Cards Overview
FUICardView
Intro
A card provides brief, related pieces of information and serves as an entry point, teaser, or preview to more detailed content. By pressing on the card, users can select the card and navigate to a dedicated page with more detailed information.
SAP Fiori for iOS Cards
The card system for SAP Fiori for iOS provides an advanced approach to utilizing cards, which offer a convenient way for your app to display content from various sources. It consists of a toolkit of nested components that enable the creation of diverse cards to meet the requirements of SAP products. These nested components encompass a wide range of functionalities, such as lists, calendars, KPIs, and more. Additionally, the card system provides enhanced customization and flexibility, along with adaptable sizing options to accommodate different form factors and layouts, such as list, masonry, or carousel layout for cards. When incorporating cards into your app, it is crucial to keep the following aspects in mind:
- A card should focus on a single topic and be coherent in itself.
- A card should serve as an entry point, teaser, or preview to more detailed content.
- A card should be a short representation of a conceptual unit.
- A card should present information in a compact and easily scannable format.
- Incorporate cards into your app design to provide users with a quick overview of various information.
- Ensure that there is a clear indication on the card when a user selects it and a web browser is opened, for example, by incorporating an icon that indicates an external page is opened.
- When designing your layout, don’t use the inset grouped style (table view with rounded corners) as a substitute for the card component: The inset grouped style does not automatically transform a component into a card.
- Don’t place unrelated elements within a card.
- Don’t overload the user by including an excessive number of UI elements within a card.

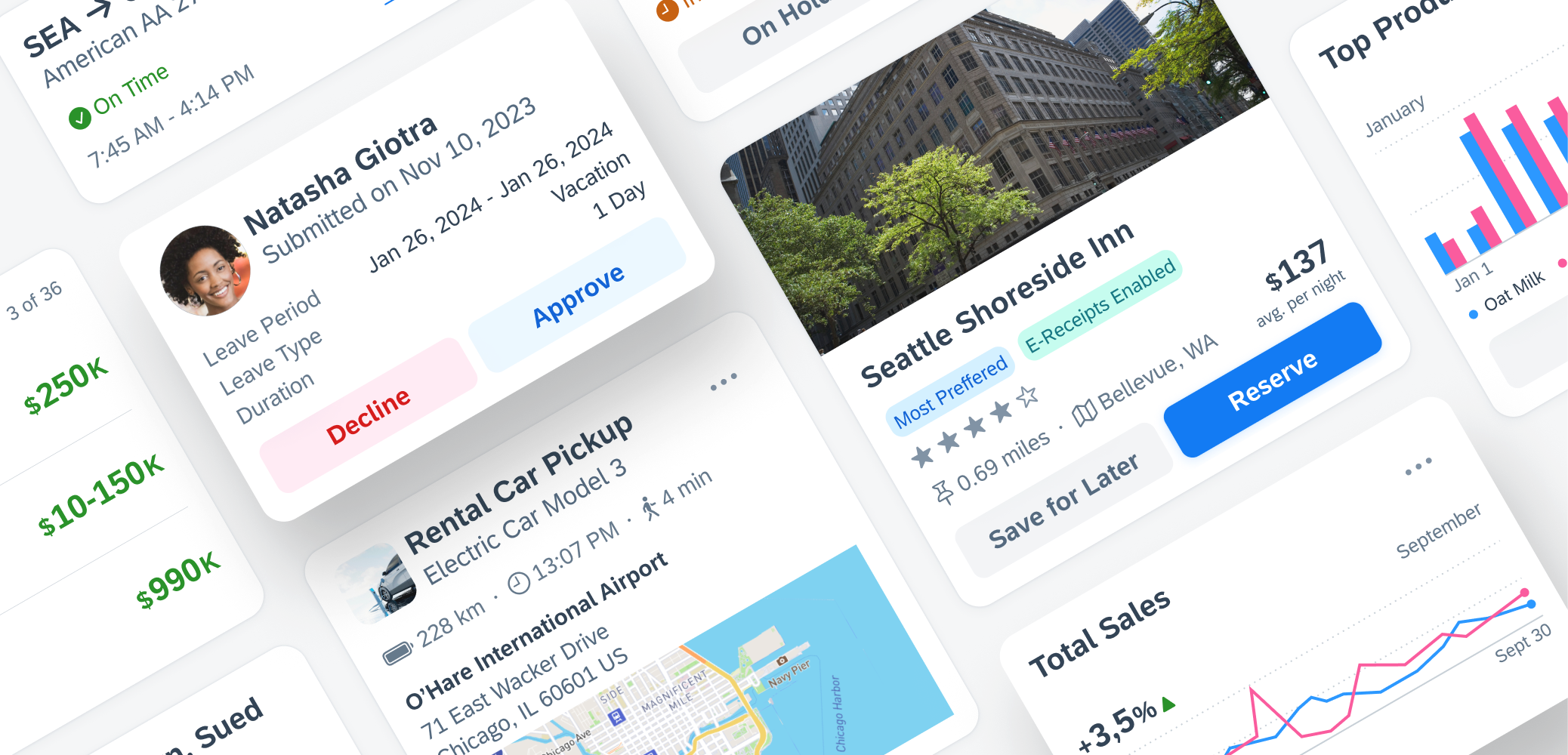
Cards should focus on one topic
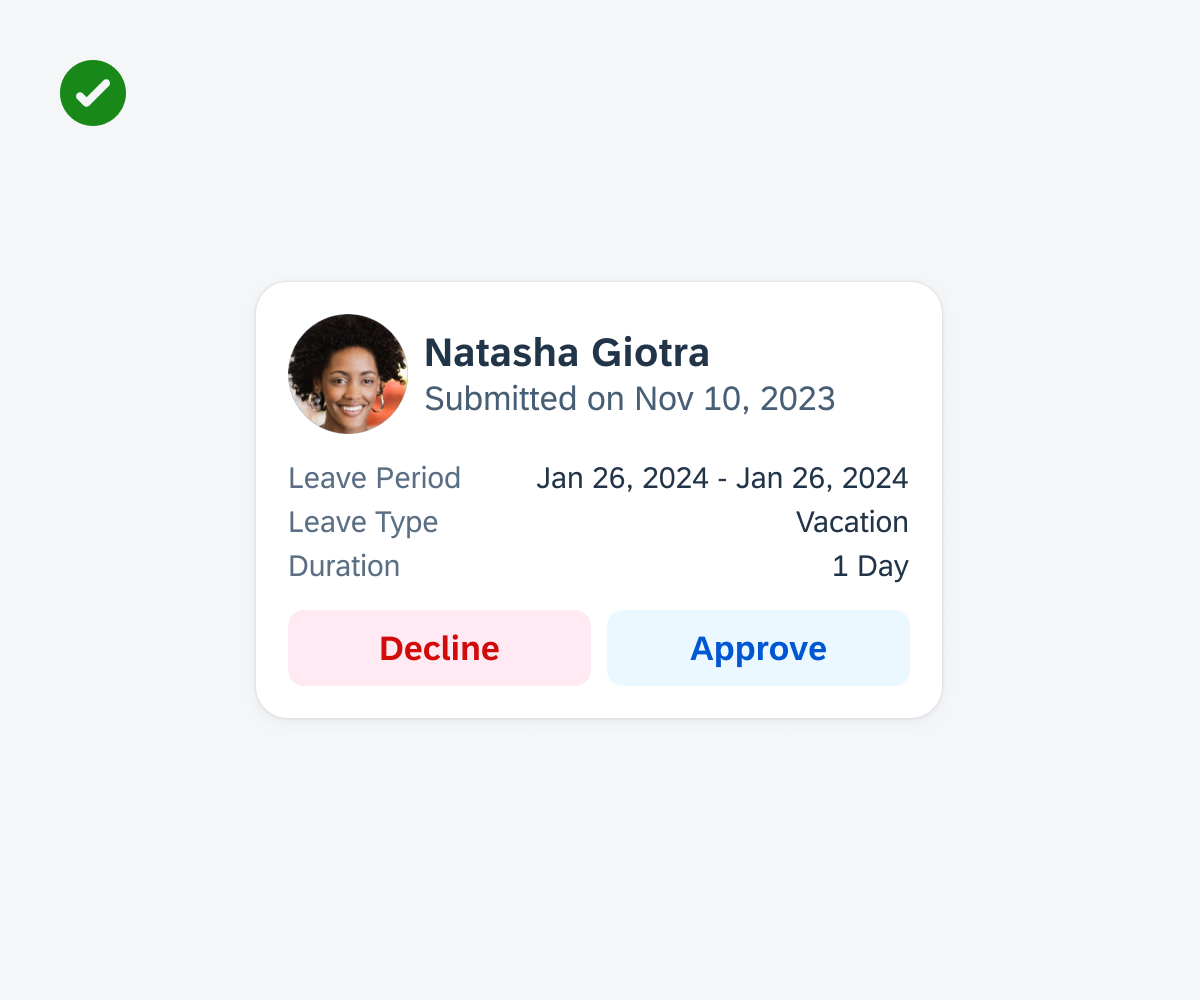
Cards should display information in a compact format
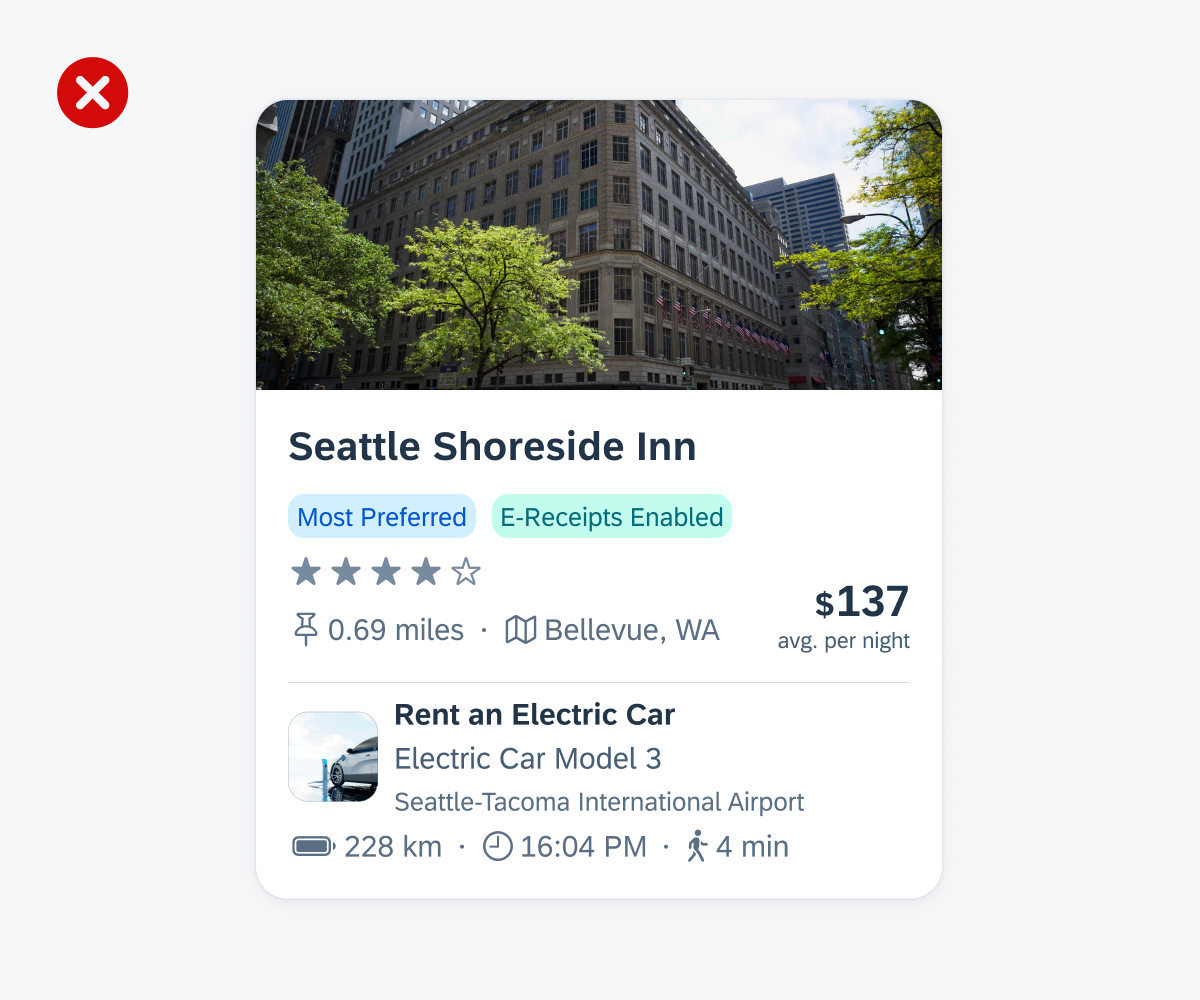
Don’t place elements within a card that do not relate to the same topic
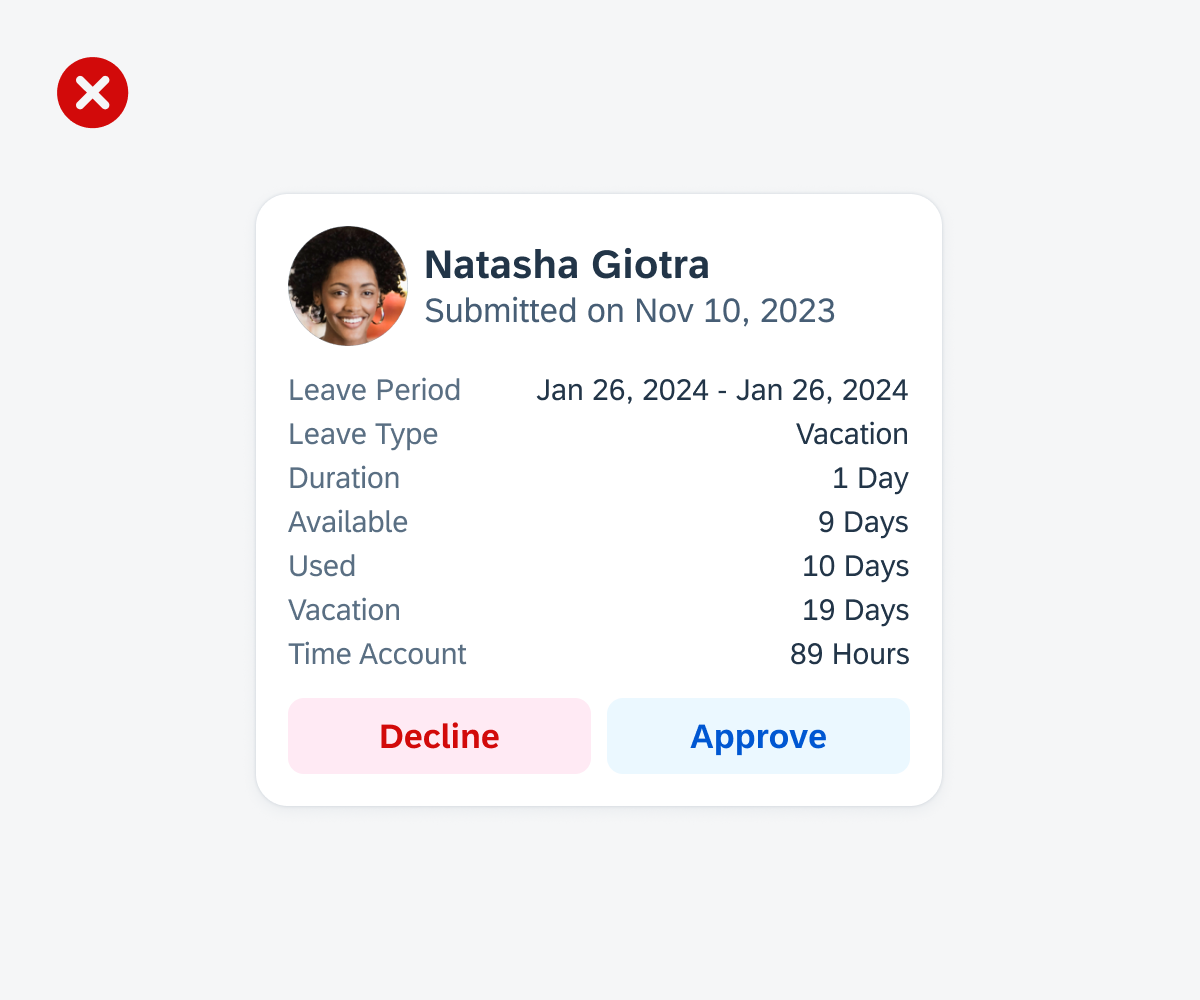
Don’t include too many UI elements within a card
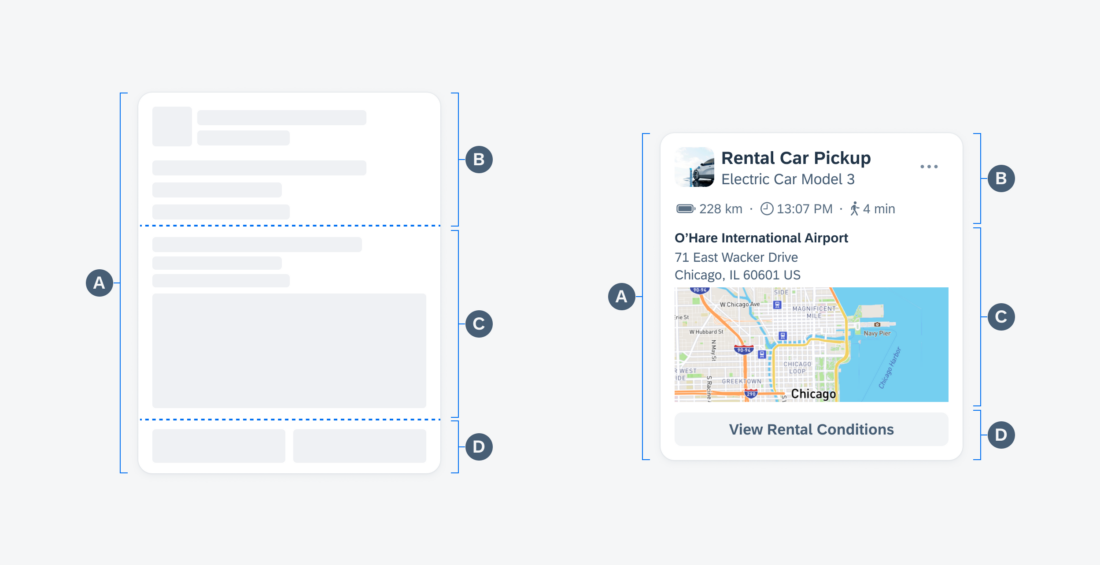
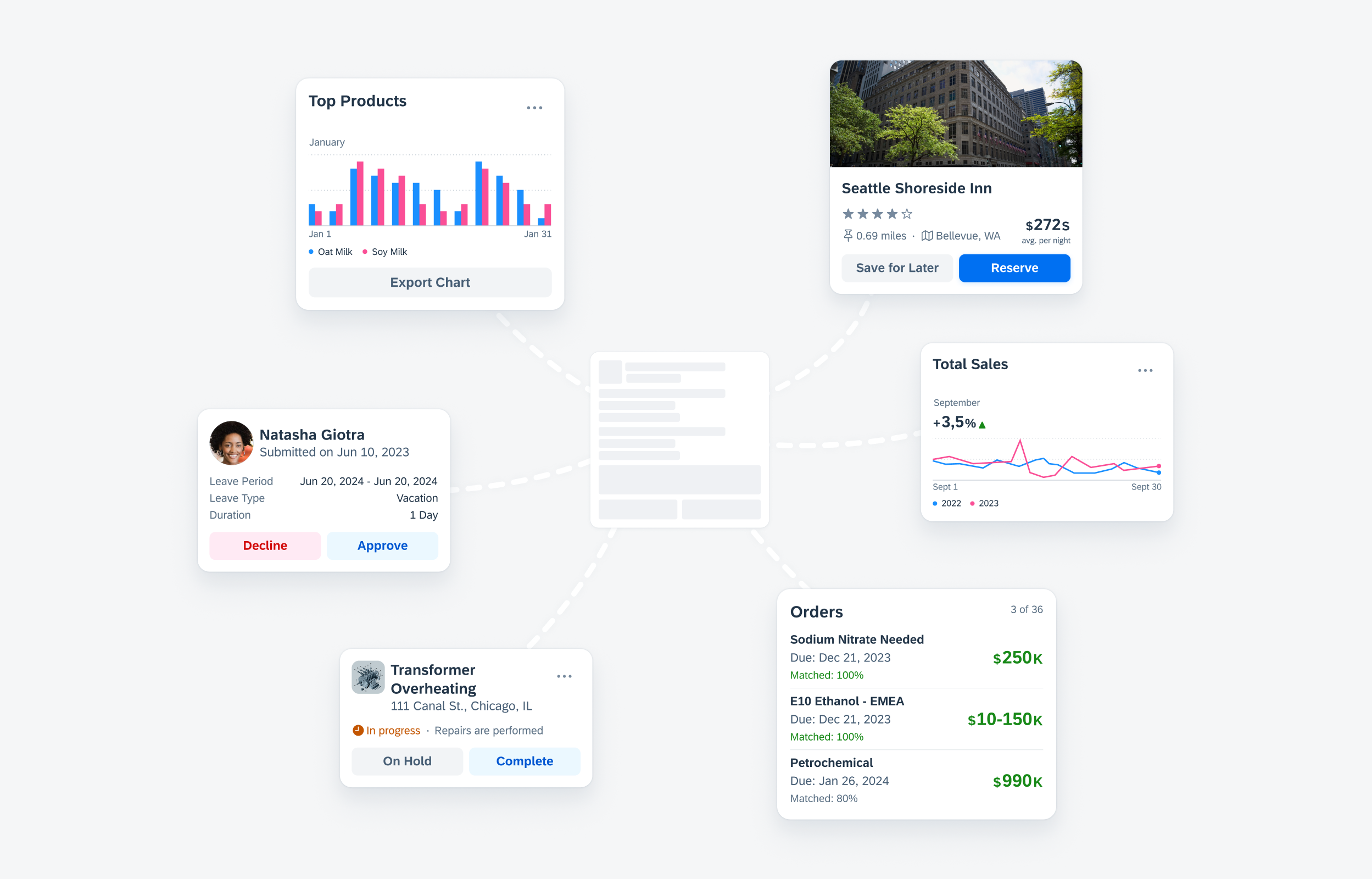
A. Card Container
The card container is the element that holds the header, body, and footer of the card.
