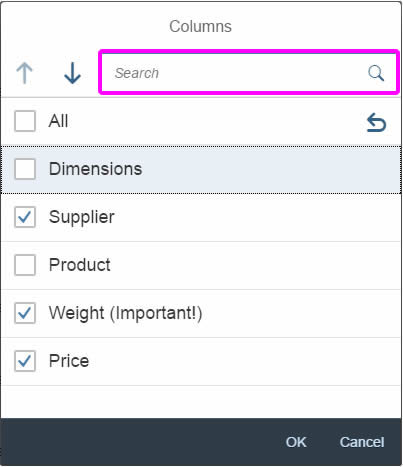
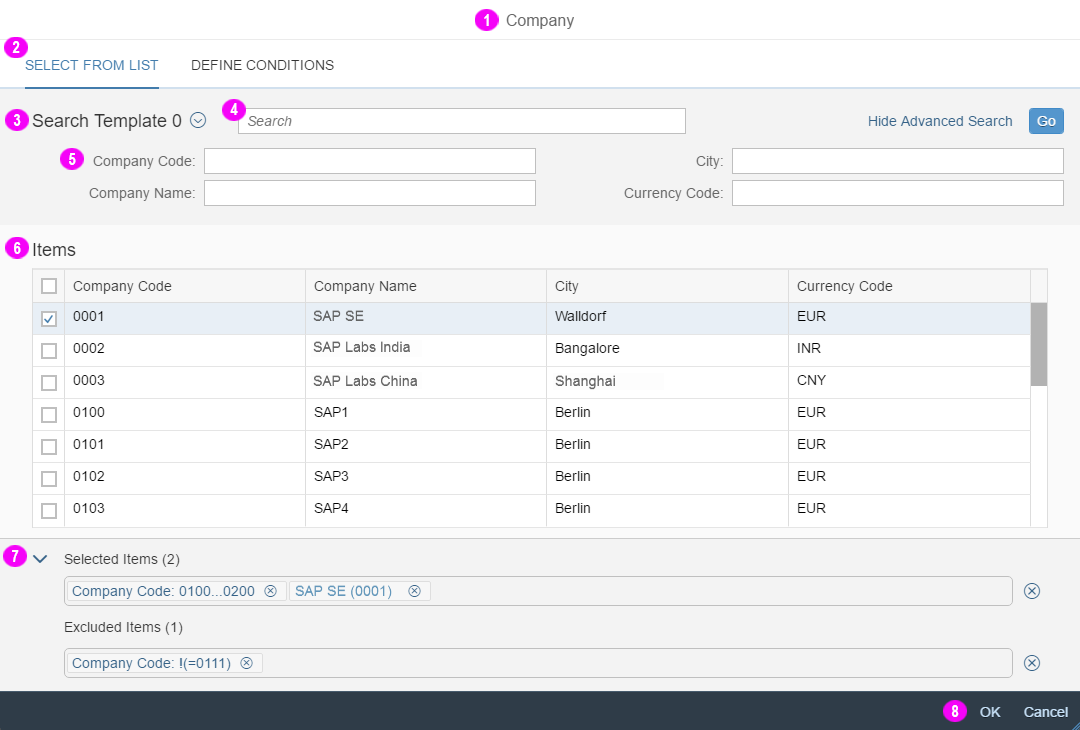
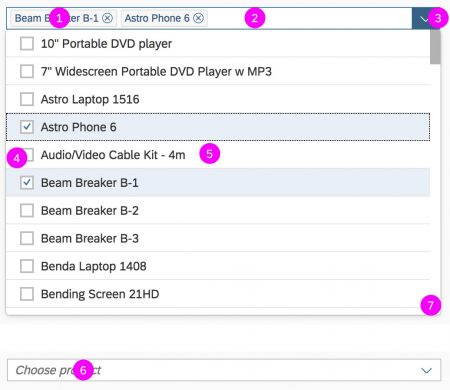
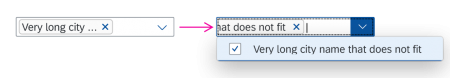
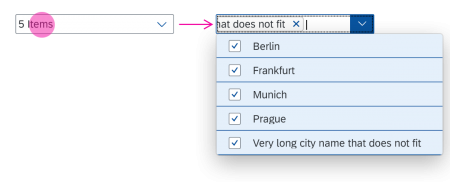
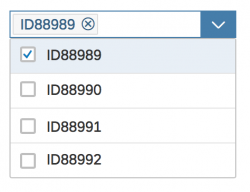
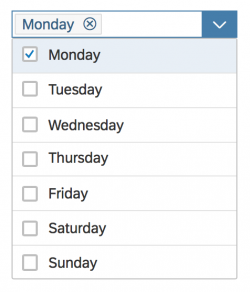
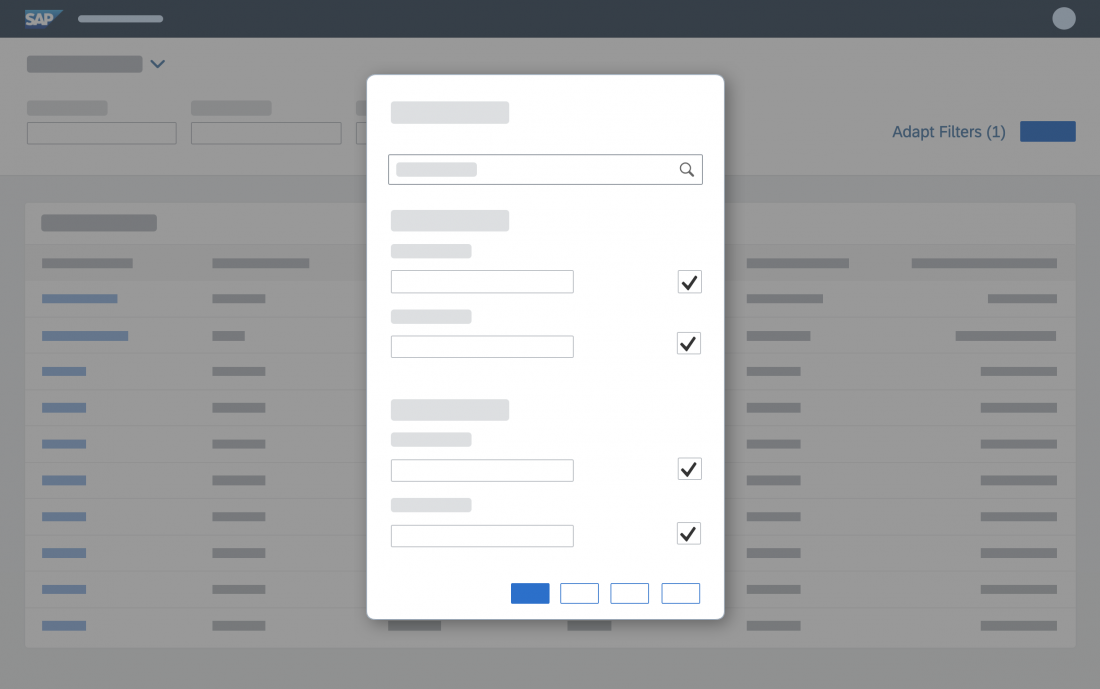
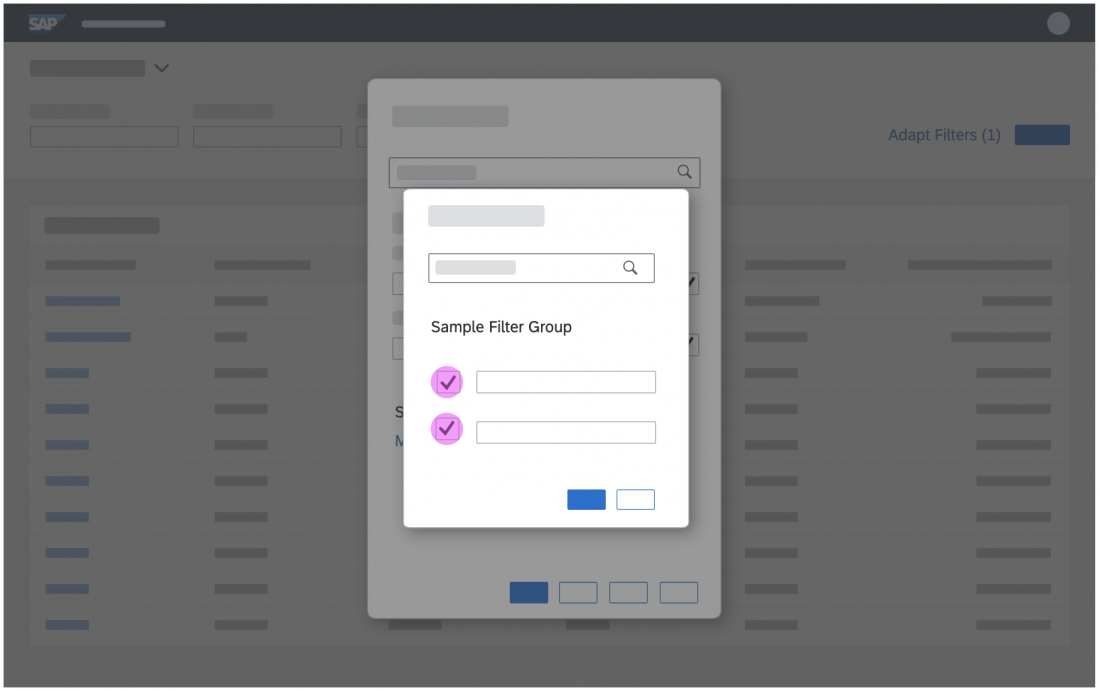
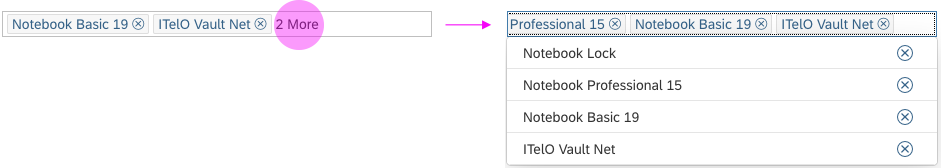
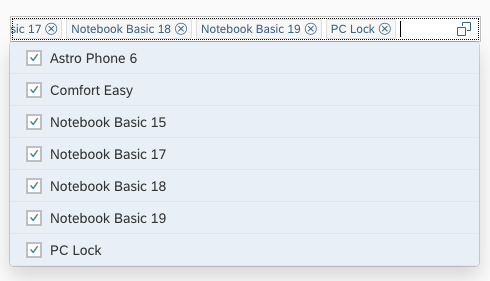
In the multi-select version of the select dialog, checkboxes are provided for choosing multiple entries. The selection is taken over when the user closes the dialog via OK. Cancel closes the dialog without taking over the selected values. An infobar indicates the number of selected items.