B. Header
The card header, the card’s uppermost part, contains essential information about the card and its associated detail page content. It provides a quick overview of fundamental details such as the title, subtitle, and status of the card. More information on the header can be found in the Card Header article.
C. Body
The card body is the central part of a card that is used to provide additional information alongside the content shown in the card header. This allows for the presentation of in-depth details, data, or graphics relevant to the card’s context. More information on the body can be found in the Card Body article.
D. Footer
The card footer, located at the bottom of the card, is used for important or routine actions that directly impact the card’s functionality, such as “Approve’ or “Submit” actions. More information on the footer can be found in the Card Footer article.
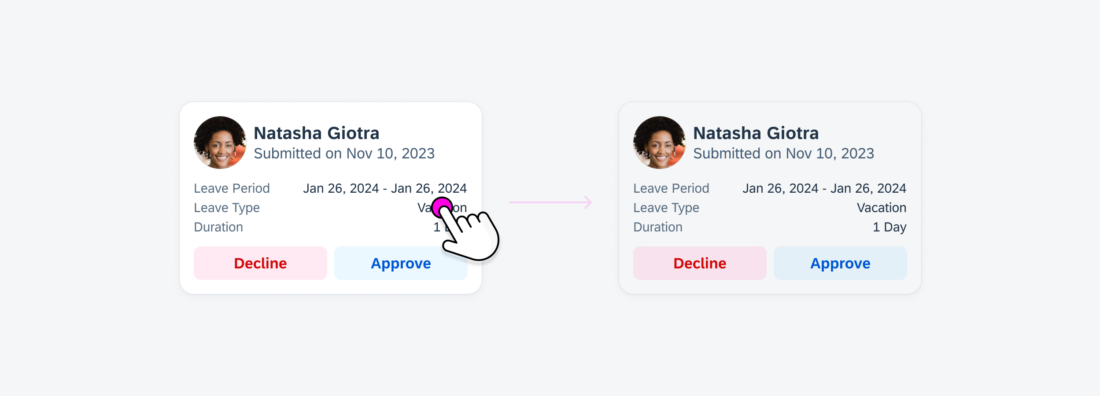
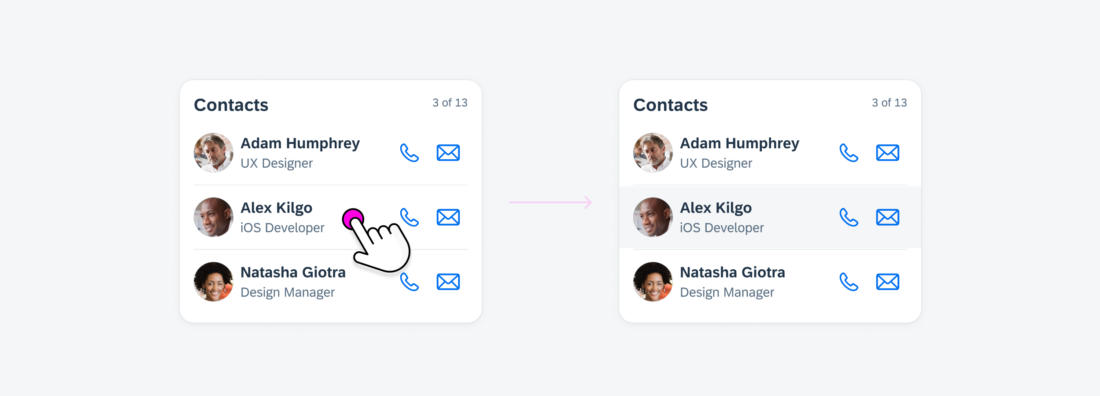
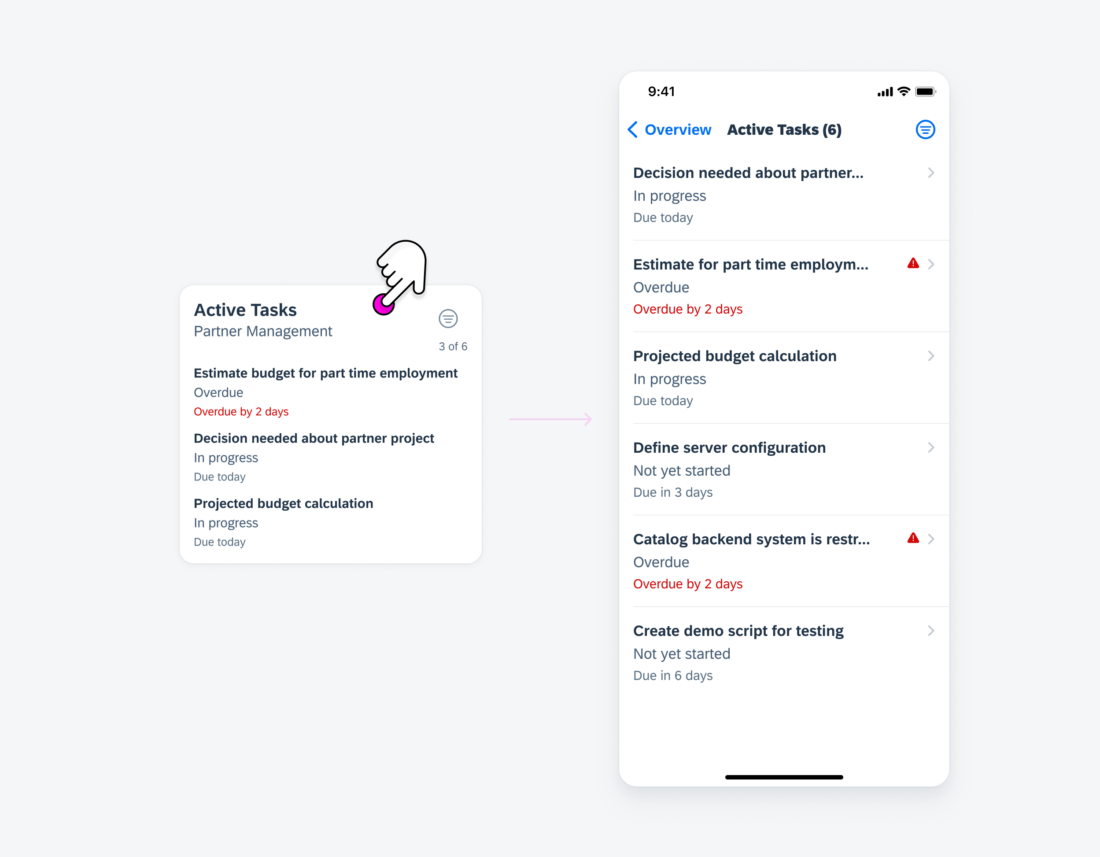
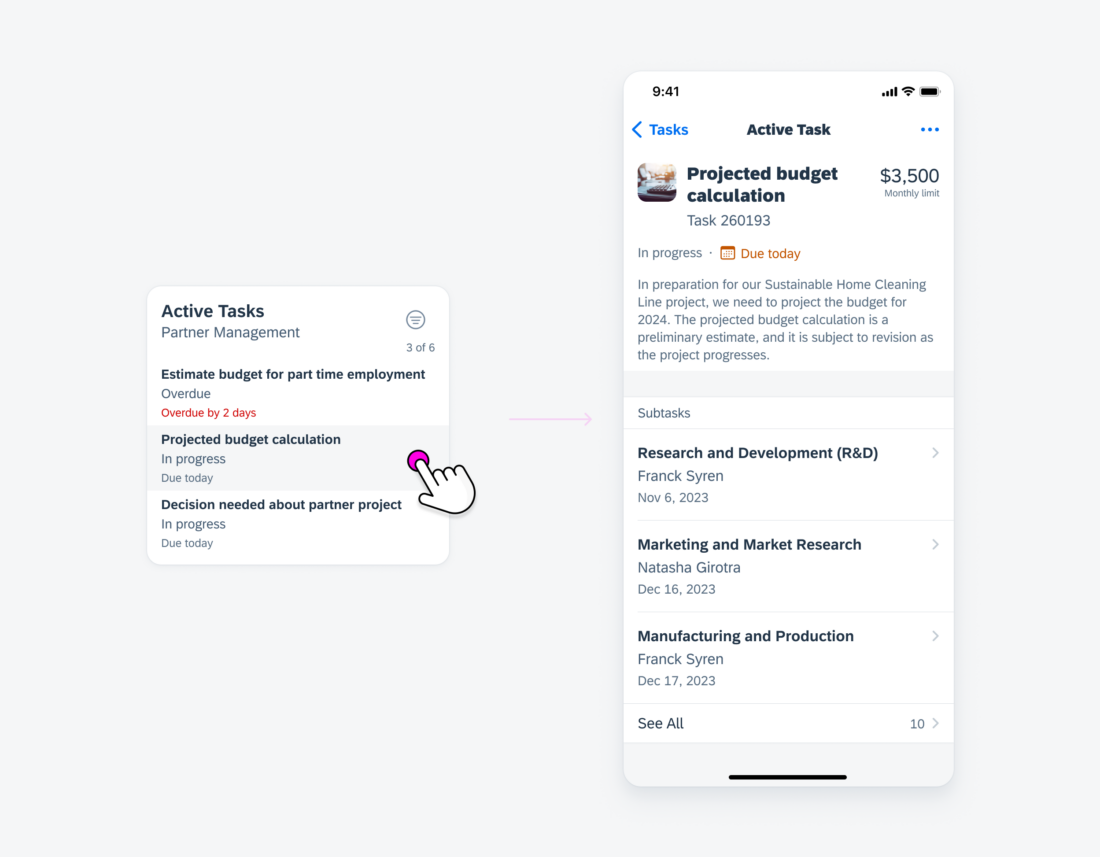
Selecting an Interactive Element
When a specific element within the card, such as an object cell, is designed to be interactive, it goes through a unique background color transition, providing a distinct visual indicator of the selection.
If the data still needs to load after selecting the element, a loading indicator appears.
Selecting an Interactive Element
When users engage with an interactive element within the card, such as an object cell, it triggers navigation to a dedicated details page that corresponds to the specific subject of that element.
Empty States
Entire Card
When there is no relevant content or data to display, it is important to include an empty state indicator within a card.
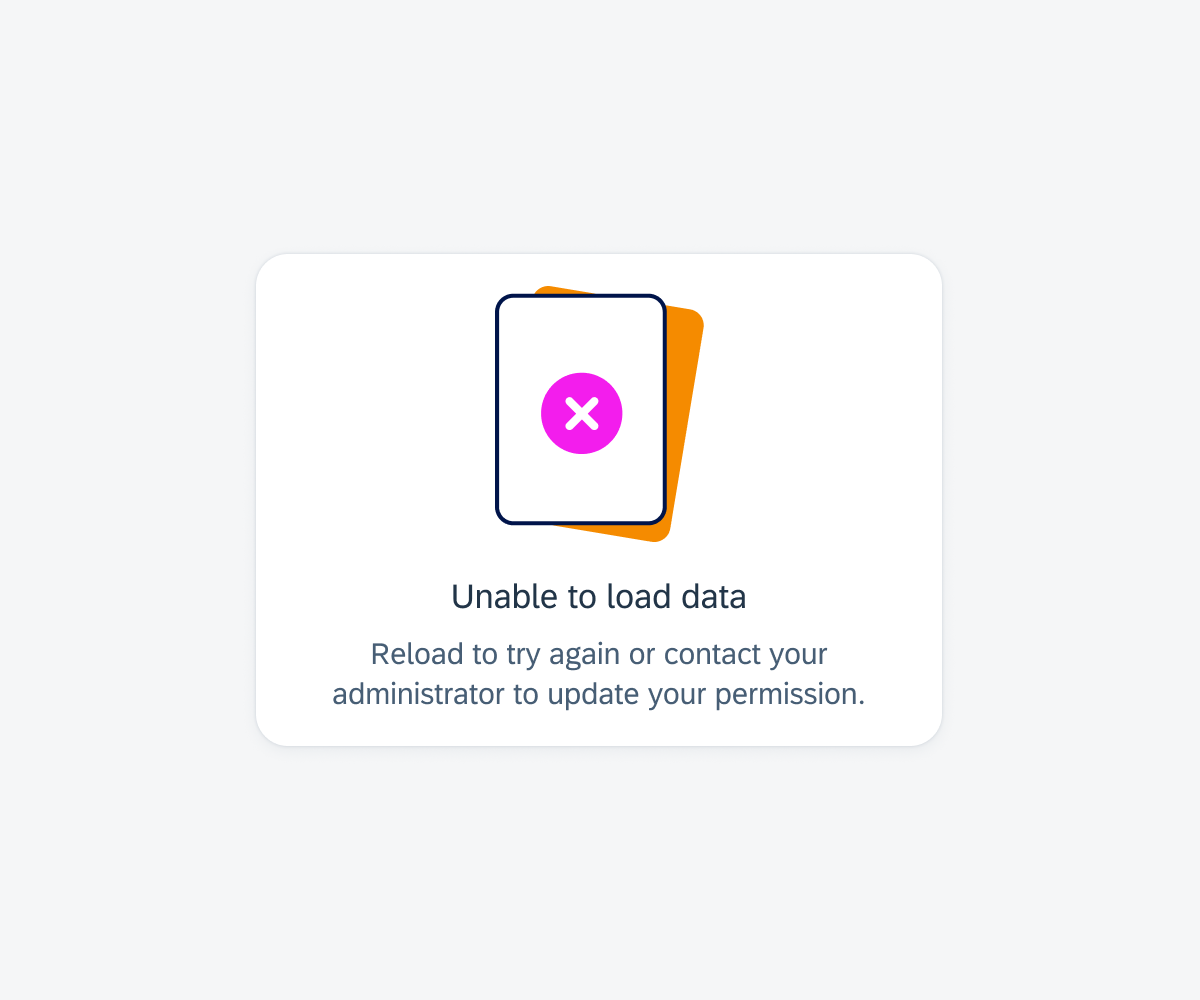
Empty state if the entire card content fails to load
Element within a Card
If a component within the card fails to load, an empty state indicator is displayed in the body container.