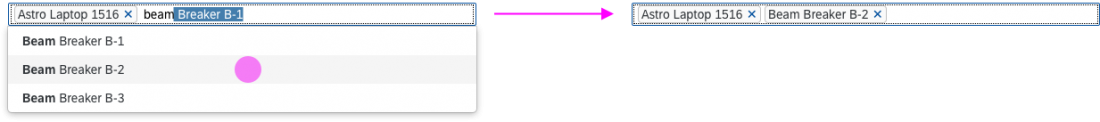
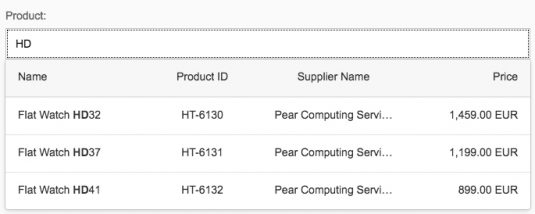
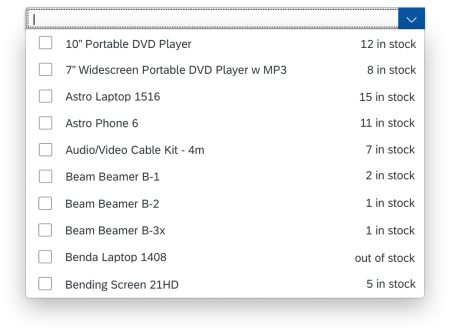
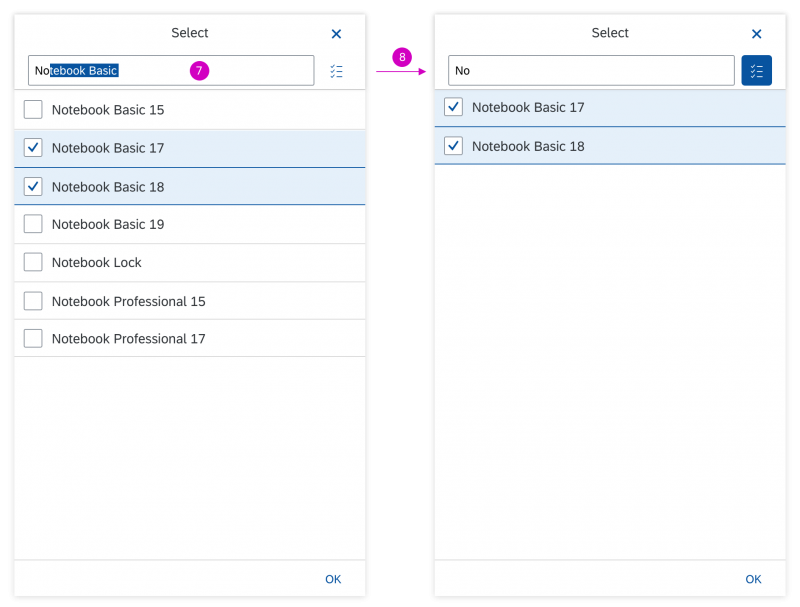
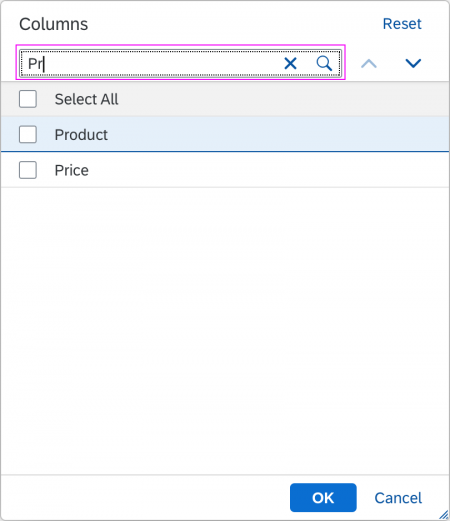
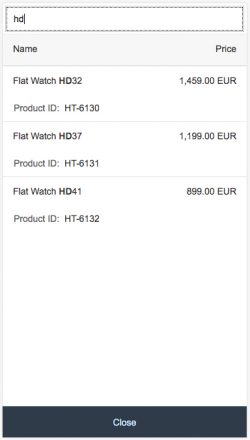
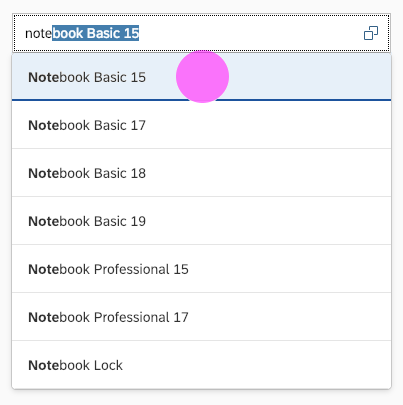
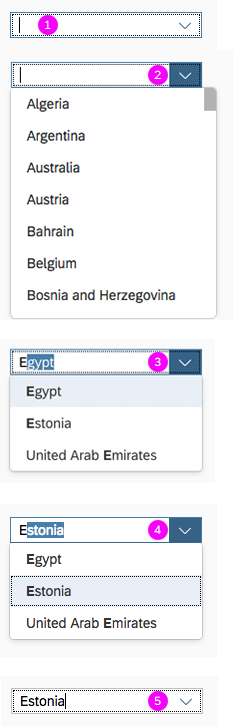
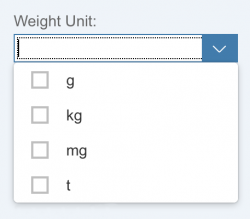
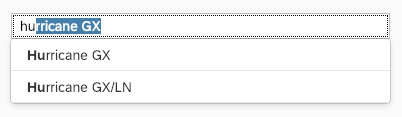
Search
The user can search items.
Resize and Drag Dialog
You can make the select dialog resizable and draggable by setting the corresponding properties (also called resizable and draggable) to “true”.
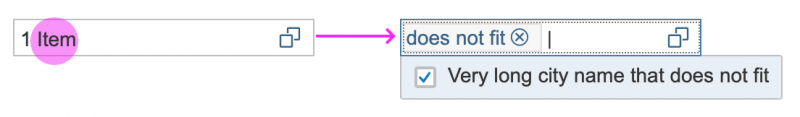
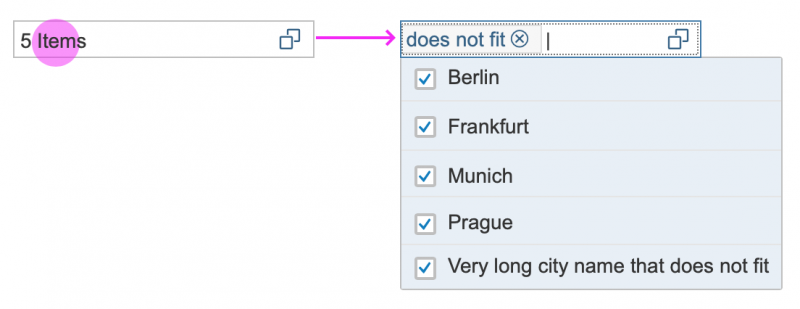
A resizable dialog makes sense if the items inside have long names or descriptions.
A draggable dialog allows users to see the app content behind the dialog.