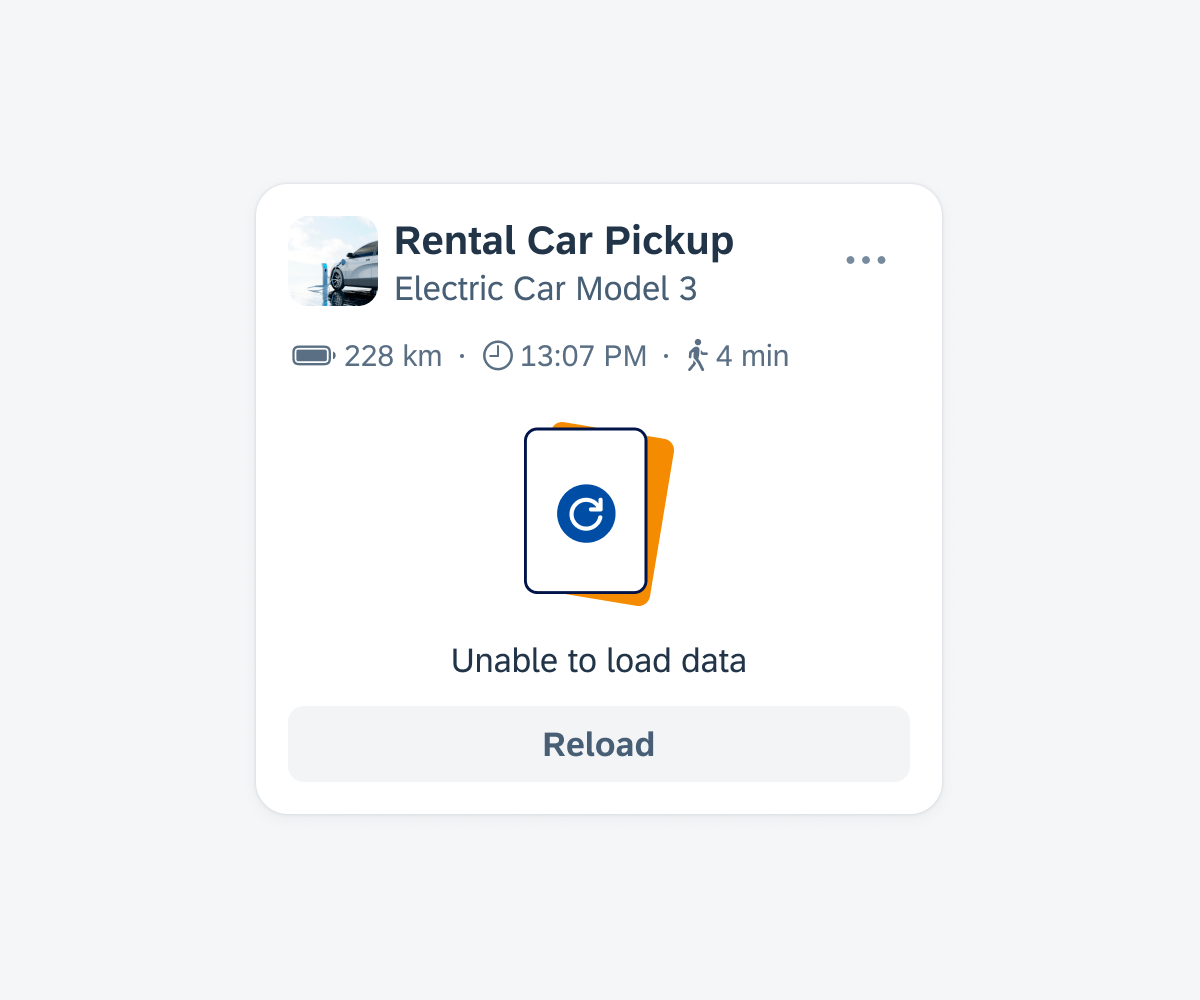
Empty state if only the card body fails to load
Skeleton Loading
Skeleton loading is used on a card when the data that fills the card still needs to be loaded. There are three skeleton loading sizes for cards. This approach allows you to select a card size that approximately reflects the loaded card size.
More information about skeleton loading can be found in Skeleton Loading.
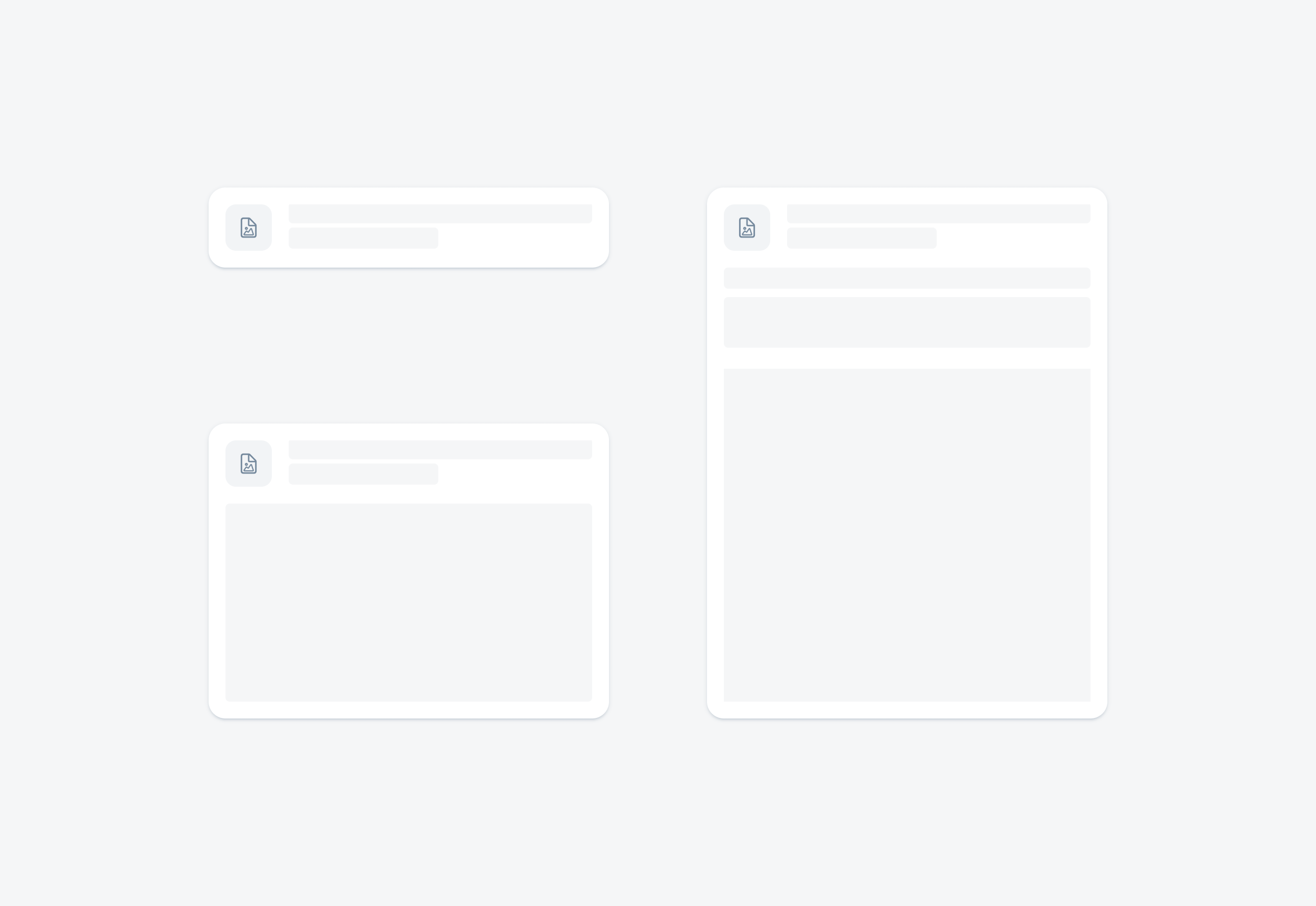
Skeleton loading on a small, medium, and large card
The card system ensures that cards adjust seamlessly to different screen sizes and orientations. For compact size classes (iPhone), cards are designed to be narrower to accommodate the limited screen width of phones, making efficient use of the available space in a portrait orientation.