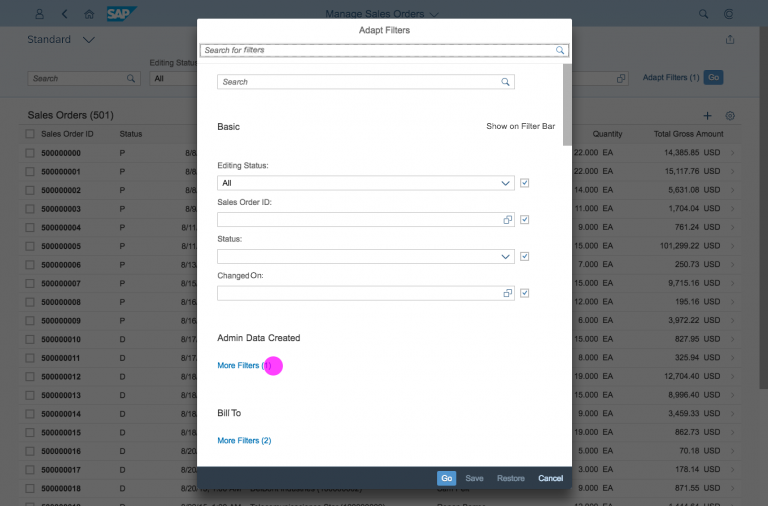
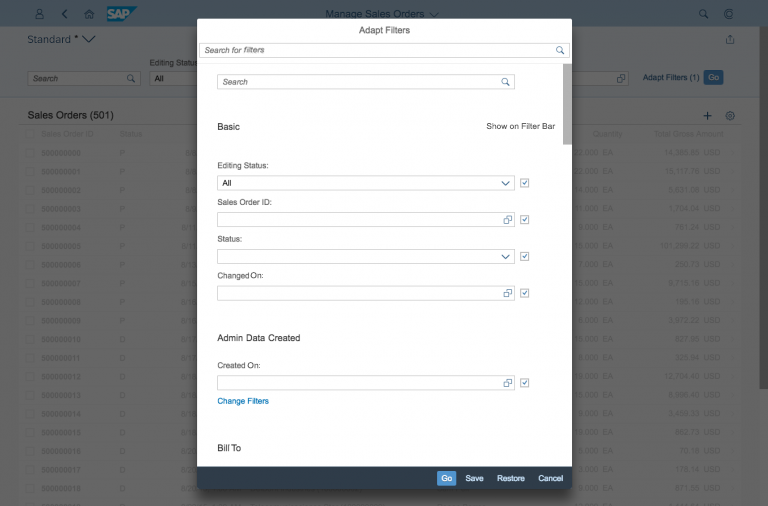
Guidelines
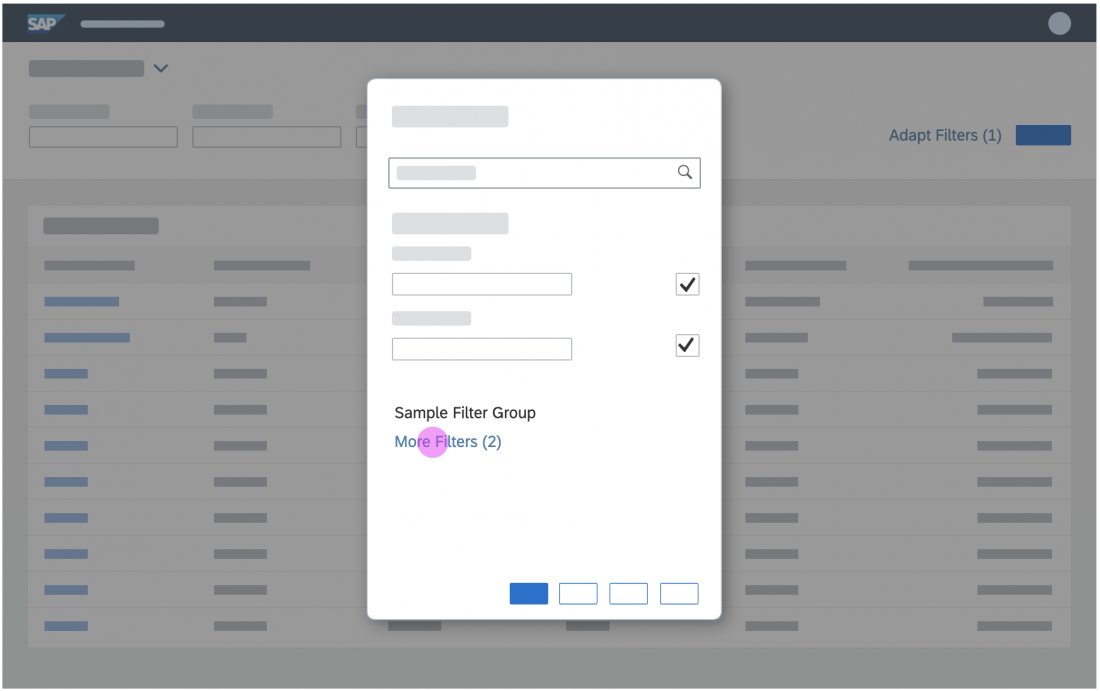
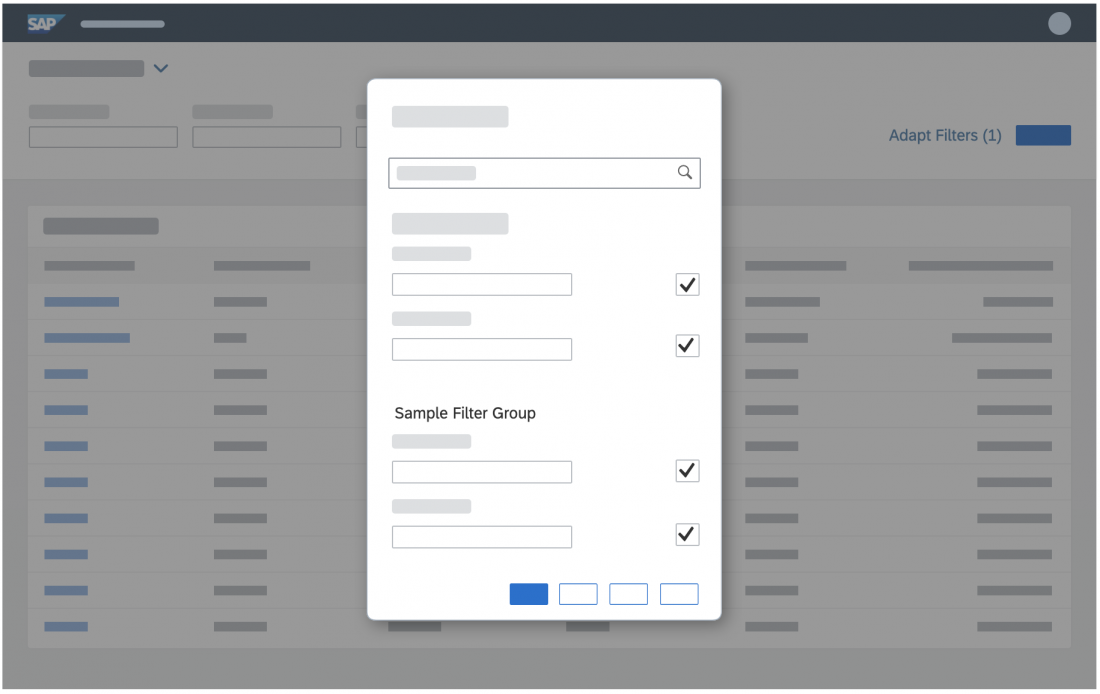
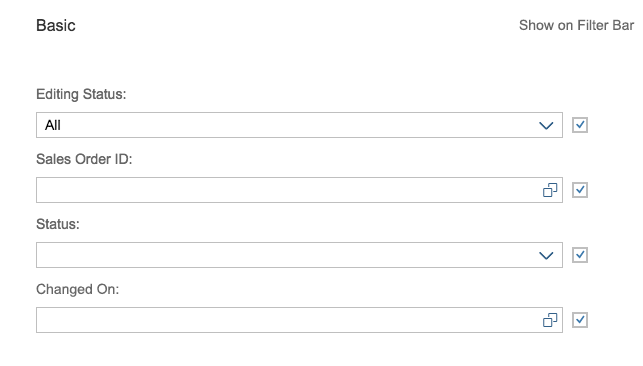
List Options
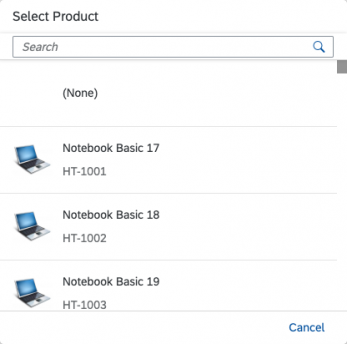
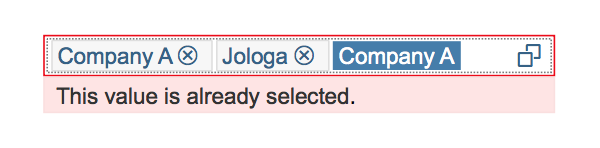
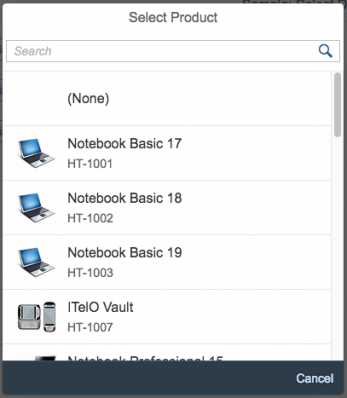
If you need to indicate that none of the selection options are selected, or you need to allow the user not to select an option, provide (None) as an option and place it at the beginning of the list.
If you need to indicate that all items apply (for example, as a list filter), provide All as an option and place it at the beginning of the list.
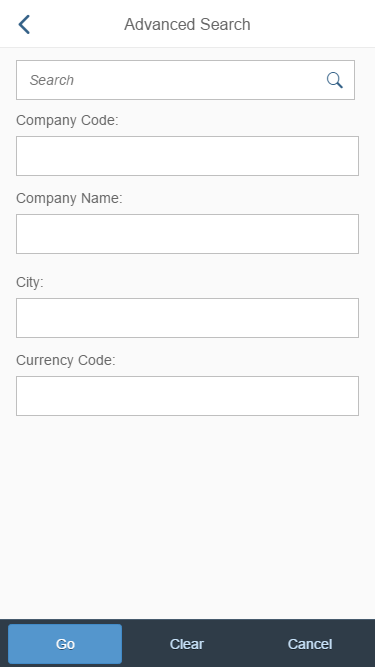
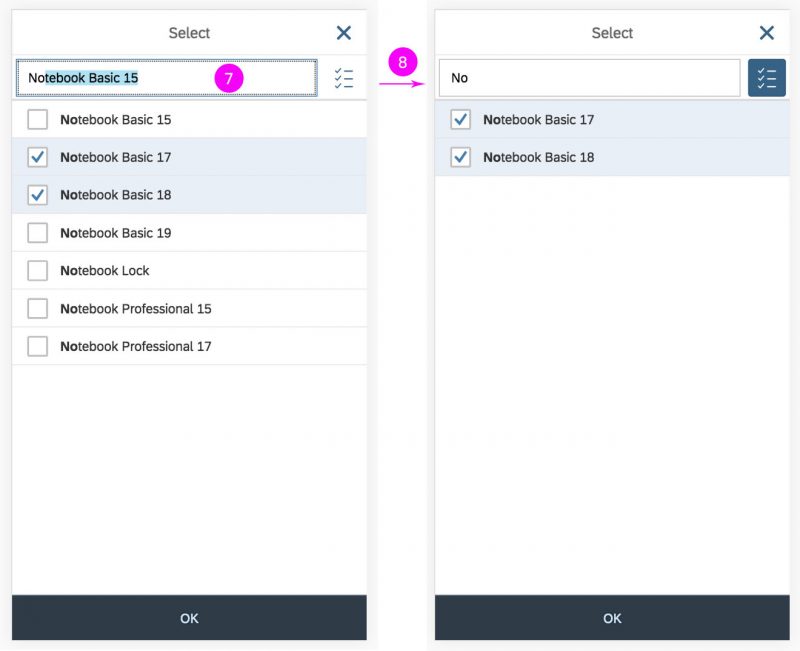
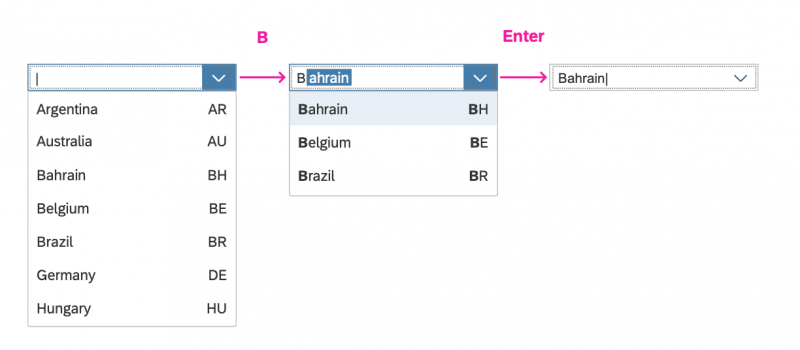
Search Behavior
Two types of search behavior are available:
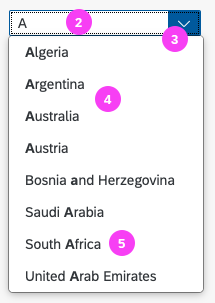
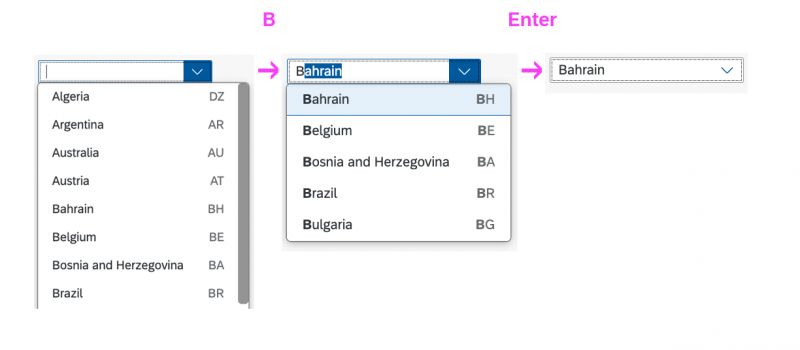
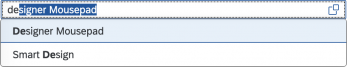
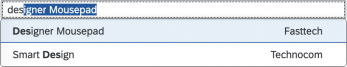
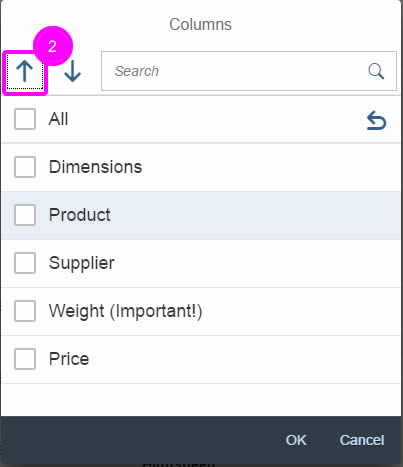
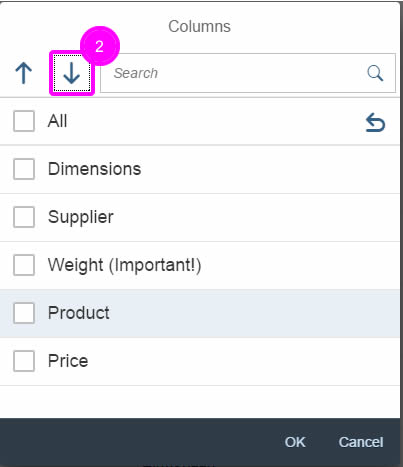
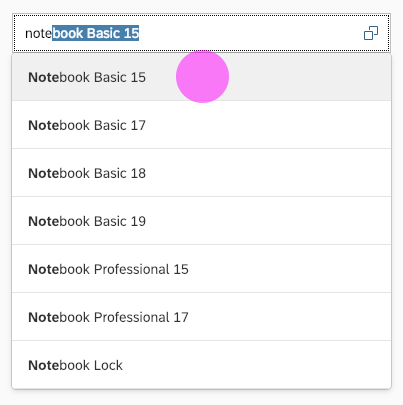
(1) A live search, also known as “search-as-you-type” (property: liveChange), which is triggered by each character that the user enters or deletes.