For regular size classes (iPad), cards can have a wider layout to take advantage of the increased screen real estate, resulting in a more spacious and visually appealing presentation of content.
AR Card
Create an AR card to display key information of an AR marker annotation with a thumbnail image, icon, or app of an object
AR card featuring the card header (with header image and main header) and card footer
Data Table Card
Create a data table card to display key data points about an object in a two-column format.
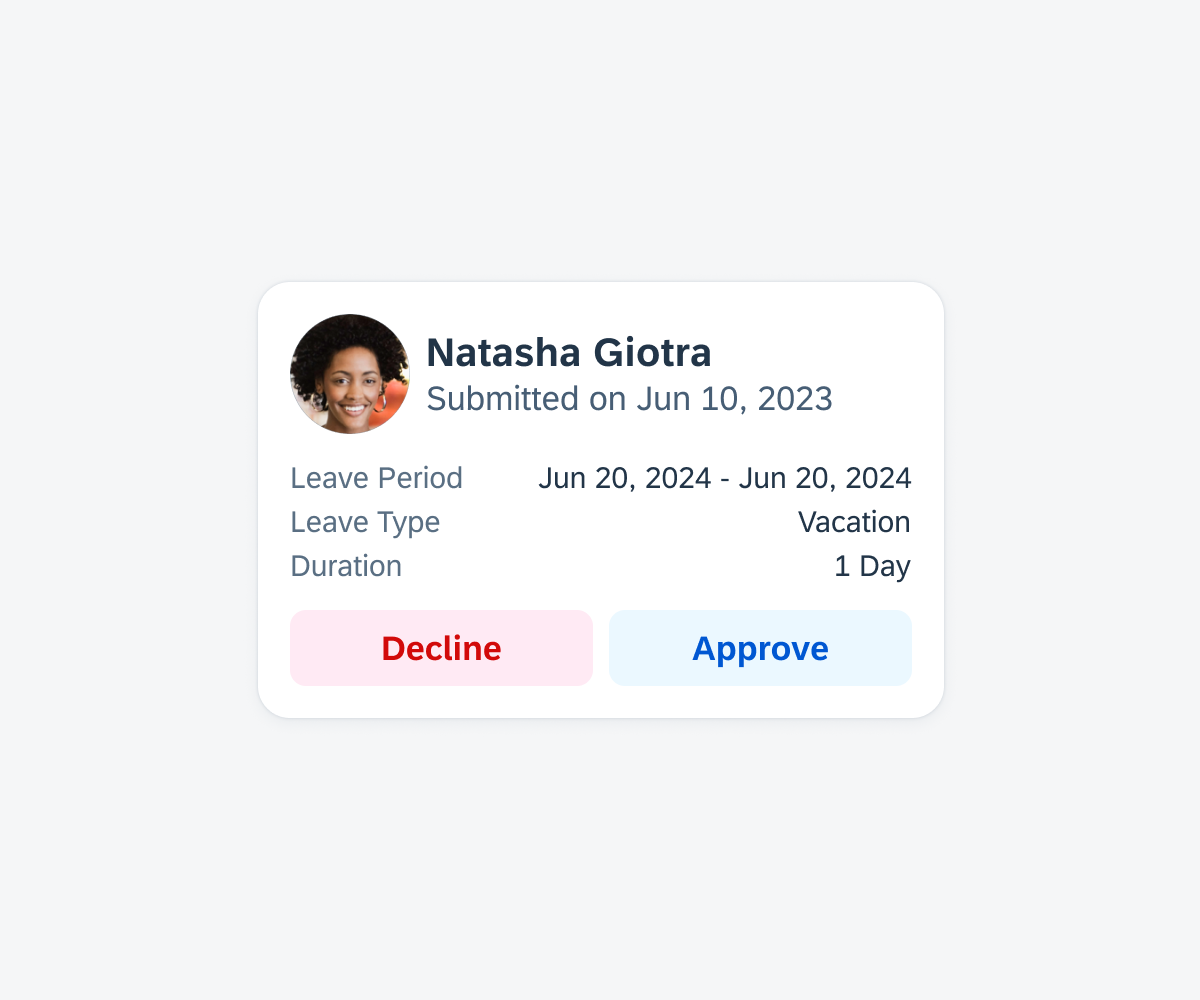
Data table card featuring the card header (with main header), card body (with data table), and card footer
Chart Card
Create a chart card to display a thumbnail view of a chart with key information.