(2) A manual search, which is triggered explicitly after the user enters text in the search field and clicks the Search icon or presses the ENTER key.
Although app developers need to decide themselves which search to use, we recommend implementing the live search whenever possible. Use the manual search only if the amount of data is too large and your app would otherwise run into performance issues. For more information, check out the article on search.
Reset/Remember Selections
By default, the selection is reset when the dialog is closed. This allows users to make a new selection when they reopen the dialog and makes sense when users need to add multiple items to a table.
However, if your use case requires selections in a dialog to be remembered so that the user can make corrections, you can set the rememberSelections function in the select dialog to “true”. When users exit the dialog by clicking Cancel, the selection is then restored to the state it was in when the dialog was opened.
This also works in single-select dialogs. There, if users click the remembered item again, the dialog closes and they do not have to explicitly click Cancel.
Infobar
In multi-selection mode, an infobar shows the number of selected items. Use the following format:
Selected: [Number of selected items]
Example: Selected: 2
Note that the infobar is not “sticky”. When the user scrolls down the list, the infobar scrolls off the screen.
Infobar States
The infobar has two states – active and non-active (non-clickable). For more information see Infobar States.
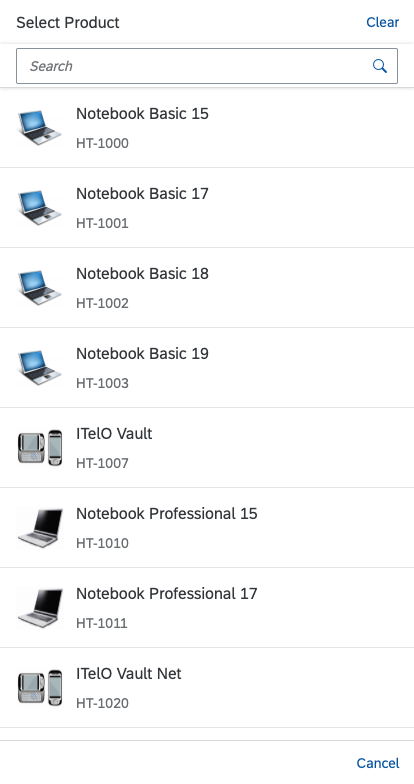
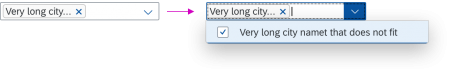
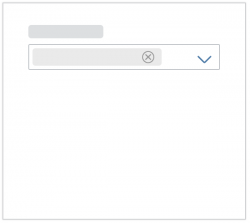
“Clear” Button
The Clear button allows users to clear all the selected items. By default, the button is not shown. To display the button, set the showClearButton property to “true”.
Content
By default, the select dialog comes with a growing feature (property: growing = “true”). We recommend disabling the growing feature and setting this property to “false”. This ensures that all items in the table are loaded at once, and that the “Items selected” count, the search, and select/deselect features all work properly.
Resources
Want to dive deeper? Follow the links below to find out more about related controls, the SAPUI5 implementation, and the visual design.
Elements and Controls
- Combo Box (guidelines)
- Select (guidelines)
- Value Help (guidelines)
- Search (guidelines)
Implementation
- No links














































































































































































































































































 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.