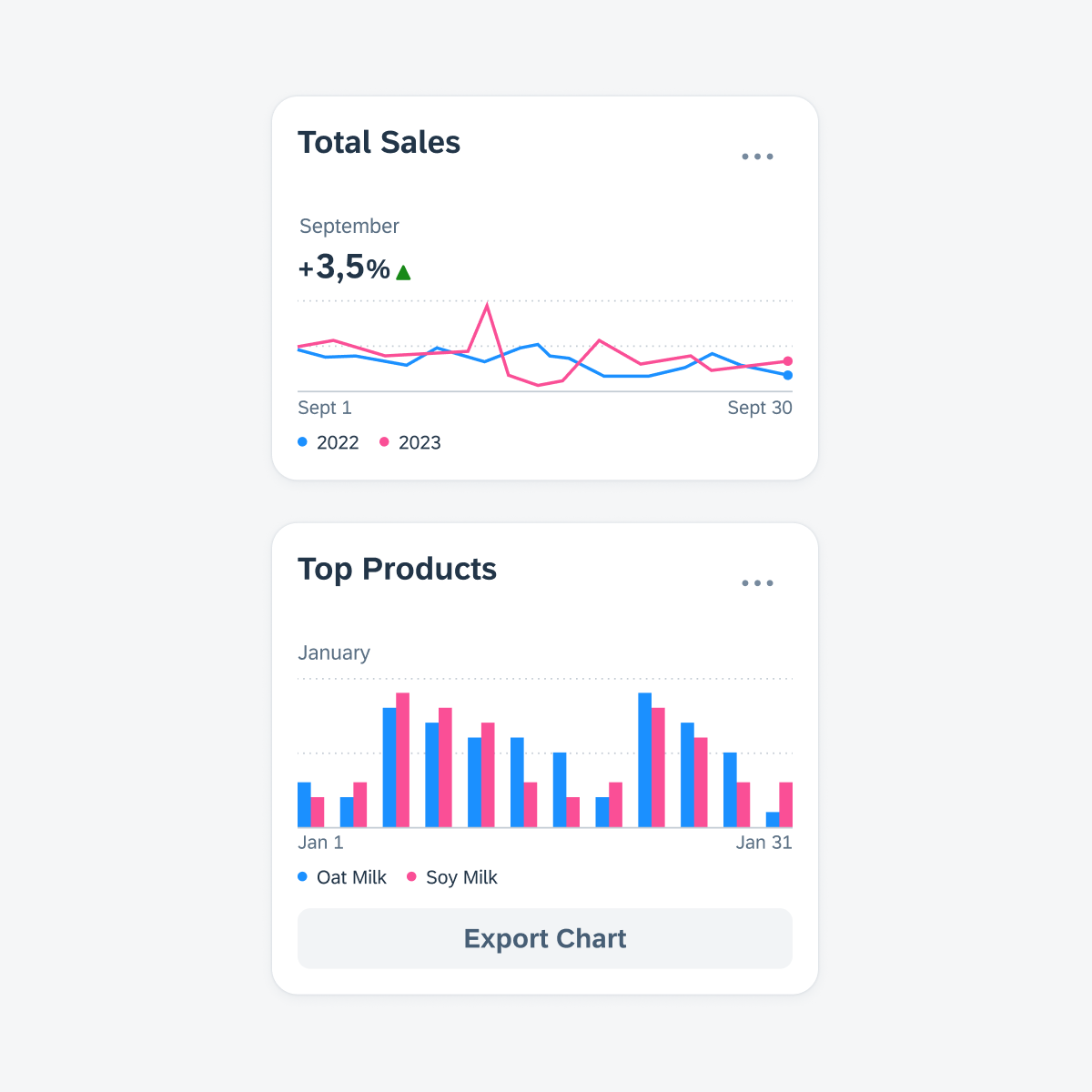
Top chart card featuring the card header (with main header) and card body (with chart component). Bottom chart card featuring the card header (with main header), card body (with chart component), and card footer.
List Card
Create a list card to display a preview of a set of items or objects in a vertical list format.
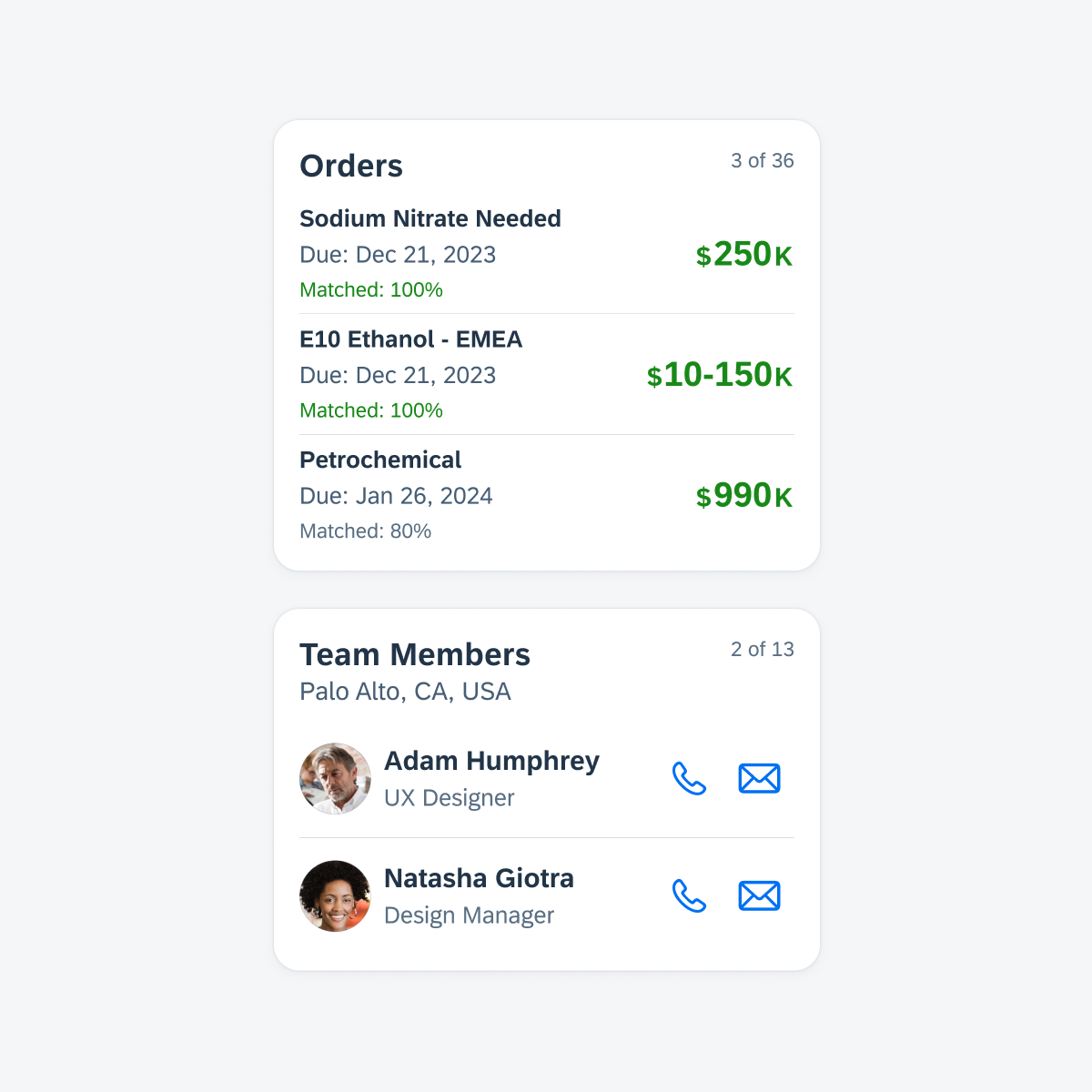
Top list card featuring the card header (with main header) and card body (with object cell components). Bottom list card featuring the card header (with main header) and card body (with contact cell components).
Object Card
Create an object card to display a preview of an object.

Top object card featuring the card header (with header image, main header, extended header), and card footer. Bottom object card featuring the card header (with main header and extended header) and card body (with object cell and KPI).
Development: FUICardView
SAP Fiori for Android: Cards Overview
SAP Fiori for Web: Card (SAPUI5), Card (Web Component)
Related Components/Patterns: Card Header, Card Body, Card Footer

 Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.
Your feedback has been sent to the SAP Fiori design team.